GPI-Space on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
GPI-Space is a parallel programming development software, developed by the Fraunhofer Institute for Industrial Mathematics (ITWM). The main concept behind the software is separation of domain and HPC knowledge and leaving each part to the respective experts while the GPI-Space as framework integrates both parts together.
GPI-Space is making use of GPI to solve big data problems more efficient than current solutions.
GPI-Space was first introduced in a domain-specific version for geology, under the name SDPA (Seismic Development and Programming Architecture) at SEG 2010 in Houston.
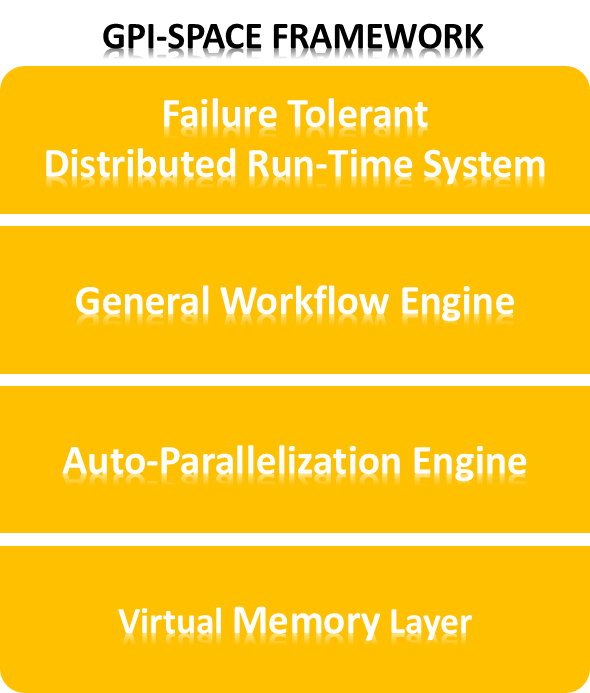 GPI Space comes with several layers, that make up the core of the parallel programming development software.
GPI Space comes with several layers, that make up the core of the parallel programming development software.
 The autoparallelization engine decides about how to ideally execute code that is fed into the system in parallel. This relieves domain programmers from the need for parallelizing their own code and leaves them focusing on their domain. HPC knowledge and experience by Fraunhofer ITWM's Competence-Center High-Performance Computing (CC-HPC) is an essential contributor to the engine's capability of generating highly optimal parallel codes.
The autoparallelization engine decides about how to ideally execute code that is fed into the system in parallel. This relieves domain programmers from the need for parallelizing their own code and leaves them focusing on their domain. HPC knowledge and experience by Fraunhofer ITWM's Competence-Center High-Performance Computing (CC-HPC) is an essential contributor to the engine's capability of generating highly optimal parallel codes.
 To showcase the validity of the GPI-Space approach, Fraunhofer first introduced it as part of the Seismic Development and Programming Architecture (SDPA) during SEG 2010 in Houston, TX to the community. In the
To showcase the validity of the GPI-Space approach, Fraunhofer first introduced it as part of the Seismic Development and Programming Architecture (SDPA) during SEG 2010 in Houston, TX to the community. In the
GPI-Space Website
Fraunhofer ITWM
{{DEFAULTSORT:GPI-Space Parallel computing
Core layers
 GPI Space comes with several layers, that make up the core of the parallel programming development software.
GPI Space comes with several layers, that make up the core of the parallel programming development software.
Runtime engine
The runtime engine is responsible to distribute the available jobs across the available systems. In a large scale HPCclusters
may refer to:
Science and technology Astronomy
* Cluster (spacecraft), constellation of four European Space Agency spacecraft
* Cluster II (spacecraft), a European Space Agency mission to study the magnetosphere
* Asteroid cluster, a small ...
, these can be heterogeneous and consist of traditional compute nodes as well as nodes with accelerator cards, such as GPU
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal ...
s or Intel's Xeon Phi
Xeon Phi is a discontinued series of x86 manycore processors designed and made by Intel. It was intended for use in supercomputers, servers, and high-end workstations. Its architecture allowed use of standard programming languages and applicati ...
. Besides the mere scheduling and distribution of jobs, the runtime engine is also adding fault-tolerance. Jobs are monitored after they have been assigned and reassigned to different resources, in case the initially assigned hardware fails. New hardware can be added dynamically.
Workflow engine
Theworkflow engine A workflow engine is a software application that manages business processes. It is a key component in workflow technology and typically makes use of a database server.
A workflow engine manages and monitors the state of activities in a workflow, su ...
translates instructions from an existing workflow in XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing data. It defines a set of rules for encoding electronic document, documents in a format that is both human-readable and Machine-r ...
format with special GPI-Space tags into the runtime environments internal instructions which are based on Petri nets
A Petri net, also known as a place/transition net (PT net), is one of several mathematical modeling languages for the description of distributed systems. It is a class of discrete event dynamic system. A Petri net is a directed bipartite grap ...
. Workflows can be arbitrary modular and use other workflows as elements, thus allowing users to predefine building blocks once and then use them in future, more complicated workflows. A graphical editor for workflows is available.
Autoparallelization engine
 The autoparallelization engine decides about how to ideally execute code that is fed into the system in parallel. This relieves domain programmers from the need for parallelizing their own code and leaves them focusing on their domain. HPC knowledge and experience by Fraunhofer ITWM's Competence-Center High-Performance Computing (CC-HPC) is an essential contributor to the engine's capability of generating highly optimal parallel codes.
The autoparallelization engine decides about how to ideally execute code that is fed into the system in parallel. This relieves domain programmers from the need for parallelizing their own code and leaves them focusing on their domain. HPC knowledge and experience by Fraunhofer ITWM's Competence-Center High-Performance Computing (CC-HPC) is an essential contributor to the engine's capability of generating highly optimal parallel codes.
Virtual memory layer
All computation with GPI-Space can be done using a fast parallel file system, such asBeeGFS
BeeGFS (formerly FhGFS) is a parallel file system developed for high-performance computing. BeeGFS includes a distributed metadata architecture for scalability and flexibility reasons. It specializes in data throughput.
BeeGFS was originally de ...
, which is very similar to other Big Data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with ...
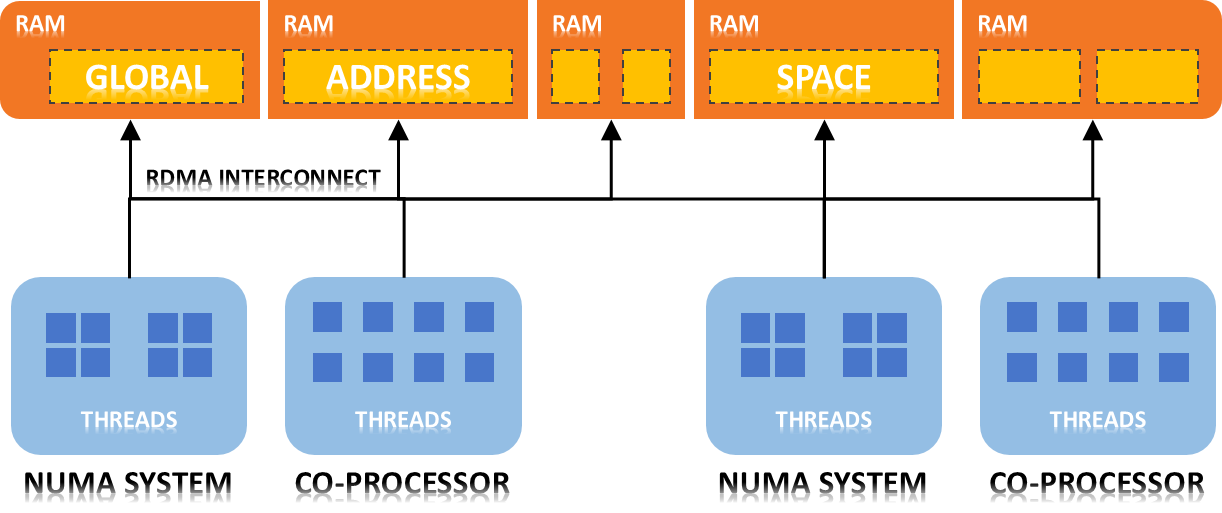
solutions available. But beyond this, GPI-Space is capable of doing all computation in memory, as well, thus omitting the higher latencies and performance bottlenecks of traditional I/O. Using Fraunhofer GPI (see also graphic "GPI Architecture"), one big block of a partitioned global address space is dynamically allocated. The RDMA capability allows for fast, single sided communication. Disk transfers to and from the virtual memory are completely asynchronous and hidden behind computation.
Seismic Development and Programming Architecture (SDPA)
 To showcase the validity of the GPI-Space approach, Fraunhofer first introduced it as part of the Seismic Development and Programming Architecture (SDPA) during SEG 2010 in Houston, TX to the community. In the
To showcase the validity of the GPI-Space approach, Fraunhofer first introduced it as part of the Seismic Development and Programming Architecture (SDPA) during SEG 2010 in Houston, TX to the community. In the seismic
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes (or generally, quakes) and the generation and propagation of elastic ...
domain exist countless legacy algorithms and codes in a variety of programming languages that have been developed over years, but that are not parallelized. Due to limited resources, it is often not feasible to rewrite those codes from scratch in a parallel version and one single programming language.
Developers at the CC-HPC have put together domain specific solutions for seismic data that includes:
* highly optimized algorithms for parallel I/O,
* fault tolerance,
* parallelization patterns for seismic data, such as traces
Traces may refer to:
Literature
* ''Traces'' (book), a 1998 short-story collection by Stephen Baxter
* ''Traces'' series, a series of novels by Malcolm Rose
Music Albums
* ''Traces'' (Classics IV album) or the title song (see below), 1969
* ''Tra ...
, gathers (which consist of several traces), or stacks which enable the autoparallelization engine to work efficiently, and
* general data management routines to handle seismic data.
In addition, there is a set of basic workflows that can be used as building blocks for more sophisticated workflows by the end user. All these components solve the parallelization problem for the seismic domain, so the domain developer can focus on his problem, without having to deal with it.
An end user of SDPA can then simply execute existing legacy codes and modules in any language in parallel with SDPA, reducing turnover time for projects significantly. SDPA is also used as a fast way to prototype new ideas and algorithms for parallel execution.
SDPA is used by several of Fraunhofer's industry partners in a production environment.
See also
* GPI *BeeGFS
BeeGFS (formerly FhGFS) is a parallel file system developed for high-performance computing. BeeGFS includes a distributed metadata architecture for scalability and flexibility reasons. It specializes in data throughput.
BeeGFS was originally de ...
References
External links
GPI-Space Website
Fraunhofer ITWM
{{DEFAULTSORT:GPI-Space Parallel computing