|
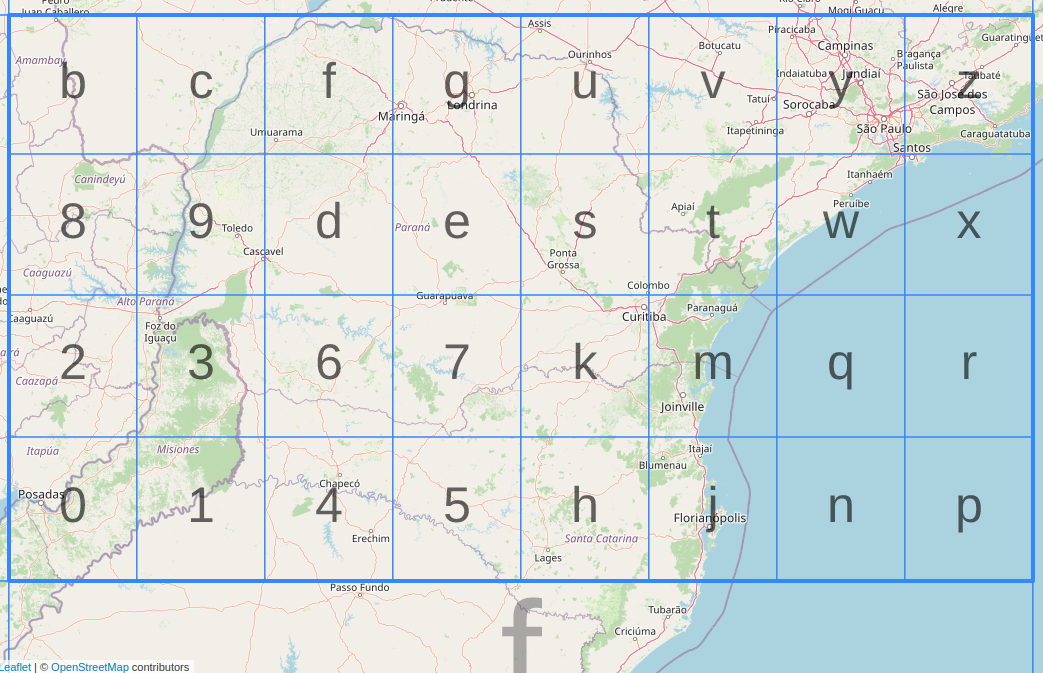
Geohash
Geohash is a public domain geocode system invented in 2008 by Gustavo Niemeyer * * * which encodes a geographic location into a short string of letters and digits. Similar ideas were introduced by G.M. Morton in 1966. It is a hierarchical spatial data structure which subdivides space into buckets of grid shape, which is one of the many applications of what is known as a Z-order curve, and generally space-filling curves. Geohashes offer properties like arbitrary precision and the possibility of gradually removing characters from the end of the code to reduce its size (and gradually lose precision). Geohashing guarantees that the longer a shared prefix between two geohashes is, the spatially closer they are together. The reverse of this is not guaranteed, as two points can be very close but have a short or no shared prefix. History The core part of the Geohash algorithm and the first initiative to similar solution was documented in a report of G.M. Morton in 1966, "A Compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geocode
A geocode is a code that represents a geographic entity (location or Geographical feature, object). It is a unique identifier of the entity, to distinguish it from others in a finite set of geographic entities. In general the ''geocode'' is a human-readable and short identifier. Typical geocodes (in bold) and entities represented by it: * ''Country code'' and subdivision code. Polygon of the administrative boundaries of a country or a subdivision. The main examples are ISO codes: ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code (e.g. AF for Afghanistan or BR for Brazil), and its subdivision conventions, such as ISO 3166-2:AF, subdivision codes (e.g. AF-GHO for Ghor province) or ISO 3166-2:BR, subdivision codes (e.g. BR-AM for Amazonas (Brazilian state), Amazonas state). * ''DGG cell ID''. Identifier of a cell of a discrete global grid: a Geohash code (e.g. ~0.023km2 cell 6vd23gq at Brazil's Geographical centre, centroid) or a Open Location Code, Plus Code (e.g. ~0.0002km2 cell 58Q8XXXX+XX with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base32
Base32 is an encoding method based on the Radix, base-32 numeral system. It uses an alphabet of 32 Numerical digit, digits, each of which represents a different combination of 5 bits (25). Since base32 is not very widely adopted, the question of notation—which characters to use to represent the 32 digits—is not as settled as in the case of more well-known numeral systems (such as hexadecimal), though Request for Comments, RFCs and unofficial and de-facto standards exist. One way to represent Base32 numbers in human-readable form is using digits 0–9 followed by the twenty-two upper-case letters A–V. However, many other variations are used in different contexts. Historically, Baudot code could be considered a modified (State (computer_science), stateful) base32 code. Base32 is often used to represent byte strings. RFC 4648 encodings The October 2006 proposed Internet standard documents base16, base32 and base64 encodings. It includes two schemes for base32, but recommends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base 32
Base32 is an encoding method based on the base-32 numeral system. It uses an alphabet of 32 digits, each of which represents a different combination of 5 bits (25). Since base32 is not very widely adopted, the question of notation—which characters to use to represent the 32 digits—is not as settled as in the case of more well-known numeral systems (such as hexadecimal), though RFCs and unofficial and de-facto standards exist. One way to represent Base32 numbers in human-readable form is using digits 0–9 followed by the twenty-two upper-case letters A–V. However, many other variations are used in different contexts. Historically, Baudot code could be considered a modified (stateful) base32 code. Base32 is often used to represent byte strings. RFC 4648 encodings The October 2006 proposed Internet standard documents base16, base32 and base64 encodings. It includes two schemes for base32, but recommends one over the other. It further recommends that regardless of precede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space-filling Curves
In mathematical analysis, a space-filling curve is a curve whose range reaches every point in a higher dimensional region, typically the unit square (or more generally an ''n''-dimensional unit hypercube). Because Giuseppe Peano (1858–1932) was the first to discover one, space-filling curves in the 2-dimensional plane are sometimes called ''Peano curves'', but that phrase also refers to the Peano curve, the specific example of a space-filling curve found by Peano. The closely related FASS curves (approximately space-Filling, self-Avoiding, Simple, and Self-similar curves) can be thought of as finite approximations of a certain type of space-filling curves. Definition Intuitively, a curve in two or three (or higher) dimensions can be thought of as the path of a continuously moving point. To eliminate the inherent vagueness of this notion, Jordan in 1887 introduced the following rigorous definition, which has since been adopted as the precise description of the notion of a ''c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latitude And Longitude
A geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a spherical or geodetic coordinate system for measuring and communicating positions directly on Earth as latitude and longitude. It is the simplest, oldest, and most widely used type of the various spatial reference systems that are in use, and forms the basis for most others. Although latitude and longitude form a coordinate tuple like a cartesian coordinate system, the geographic coordinate system is not cartesian because the measurements are angles and are not on a planar surface. A full GCS specification, such as those listed in the EPSG and ISO 19111 standards, also includes a choice of geodetic datum (including an Earth ellipsoid), as different datums will yield different latitude and longitude values for the same location. History The invention of a geographic coordinate system is generally credited to Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who composed his now-lost ''Geography'' at the Library of Alexandria in the 3rd century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z-order Curve
In mathematical analysis and computer science, functions which are Z-order, Lebesgue curve, Morton space-filling curve, Morton order or Morton code map multidimensional data to one dimension while preserving locality of the data points (two points close together in multidimensions with high probability lie also close together in Morton order). It is named in France after Henri Lebesgue, who studied it in 1904, and named in the United States after Guy Macdonald Morton, who first applied the order to file sequencing in 1966. The z-value of a point in multidimensions is simply calculated by bit interleaving the binary representations of its coordinate values. However, when querying a multidimensional search range in these data, using binary search is not really efficient: It is necessary for calculating, from a point encountered in the data structure, the next possible Z-value which is in the multidimensional search range, called BIGMIN. The BIGMIN problem has first been stated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographical Coordinate System
A geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a spherical or geodetic coordinate system for measuring and communicating positions directly on Earth as latitude and longitude. It is the simplest, oldest, and most widely used type of the various spatial reference systems that are in use, and forms the basis for most others. Although latitude and longitude form a coordinate tuple like a cartesian coordinate system, the geographic coordinate system is not cartesian because the measurements are angles and are not on a planar surface. A full GCS specification, such as those listed in the EPSG and ISO 19111 standards, also includes a choice of geodetic datum (including an Earth ellipsoid), as different datums will yield different latitude and longitude values for the same location. History The invention of a geographic coordinate system is generally credited to Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who composed his now-lost ''Geography'' at the Library of Alexandria in the 3rd century&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geotagging
Geotagging, or GeoTagging, is the process of adding geographical identification metadata to various media such as a geotagged photograph or video, websites, SMS messages, QR Codes or RgSSfeeds and is a form of geospatial metadata. This data usually consists of latitude and longitude coordinates, though they can also include altitude, bearing, distance, accuracy data, and place names, and perhaps a time stamp. Geotagging can help users find a wide variety of location-specific information from a device. For instance, someone can find images taken near a given location by entering latitude and longitude coordinates into a suitable image search engine. Geotagging-enabled information services can also potentially be used to find location-based news, websites, or other resources. Geotagging can tell users the location of the content of a given picture or other media or the point of view, and conversely on some media platforms show media relevant to a given location. The geog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edge Case
An edge case is a problem or situation that occurs only at an extreme (maximum or minimum) operating parameter. For example, a stereo speaker might noticeably distort audio when played at maximum volume, even in the absence of any other extreme setting or condition. An edge case can be expected or unexpected. In engineering, the process of planning for and gracefully addressing edge cases can be a significant task, and yet this task may be overlooked or underestimated. Some common causes of edge cases are: * Unpredictable user behavior * Evolution of use cases (e.g. user behavior may change over time) * Limited test coverage * Product complexity (for instance, in distributed systems or microservice architectures) * Resource limitations (e.g. limited processing power, computer memory, or computer storage) * Other external causes Some basic examples of edge cases include: * A long username in an app overflows and displays incorrectly * A booking system does not handle reservati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textual Representation
In literary theory, textuality comprises all of the attributes that distinguish the communicative content under analysis as an object of study. It is associated with structuralism and post-structuralism. Explanation Textuality is not just about the written word; it also comprises the placement of the words and the reader’s interpretation. There is not a set formula to describe a text’s textuality; it is not a simple procedure. This summary is true even though the interpretation that a reader develops from that text may decide the identity and the definitive meanings of that text. Textuality, as a literary theory, is that which constitutes a text in a particular way. The text is an undecidable (there is an inexistence of an effective or "strict" method of writing or structure). Aspects Being textual includes innumerable elements and aspects. Each and every form of text and text in that form of literature embraces and consists of its own individual and personal characteristic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jutland, Denmark
Jutland (; , ''Jyske Halvø'' or ''Cimbriske Halvø''; , ''Kimbrische Halbinsel'' or ''Jütische Halbinsel'') is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany (Schleswig-Holstein). It stretches from the Grenen spit in the north to the confluence of the Elbe and the Sude in the southeast. The historic southern border river of Jutland as a cultural-geographical region, which historically also included Southern Schleswig, is the Eider. The peninsula, on the other hand, also comprises areas south of the Eider: Holstein, the former duchy of Lauenburg, and most of Hamburg and Lübeck. Jutland's geography is flat, with comparatively steep hills in the east and a barely noticeable ridge running through the center. West Jutland is characterised by open lands, heaths, plains, and peat bogs, while East Jutland is more fertile with lakes and lush forests. The southwestern coast is characterised by the Wadden Sea, a large, un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |