|
Geology Of Romania
The geology of Romania is structurally complex, with evidence of past crustal movements and the incorporation of different blocks or platforms to the edge of Europe, driving recent mountain building of the Carpathian Mountains. Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the southeast, Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, and Moldova to the east. Structural geology Geologists subdivide Romania into several structural groupings: *Scythian Platform: A platform spanning from eastern Romania to Crimea. Complex folding of Precambrian and Paleozoic basement rocks, slate, Ordovician sandstone, Silurian shale, and Devonian marl and sandstone. Platform cover rocks include Devonian limestone, Triassic basic detrital rocks, carbonates, Jurassic marl, and sand as well as Neogene shallow water sediments typical of the Carpathian Foreland. * Moesian Platform: Southe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
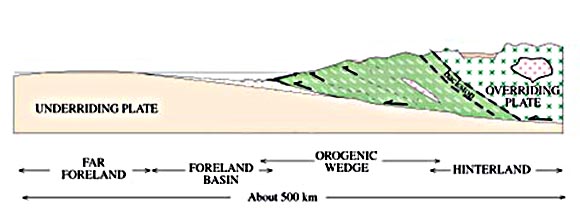
Nappe
In geology, a nappe or thrust sheet is a large sheetlike body of rock that has been moved more than or above a thrust fault from its original position. Nappes form in compressional tectonic settings like continental collision zones or on the overriding plate in active subduction zones. Nappes form when a mass of rock is forced (or "thrust") over another rock mass, typically on a low angle fault plane. The resulting structure may include large-scale recumbent folds, shearing along the fault plane,Twiss, Robert J. and Eldridge M. Moores, ''Structural Geology,'' W. H. Freeman, 1992, p. 236 imbricate thrust stacks, fensters and klippes. The term stems from the French word for ''tablecloth'' in allusion to a rumpled tablecloth being pushed across a table. History Nappes or nappe belts are a major feature of the European Alps, Dinarides, Carpathians and Balkans. Since the 19th century many geologists have uncovered areas with large-scale overthrusts. Some of these were su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleocene
The Paleocene ( ), or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by an asteroid impact (Chicxulub impact) and possibly volcanism (Deccan Traps), marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senonian
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and Ape, hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flysch
Flysch () is a sequence of sedimentary rock layers that progress from deep-water and turbidity flow deposits to shallow-water shales and sandstones. It is deposited when a deep basin forms rapidly on the continental side of a mountain building episode. Examples are found near the North American Cordillera, the Alps, the Pyrenees and the Carpathians. Sedimentological properties Flysch consists of repeated sedimentary cycles with upwards fining of the sediments. There are sometimes coarse conglomerates or breccias at the bottom of each cycle, which gradually evolve upwards into sandstone and shale/mudstone. Flysch typically consists of a sequence of shales rhythmically interbedded with thin, hard, graywacke-like sandstones. Typically the shales do not contain many fossils, while the coarser sandstones often have fractions of micas and glauconite. Tectonics In a continental collision, a subducting tectonic plate pushes on the plate above it, making the rock fold, often t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleogene
The Paleogene Period ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Ma. It is the first period of the Cenozoic Era, the tenth period of the Phanerozoic and is divided into the Paleocene, Eocene, and Oligocene epochs. The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the time now covered by the Paleogene Period and subsequent Neogene Period; despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. Paleogene is often abbreviated "Pg", although the United States Geological Survey uses the abbreviation "" for the Paleogene on the Survey's geologic maps. Much of the world's modern vertebrate diversity originated in a rapid surge of diversification in the early Paleogene, as survivors of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event took advantage of empty ecolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Craton
A craton ( , , or ; from "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and rifting of continents, cratons are generally found in the interiors of tectonic plates; the exceptions occur where geologically recent rifting events have separated cratons and created passive margins along their edges. Cratons are characteristically composed of ancient crystalline basement rock, which may be covered by younger sedimentary rock. They have a thick crust and deep lithospheric roots extending several hundred kilometres into Earth's mantle. Terminology The term ''craton'' is used to distinguish the stable portion of the continental crust from regions that are more geologically active and unstable. Cratons are composed of two layers: a continental '' shield'', in which the basement rock crops out at the surface, and a '' platform'' which o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era and the seventh period of the Phanerozoic Eon. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles such as the dinosaurs, and of Gymnosperm, gymnosperms such as cycads, ginkgoaceae and Araucariaceae, araucarian conifers; a hot Greenhouse and icehouse earth, greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since Cambrian explosion, complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic. The era began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the largest mass extinction in Earth's history, and ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, another mass extinction whose victims included the non-avian dinosaurs, Pterosaur, pterosaurs, Mosasaur, mosasaurs, and Plesiosaur, plesiosaurs. The Mesozoic was a time of significant tectonic, climatic, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic is subdivided into six period (geology), geologic periods (from oldest to youngest), Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. Some geological timescales divide the Paleozoic informally into early and late sub-eras: the Early Paleozoic consisting of the Cambrian, Ordovician and Silurian; the Late Paleozoic consisting of the Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. The name ''Paleozoic'' was first used by Adam Sedgwick (1785–1873) in 1838 to describe the Cambrian and Ordovician periods. It was redefined by John Phillips (geologist), John Phillips (1800–1874) in 1840 to cover the Cambrian to Permian periods. It is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek ''palaiós'' (π� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterozoic
The Proterozoic ( ) is the third of the four geologic eons of Earth's history, spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8 Mya, and is the longest eon of Earth's geologic time scale. It is preceded by the Archean and followed by the Phanerozoic, and is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". The Proterozoic is subdivided into three geologic eras (from oldest to youngest): the Paleoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic. It covers the time from the appearance of free oxygen in Earth's atmosphere to just before the proliferation of complex life on the Earth during the Cambrian Explosion. The name ''Proterozoic'' combines two words of Greek origin: meaning "former, earlier", and , meaning "of life". Well-identified events of this eon were the transition to an oxygenated atmosphere during the Paleoproterozoic; the evolution of eukaryotes via symbiogenesis; several global glaciations, which produced the 300 million years-long Huronian glaciation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |