|
George E. Fox
George Edward Fox (born December 17, 1945) is an astrobiologist, a Professor Emeritus and researcher at the University of Houston. He is an elected fellow of the American Academy of Microbiology, the American Association for the Advancement of Science, American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering and the International Astrobiology Society. Fox received his B.S. degree in 1967, and completed his Ph.D. degree in 1974; both in chemical engineering at Syracuse University. From the Fall of 1973 until 1977, Fox was a research associate with Carl R. Woese at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Their collaboration initially focused on 5S ribosomal RNA where they established the use of a comparative sequence approach to predict RNA secondary structure. Next, utilizing 16S ribosomal RNA finger printing technology developed in the Woese laboratory in large part by Mitchell Sogin, Fox and Woese discovered the third form of life now known as the Archaea. It ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John W
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died ), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (died ), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus Christ * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope John (disambigu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Illinois At Urbana-Champaign
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC, U of I, Illinois, or University of Illinois) is a public land-grant research university in the Champaign–Urbana metropolitan area, Illinois, United States. Established in 1867, it is the founding campus and flagship institution of the University of Illinois System. With over 59,000 students, the University of Illinois is one of the largest public universities by enrollment in the United States. The university contains 16 schools and colleges and offers more than 150 undergraduate and over 100 graduate programs of study. The university holds 651 buildings on and its annual operating budget in 2016 was over $2 billion. The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign also operates a research park home to innovation centers for over 90 start-up companies and multinational corporations. The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign is a member of the Association of American Universities and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Purpose: Because living persons may suffer personal harm from inappropriate information, we should watch their articles carefully. By adding an article to this category, it marks them with a notice about sources whenever someone tries to edit them, to remind them of WP:BLP (biographies of living persons) policy that these articles must maintain a neutral point of view, maintain factual accuracy, and be properly sourced. Recent changes to these articles are listed on Special:RecentChangesLinked/Living people. Organization: This category should not be sub-categorized. Entries are generally sorted by family name In many societies, a surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full name of a person, although several give .... Maintenance: Individuals of advanced age (over 90), for whom there has been no new documentation in the last ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1945 Births
1945 marked the end of World War II, the fall of Nazi Germany, and the Empire of Japan. It is also the year concentration camps were liberated and the only year in which atomic weapons have been used in combat. Events World War II will be abbreviated as “WWII” January * January 1 – WWII: ** Germany begins Operation Bodenplatte, an attempt by the ''Luftwaffe'' to cripple Allied air forces in the Low Countries. ** Chenogne massacre: German prisoners are allegedly killed by American forces near the village of Chenogne, Belgium. * January 6 – WWII: A German offensive recaptures Esztergom, Hungary from the Soviets. * January 9 – WWII: American and Australian troops land at Lingayen Gulf on western coast of the largest Philippine island of Luzon, occupied by Japan since 1942. * January 12 – WWII: The Soviet Union begins the Vistula–Oder Offensive in Eastern Europe, against the German Army. * January 13 – WWII: The Soviet Union begins the East Prussia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-domain System
The three-domain system is a taxonomic classification system that groups all cellular life into three domains, namely Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya, introduced by Carl Woese, Otto Kandler and Mark Wheelis in 1990. The key difference from earlier classifications such as the two-empire system and the five-kingdom classification is the splitting of Archaea (previously named "archaebacteria") from Bacteria as completely different organisms. The three domain hypothesis is considered obsolete by some since it is thought that eukaryotes do not form a separate domain of life; instead, they arose from a fusion between two different species, one from within Archaea and one from within Bacteria. (see Two-domain system) Background Woese argued, on the basis of differences in 16S rRNA genes, that bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes each arose separately from an ancestor with poorly developed genetic machinery, often called a progenote. To reflect these primary lines of descent, he tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more or less common within a population over successive generations. The process of evolution has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation. The scientific theory of evolution by natural selection was conceived independently by two British naturalists, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, in the mid-19th century as an explanation for why organisms are adapted to their physical and biological environments. The theory was first set out in detail in Darwin's book ''On the Origin of Species''. Evolution by natural selection is established by observable facts about living organisms: (1) more offspring are often produced than can possibly survive; (2) phenotypic variatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woese
Carl Richard Woese ( ; July 15, 1928 – December 30, 2012) was an American microbiologist and biophysicist. Woese is famous for defining the Archaea (a new domain of life) in 1977 through a pioneering phylogenetic taxonomy of 16S ribosomal RNA, a technique that has revolutionized microbiology. He also originated the RNA world hypothesis in 1967, although not by that name. Woese held the Stanley O. Ikenberry Chair and was professor of microbiology at the University of Illinois Urbana–Champaign. Life and education Woese was born in Syracuse, New York on July 15, 1928. His family was German American. Woese attended Deerfield Academy in Massachusetts. He received a bachelor's degree in mathematics and physics from Amherst College in 1950. During his time at Amherst, Woese took only one biology course (Biochemistry, in his senior year) and had "no scientific interest in plants and animals" until advised by William M. Fairbank, then an assistant professor of physics at Amherst, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progenote
The first universal common ancestor (FUCA) is thought to be a non-cellular entity that was the earliest organism with a genetic code capable of biological translation of RNA molecules into peptides to produce proteins. Its descendants would include the last universal common ancestor (LUCA) and every modern cell. FUCA would also be the ancestor of ancient sister lineages of LUCA, none of which have modern descendants, but which are thought to have horizontally transferred some of their genes into the genome of early descendants of LUCA. FUCA is thought to have been composed of progenotes, proposed ancient biological systems that would have used RNA for their genome and self-replication. By comparison, LUCA would have had a complex metabolism and a DNA genome with hundreds of genes and gene families. Origins Long before the appearance of compartmentalized biological entities like FUCA, life had already begun to organize itself and emerge in a hypothesized pre-cellular era ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even though the domain Archaea Cladistics, cladistically includes eukaryotes, the term "archaea" (: archaeon , from the Greek "ἀρχαῖον", which means ancient) in English still generally refers specifically to prokaryotic members of Archaea. Archaea were initially Taxonomy (biology), classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (, in the Archaebacteria Kingdom (biology), kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from Bacteria and Eukaryote, Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phylum, phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been Isolation (microbiology), isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their Gene, gene s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitchell Sogin
Mitchell Sogin is an American microbiologist. He is a distinguished senior scientist at the Marine Biological Laboratory in Woods Hole, Massachusetts. His research investigates the evolution, diversity,and distribution of single-celled organisms. Early life and education Sogin grew up in Chicago and went to the University of Illinois on a swimming scholarship, intending to become a doctor. Instead he continued on at the university to complete a MS in Industrial Microbiology under Z. John Ordal in 1967 and a PhD in Microbiology and Molecular Biology under Carl R. Woese in 1972. Career Sogin obtained a BS in Chemistry and Microbiology at the University of Illinois, Urbana in 1967. He went on to join the staff at National Jewish Health, Denver, Colorado where he was an NIH Postdoctoral Fellow in the lab of Norman R. Pace from 1972-1976 and then a senior staff member from 1976-1989. Sogin became a professor at the University of Colorado Health Sciences Center in 1980 and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16S Ribosomal RNA
16S ribosomal RNA (or 16 S rRNA) is the RNA component of the 30S subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome ( SSU rRNA). It binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and provides most of the SSU structure. The genes coding for it are referred to as 16S rRNA genes and are used in reconstructing phylogenies, due to the slow rates of evolution of this region of the gene. Carl Woese and George E. Fox were two of the people who pioneered the use of 16S rRNA in phylogenetics in 1977. Multiple sequences of the 16S rRNA gene can exist within a single bacterium. Terminology The descriptor ''16S'' refers to the size of these ribosomal subunits as reflected indirectly by the speed at which they sediment when samples are centrifuged. Thus ''16S'' means 16 Svedburg units. Functions * Like the large (23S) ribosomal RNA, it has a structural role, acting as a scaffold defining the positions of the ribosomal proteins. * The 3-end contains the anti- Shine-Dalgarno sequence, which binds upstream ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
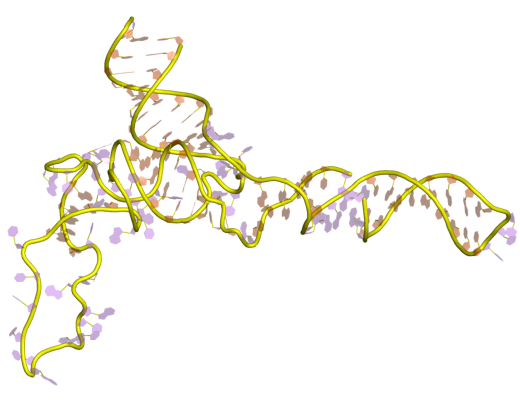
5S Ribosomal RNA
The 5S ribosomal RNA (5S rRNA) is an approximately 120 nucleotide-long ribosomal RNA molecule with a mass of 40 kDa. It is a structural and functional component of the large subunit of the ribosome in all domains of life (bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes), with the exception of mitochondrial ribosomes of fungi and animals. The designation 5S refers to the molecule's sedimentation coefficient in an ultracentrifuge, which is measured in Svedberg units (S). Biosynthesis In prokaryotes, the 5S rRNA gene is typically located in the rRNA operons downstream of the small and the large subunit rRNA, and co-transcribed into a polycistronic precursor. A particularity of eukaryotic nuclear genomes is the occurrence of multiple 5S rRNA gene copies (5S rDNA) clustered in tandem repeats, with copy number varying from species to species. Eukaryotic 5S rRNA is synthesized by RNA polymerase III, whereas other eukaryotic rRNAs are cleaved from a 45S precursor transcribed by RNA polymerase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |