|
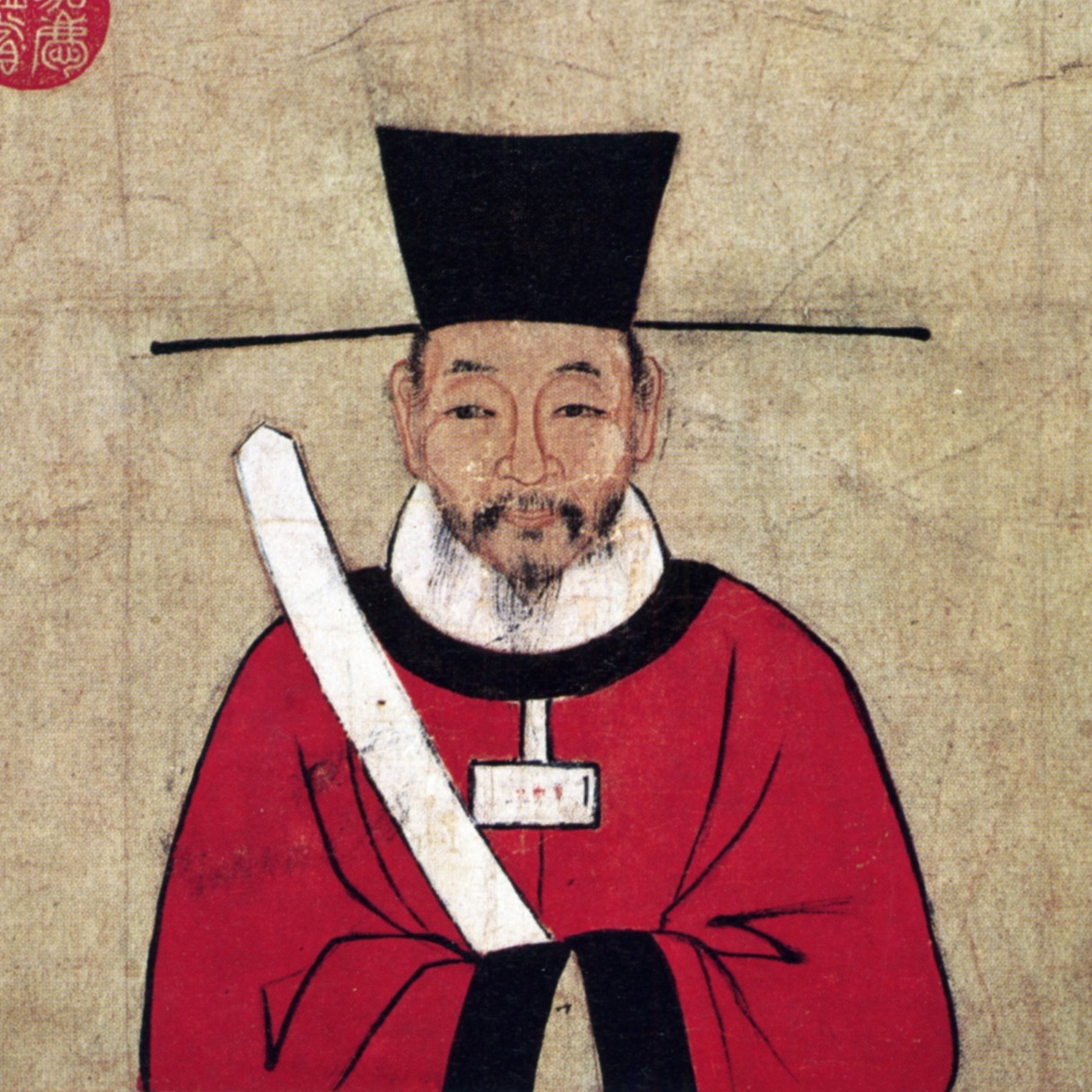
Gao Heng
Gao Heng (; July or August 570 – 577), often known in historiography as the Youzhu of Northern Qi (, meaning 'child ruler'), was the last emperor of the Chinese Northern Qi dynasty. In 577, the Northern Qi was under a major attack by the rivaling Northern Zhou dynasty. Gao Heng's father Gao Wei, then emperor, wanted to try to deflect ill omens that portended a change in imperial status. He and therefore passed the throne to Gao Heng. Later that year, after they fled in face of Northern Zhou forces' arrival, they were captured and taken to the Northern Zhou capital Chang'an. There in winter 577, the Emperor Wu of Northern Zhou ordered them, as well as other members of the Gao clan, to commit suicide. Northern Qi territories were annexed by the Northern Zhou, marking the collapse of the Northern Qi dynasty. Gao Jie (高湝) succeeded to the Northern Qi throne thereafter, although this was only nominal due to the dynasty's ''de facto'' end. For several years Gao Wei's cousin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gao (surname)
Gao () is an East Asian surname of Chinese origin that can be literally translated as "high" or "tall". There are approximately 17 million living people with this surname. Some places, such as Taiwan, usually romanise this family name into "Kao". In Hong Kong, it is romanized to "Ko". In Macau, it is romanized to "Kou". In English, it is romanized to "Kauh". In 2019 it was the 19th most common surname in Mainland China. The Korean surname, "Ko (Korean surname), Ko" or "Koh", is derived from and written with the same Chinese character (高). Romanisation and pronunciation Origin According to ''Lüshi Chunqiu'', the earliest figure with the Gao surname was Gao Yuan (高元) who created dwellings in antiquity. Zhuanxu, the grandson of the Yellow Emperor, was also known as Gao Yang (高陽). Another origin of Gao is the Jiang (surname 姜), Jiang (姜) surname. According to the Song dynasty encyclopedia ''Tongzhi (encyclopedia), Tongzhi'', an early ancestor was Gao Xi (高傒) w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanxi
Shanxi; Chinese postal romanization, formerly romanised as Shansi is a Provinces of China, province in North China. Its capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi and Datong. Its one-character abbreviation is (), after the Jin (Chinese state), state of Jin that existed there during the Spring and Autumn period (). The name ''Shanxi'' means 'west of the mountains', a reference to its location west of the Taihang Mountains. Shanxi borders Hebei to the east, Henan to the south, Shaanxi to the west and Inner Mongolia to the north. Shanxi's terrain is characterised by a plateau bounded partly by mountain ranges. Shanxi's culture is largely dominated by the ethnic Han Chinese, Han majority, who make up over 99% of its population. Jin Chinese is considered by some linguists to be a distinct language from Mandarin and its geographical range covers most of Shanxi. Both Jin and Mandarin are spoken in Shanxi. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zizhi Tongjian
The ''Zizhi Tongjian'' (1084) is a chronicle published during the Northern Song dynasty (960–1127) that provides a record of Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynasties and spanning almost 1400 years. The main text is arranged into 294 scrolls (), each equivalent to a chapter—totaling around 3 million Chinese characters. In 1065, Emperor Yingzong of Song commissioned his official, Sima Guang (1019–1086), to lead a project to compile a Universal history (genre), universal history of China, and granted him funding and the authority to appoint his own staff. His team took 19 years to complete the work and in 1084 it was presented to Emperor Yingzong's successor Emperor Shenzong of Song. It was well-received and has proved to be immensely influential among both scholars and the general public. Endymion Wilkinson regards it as reference quality: "It had an enormous influence on later Chinese historical writing, either directly or through its many a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tian Wang
Heavenly King or Tian Wang (), also translated as Heavenly Prince, is a Chinese title for various religious deities and divine leaders throughout history, as well as an alternate form of the term ''Son of Heaven'', referring to the emperor. The Chinese term for Heavenly King consists of two Chinese characters: 天 (''tiān''), meaning "heaven" or "sky", and 王 (''wáng''), which could mean either "king" or "prince" depending on the context. The term was most notably used in its most recent sense as the title of the kings of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom, but is also used in religious (particularly Buddhist) contexts as well. Historical uses Spring and Autumn period In the Spring and Autumn period, the term ''Heavenly King'' was used to at least some extent to refer to the kings of the various Chinese states of the time. On the second page of the first text of the Spring and Autumn Annals, the term ''Heavenly King'' is used in the description of how the King of Zhou helped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Northern Qi
The ''Book of Northern Qi'' (), was the official history of the Chinese dynasty Northern Qi. It was written by the Tang dynasty historian Li Baiyao (李百藥) and was completed in 636. It is listed among the official Twenty-Four Histories of China. The original book contained 50 chapters but it was found during the Song dynasty that only 17 chapters were intact. The rest are lost. Contents Annals (紀) {, class=wikitable width=100% , - ! width=10%, # !! width=35%, Title !! width=35%, Translation !! width=20%, Notes , - , Volume 1 , , 帝紀第1 神武帝上 , , Emperor Shenwu , , , - , Volume 2 , , 帝紀第2 神武帝下 , , Emperor Shenwu , , , - , Volume 3 , , 帝紀第3 文襄帝 , , Emperor Wenxiang , , , - , Volume 4 , , 帝紀第4 文宣帝 , , Emperor Wenxuan , , , - , Volume 5 , , 帝紀第5 廢帝 , , Emperor Fei , , , - , Volume 6 , , 帝紀第6 孝昭帝 , , Emperor Xiaozhao , , , - , Volume 7 , , 帝紀第7 武成� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shandong
Shandong is a coastal Provinces of China, province in East China. Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilization along the lower reaches of the Yellow River. It has served as a pivotal cultural and religious center for Taoism, Chinese Buddhism and Confucianism. Shandong's Mount Tai is the most revered mountain of Taoism and a site with one of the longest histories of continuous religious worship in the world. The Buddhist temples in the mountains south of the provincial capital of Jinan were once among the foremost Buddhist sites in China. The city of Qufu was the birthplace of Confucius, and later became the center of Confucianism. Shandong's location at the intersection of ancient and modern north–south and east–west trading routes has helped establish it as an economic center. After a period of political instability and economic hardship beginning in the late 19th century, Shandong has experienced rapid growth in recent de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liaocheng
Liaocheng ( zh, s=, p=Liáochéng), is a prefecture-level city in western Shandong province, China. It borders the provincial capital of Jinan to the southeast, Dezhou to the northeast, Tai'an to the south, and the provinces of Hebei and Henan to the west. The Grand Canal flows through the city center. Its population was 5,789,863 at the 2010 census whom 1,229,768 lived in the built-up area made up of Donchangfu district, even though large parts remain rural. During the Song dynasty, the area of present-day Liaocheng included the prefectures of Bo and Ji. In 2007, the city is named China's top ten livable cities by Chinese Cities Brand Value Report, which was released at 2007 Beijing Summit of China Cities Forum. Administration The prefecture-level city of Liaocheng administers eight county-level divisions, including two districts, one county-level city, and five counties. * Dongchangfu District () * Chiping District () * Linqing City () * Yanggu County () * Dong'e Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Dynasty
The Chen dynasty (), alternatively known as the Southern Chen (南陳 / 南朝陳) in historiography, was a Dynasties in Chinese history, Chinese imperial dynasty and the fourth and last of the Northern and Southern dynasties#Southern dynasties, Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. Following the Liang dynasty, the Chen dynasty was founded by Emperor Wu of Chen, Chen Baxian (Emperor Wu). The Chen dynasty further strengthened and revitalized the economy and culture of southern China, and made territorial expansions northward, laying the foundation for future dynasties. It was conquered by the Sui dynasty in 589, marking an end to the Northern and Southern dynasties period in Chinese history. The descendants of the Chen imperial family continued to hold powerful high-ranking positions in the imperial courts of both the Sui and Tang dynasty, Tang dynasties. History Founding and expansion: Chen Baxian In the twilight of the Liang dynasty (548–55 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow River
The Yellow River, also known as Huanghe, is the second-longest river in China and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system on Earth, with an estimated length of and a Drainage basin, watershed of . Beginning in the Bayan Har Mountains, the river flows generally eastwards before entering the long Ordos Loop, which runs northeast at Gansu through the Ordos Plateau and turns east in Inner Mongolia. The river then turns sharply southwards to form the border between Shanxi and Shaanxi, turns eastwards at its confluence with the Wei River, and flows across the North China Plain before emptying into the Bohai Sea. The river is named for the yellow color of its water, which comes from the large amount of sediment discharged into the water as the river flows through the Loess Plateau. The Yellow River basin was the birthplace of Yellow River civilization, ancient Chinese civilization. According to traditional Chinese historiography, the Xia dynasty originated on it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taishang Huang
In Chinese history, a Taishang Huang or Taishang Huangdi is an honorific and institution of a retired emperor. The former emperor had, at least in name, abdicated in favor of someone else. Although no longer the reigning sovereign, there are instances where the retired emperor became a power behind the throne, often exerting more power than the reigning emperor. History Origin The title ''Taishang Huangdi'' was first used when Qin Shi Huangdi bestowed it upon his deceased father, King Zhuangxiang. Development Emperor Gaozu of Han bestowed the title ''Taishang Huangdi'' on his then-living father Liu Taigong. He bestowed it onto his father to express filial piety. Furthermore, it was intended to preserve the social hierarchy between father and son, as the former was a commoner and the latter was a dynastic founder. In 301, during the War of the Eight Princes, Sima Lun became the emperor by forcing his puppet Emperor Hui of Jin to become the ''Taishang Huang''. The title h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebei
Hebei is a Provinces of China, province in North China. It is China's List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, sixth-most populous province, with a population of over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. It borders Shanxi to the west, Henan to the south, Shandong and Liaoning to the east, and Inner Mongolia to the north; in addition, Hebei entirely surrounds the direct-administered municipalities of Beijing and Tianjin on land. Its population is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu people, Manchu, 0.8% Hui people, Hui, and 0.3% Mongols in China, Mongol. Varieties of Chinese spoken include Jilu Mandarin, the Beijing dialect of Mandarin, and Jin Chinese. During the Spring and Autumn period, Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods (771–226 BC), the region was ruled by the states of Yan (state), Yan and Zhao (state), Zhao. During the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368), the region was called Zhongshu Sheng, Zhongshu. It was called North Zhili during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handan
Handan is a prefecture-level city located in the southwest of Hebei province, China. The southernmost prefecture-level city of the province, it borders Xingtai on the north, and the provinces of Shanxi on the west, Henan on the south and Shandong on the east. At the 2010 census, its population was 9,174,683 inhabitants whom 2,845,790 lived in the built-up (''or metro'') area made of 5 urban districts. Yongnian District in Handan and Shahe City in Xingtai have largely formed into a single conurbation. Handan is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities#East Asia, oldest cities in China, first settled around 6500 BC by the Cishan culture. Throughout the city's long history, it contributed significantly to Chinese culture, serving as the capital of Zhao (state), State of Zhao, was northern China's political, economic and cultural center, and home to Tai chi and the first compass, made from stones collected in the nearby Mount Ci (magnet mountain). Handan is designate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |