|
Giogha
Gigha ( ; ; ) or the Isle of Gigha (and formerly Gigha Island) is an island off the west coast of Kintyre in Scotland. The island forms part of Argyll and Bute and has a population of 163 people. The climate is mild with higher than average sunshine hours and the soils are fertile. The main settlement is Ardminish. Gigha has been inhabited continuously since prehistoric times. It may have had an important role during the Kingdom of Dalriada and is the ancestral home of Clan MacNeill. It fell under the control of the Norse and the Lords of the Isles before becoming incorporated into modern Scotland and saw a variety of conflicts during the medieval period. The population of Gigha peaked at over 700 in the eighteenth century, but during the 20th century the island had numerous owners, which caused various problems in developing the island. At the beginning of the 21st century the population had fallen to 98, however a "community buy-out" in 2002 has transformed the island, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scots Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic (, ; endonym: ), also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic, is a Celtic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a member of the Goidelic branch of Celtic, Scottish Gaelic, alongside both Irish and Manx, developed out of Old Irish. It became a distinct spoken language sometime in the 13th century in the Middle Irish period, although a common literary language was shared by the Gaels of both Ireland and Scotland until well into the 17th century. Most of modern Scotland was once Gaelic-speaking, as evidenced especially by Gaelic-language place names. In the 2011 census of Scotland, 57,375 people (1.1% of the Scottish population, three years and older) reported being able to speak Gaelic, 1,275 fewer than in 2001. The highest percentages of Gaelic speakers were in the Outer Hebrides. Nevertheless, there is a language revival, and the number of speakers of the language under age 20 did not decrease between the 2001 and 2011 censuses. In the 2022 census ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrides
The Hebrides ( ; , ; ) are the largest archipelago in the United Kingdom, off the west coast of the Scotland, Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebrides. These islands have a long history of occupation (dating back to the Mesolithic period), and the culture of the inhabitants has been successively influenced by the cultures of Celtic language, Celtic-speaking, Old Norse language, Norse-speaking, and English language, English-speaking peoples. This diversity is reflected in the various names given to the islands, which are derived from the different languages that have been spoken there at various points in their history. The Hebrides are where much of Scottish Gaelic literature and Gaelic music has historically originated. Today, the economy of the islands is dependent on crofting, fishing, tourism, the oil industry, and renewable energy. The Hebrides have less biodiversity t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hákonar Saga Hákonarsonar
''Hákonar saga Hákonarsonar'' ("The Saga of Haakon Haakonarson") or ''Hákonar saga gamla'' ("The Saga of Old Haakon") is an Old Norse Kings' Saga, telling the story of the life and reign of King Haakon Haakonarson of Norway. Content and style The circumstances of the saga's composition are exceptionally well understood, as they are recorded in some detail in ''Sturlunga saga'' (particularly ''Sturlu þáttr''): the saga was written in the 1260s (apparently 1264–65) by the Icelandic historian and chieftain Sturla Þórðarson (nephew of the noted historian Snorri Sturluson). Sturla Þórðarson was at the court of Haakon's son Magnus Lagabøte when Magnus learned of his father's death in Kirkwall in Orkney. Magnus is said to have immediately commissioned Sturla to write his father's saga. This was awkward for Sturla: 'King Hákon had instigated the death of Sturla's uncle, Snorri Sturluson, in 1241. Sturla rightly regarded Hákon as his most dangerous enemy, for he had ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argyll Group
The Argyll Group is a thick sequence of metamorphosed Neoproterozoic sedimentary rocks that outcrop across the Central Highlands of Scotland, east of the Great Glen, as well as appearing in the north of Ireland. It is a subdivision of the Dalradian Supergroup and is itself divided into four units; from oldest to youngest these are the Islay, Easdale, Crinan and Tayvallich subgroups. Islay Subgroup The lower boundary of the Islay Subgroup and hence the Argyll Group as a whole is defined at the base of the Port Askaig Tillite Formation, a diamictite which displays limestone clasts overlain by quartzite and granite clasts. The tillite is thickest in its type area and on the Garvellachs. The Schiehallion Boulder Bed of the eastern Grampians correlates with this tillite. The tillite is overlain by the Bonahaven Dolomite and then the Jura Quartzite which can reach up to 5 km thick but which is more typically between 500 and 1000m thick. Psammites and pelites occur within the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the last of the three geologic eras of the Proterozoic geologic eon, eon, spanning from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago, and is the last era of the Precambrian "supereon". It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic era and succeeded by the Paleozoic era of the Phanerozoic eon, and is further subdivided into three geologic period, periods, the Tonian, Cryogenian and Ediacaran. One of the most severe glaciation events known in the geologic record occurred during the Cryogenian period of the Neoproterozoic, when global ice sheets may have reached the equator and created a "Snowball Earth" lasting about 100 million years. The earliest fossils of complex life are found in the Tonian period in the form of ''Otavia'', a primitive sponge, and the earliest fossil evidence of metazoan evolutionary radiation, radiation are found in the Ediacaran period, which included the namesaked Ediacaran biota as well as the oldest definitive cnidarians and bilaterians in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metasedimentary Rock
In geology, metasedimentary rock is a type of metamorphic rock. Such a rock was first formed through the deposition and solidification of sediment Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of .... Then, the rock was buried underneath subsequent rock and was subjected to high pressures and temperatures, causing the rock to recrystallize. The overall composition of a metasedimentary rock can be used to identify the original sedimentary rock, even where they have been subject to high-grade metamorphism and intense deformation. Types of metasedimentary rocks See also * References Metamorphic petrology {{Rock-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
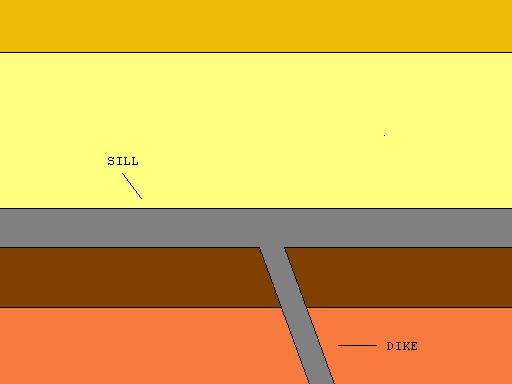
Sill (geology)
In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. A sill is a ''concordant intrusive sheet'', meaning that it does not cut across preexisting rock beds. Stacking of sills builds a sill complex. and a large magma chamber at high magma flux. In contrast, a dike is a discordant intrusive sheet, which does cut across older rocks. Formation Sills are fed by dikes, except in unusual locations where they form in nearly vertical beds attached directly to a magma source. The rocks must be brittle and fracture to create the planes along which the magma intrudes the parent rock bodies, whether this occurs along preexisting planes between sedimentary or volcanic beds or weakened planes related to foliation in metamorphic rock. These planes or weakened areas allow the intrusion of a thin sheet-like body of magma paralleling the existi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing Rock (geology), rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or Texture (geology), texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. Metamorphism is distinct from weathering or diagenesis, which are changes that take place at or just beneath Earth's surface. Various forms of metamorphism exist, including Regional metamorphism, regional, Contact metamorphism, contact, Hydrothermal metamorphism, hydrothermal, Shock metamorphism, shock, and Dynamic metamorphism, dynamic metamorphism. These differ in the characteristic temperatures, pressures, and rate at which they take place and in the extent to which reactive fluids are involved. Metamorphism occurring at increasing pressure and temperature conditions is known as ''prograde metamorphism'', while decreasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous Rock
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form natural glasses. Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces, extended crust and oceanic crust. Geological significance Igneous and metamorphic rocks make up 90–95% of the top of the Earth's crust by volume. Igneous rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibolite
Amphibolite () is a metamorphic rock that contains amphibole, especially hornblende and actinolite, as well as plagioclase feldspar, but with little or no quartz. It is typically dark-colored and dense, with a weakly foliated or schistose (flaky) structure. The small flakes of black and white in the rock often give it a salt-and-pepper appearance. Amphibolite frequently forms by metamorphism of mafic igneous rocks, such as basalt. However, because metamorphism creates minerals entirely based upon the chemistry of the protolith, certain 'dirty marls' and volcanic sediments may also metamorphose to an amphibolite assemblage. Deposits containing dolomite and siderite also readily yield amphibolite ( tremolite-schist, grunerite-schist, and others) especially where there has been a certain amount of contact metamorphism by adjacent granitic masses. Metamorphosed basalt (metabasalt) creates ''ortho-amphibolite'' and other chemically appropriate lithologies create ''par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argyllshire
Argyll (; archaically Argyle; , ), sometimes called Argyllshire, is a historic county and registration county of western Scotland. The county ceased to be used for local government purposes in 1975 and most of the area now forms part of the larger Argyll and Bute council area. Argyll is of ancient origin, and broadly corresponds to the ancient kingdom of less the parts which were in Ireland. Argyll was also a medieval bishopric with its cathedral at Lismore. In medieval times the area was divided into a number of provincial lordships. One of these, covering only the central part of the later county, was called Argyll. It was initially an earldom, elevated to become a dukedom in 1701 with the creation of the Duke of Argyll. Other lordships in the area included Cowal, Kintyre, Knapdale, and Lorn. From at least the 14th century there was a Sheriff of Argyll, whose jurisdiction was gradually extended; from 1633 the shire covered all these five provinces. Shires gradual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fricative
A fricative is a consonant produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate in the case of German (the final consonant of '' Bach''); or the side of the tongue against the molars, in the case of Welsh (appearing twice in the name '' Llanelli''). This turbulent airflow is called frication. A particular subset of fricatives are the sibilants. When forming a sibilant, one still is forcing air through a narrow channel, but in addition, the tongue is curled lengthwise to direct the air over the edge of the teeth. English , , , and are examples of sibilants. The usage of two other terms is less standardized: "Spirant" is an older term for fricatives used by some American and European phoneticians and phonologists for non-sibilant fricatives. "Strident" could mean just "sibilant", but some authors include also lab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |