|
Gakuen-ji
is a Buddhist temple located in the Besshō neighborhood of the city of Izumo, Shimane Prefecture, Japan. The temple's full name is . It belongs to the Tendai sect of Japanese Buddhism, and its ''honzon'' is a statue of Senjū Kannon and Yakushi Nyōrai. Its ground so have been designated a National Historic Site since 2016 History The early history of the temple is unknown. According to the temple's own legend, during the second year of Empress Suiko (594), Chishun Shōnin of Shinano prayed at the Uro-no-taki Waterfall at Mount Tabushi and healed Empress Suiko's eye disease, so a temple was built by imperial request. The name of the temple, Gakuen-ji, comes from the legend that when Chishun Shōnin was training near Uro-no-taki Falls, he accidentally dropped a Buddhist object into the basin of the waterfall, and a "crocodile" offered it back to him. Manpuku-ji, another temple in Izumo city shares the same legend. Shimane Prefecture, where Gakuen-ji is located, and neighb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century Before the Common Era, BCE. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to Western world, the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of bhavana, development which leads to Enlightenment in Buddhism, awakening and moksha, full liberation from ''Duḥkha, dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ennin
, better known in Japan by his posthumous name, Jikaku Daishi (), was a priest of the Tendai school of Buddhism in Japan, and its third . Ennin was instrumental in expanding the Tendai Order's influence, and bringing back crucial training and resources from China, particularly esoteric Buddhist training and Pure Land teachings. He is most well known for integrating esoteric practices ('' Taimitsu'') with the teachings of the ''Lotus Sutra.'' His journey to Tang China (838–847) and his subsequent writings profoundly influenced Japanese Buddhism. Life Birth and origin He was born into the Mibu () family in Shimotsuke Province (present-day Tochigi Prefecture), Japan and entered the Buddhist priesthood at Enryaku-ji on Mt. Hiei (Hieizan) near Kyoto at the age of 15. Studying under Saichō, the founder of Japanese Tendai Buddhism, Ennin excelled in his studies, particularly in the ''Lotus Sutra'' and Tiantai meditation practices. After Saichō’s death, Ennin sought to de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanboku-chō Period
The , also known as the Northern and Southern Courts period, was a period in Japanese history between 1336-1392 CE, during the formative years of the Ashikaga shogunate, Muromachi (Ashikaga) shogunate. Ideologically, the two courts fought for 50 years, with the South giving up to the North in 1392. In reality the Northern court was under the power of the Ashikaga shogunate and had little real independence. The destruction of the Kamakura shogunate of 1333 and the failure of the Kenmu Restoration in 1336 opened up a legitimacy crisis for the new shogunate. Institutional changes in the estate system (''shōen'') that formed the bedrock of the income of nobles and warriors altered the status of the various social groups. The establishment of the Ashikaga shogunate broadened the economic base of the warriors, while undercutting the noble proprietors. However, this trend had started already with the Kamakura Shogun#Shogunate, ''bakufu''. Background During the early period, there ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
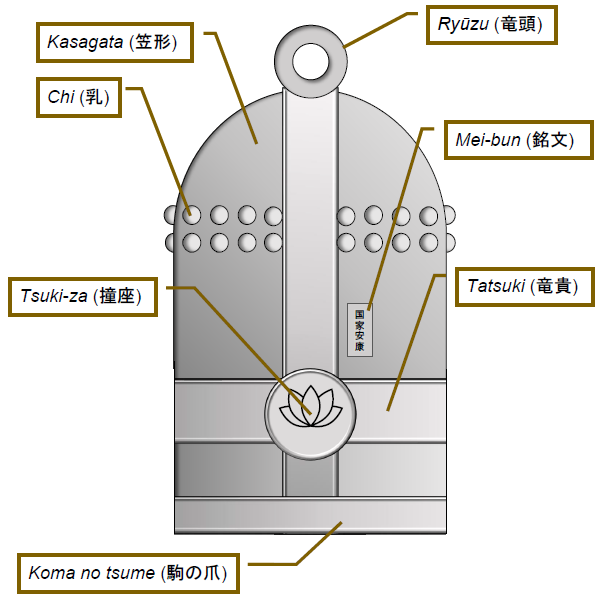
Bonshō
, also known as or are large bell (instrument), bells found in Buddhist temples in Japan, Buddhist temples throughout Japan, used to summon the monks to prayer and to demarcate periods of time. Rather than containing a clapper, are struck from the outside, using either a handheld mallet or a beam suspended on ropes. The bells are usually made from bronze, using a form of Casting (metalworking)#Expendable mold casting, expendable mould casting. They are typically augmented and ornamented with a variety of Boss (architecture), bosses, raised bands and inscriptions. The earliest of these bells in Japan date to around 600 Common Era, CE, although the general design is of much earlier Chinese origin and shares some of the features seen in ancient Chinese bells. The bells' penetrating and pervasive tone carries over considerable distances, which led to their use as signals, timekeepers and alarms. In addition, the sound of the bell is thought to have supernatural properties; it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
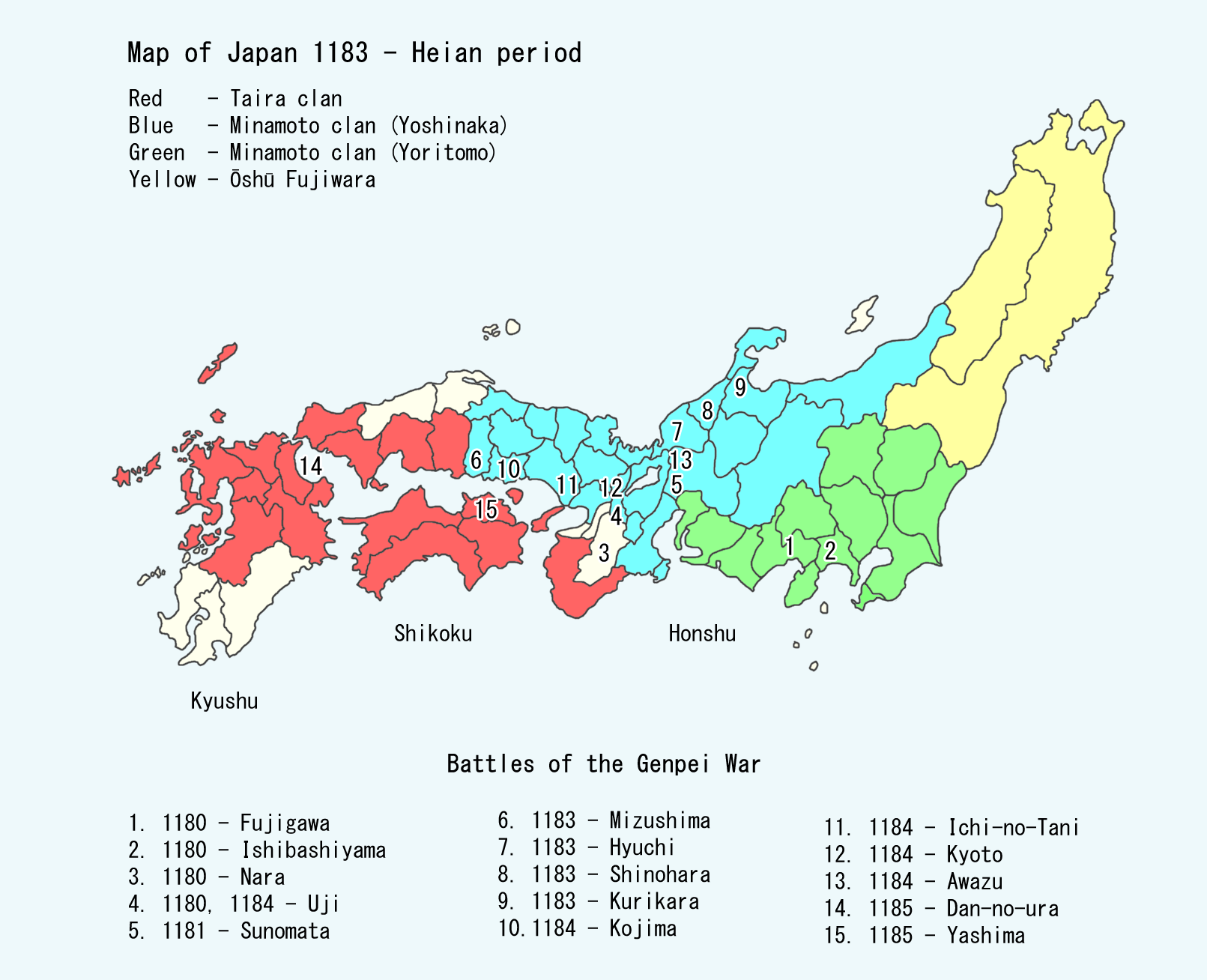
Battle Of Dannoura
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas battl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taira Clan
The was one of the four most important Japanese clans, clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian period, Heian period of History of Japan, Japanese history – the others being the Minamoto clan, Minamoto, the Fujiwara clan, Fujiwara, and the Tachibana clan (kuge), Tachibana. The clan is divided into four major groups, named after the Emperor of Japan, emperors they descended from: Emperor Kanmu, Kanmu Heishi, Emperor Ninmyō, Ninmyō Heishi, Emperor Montoku, Montoku Heishi, and Emperor Kōkō, Kōkō Heishi, the most influential of which was the Kanmu Heishi line. In the twilight of the Heian period, the Taira controlled the boy emperor Emperor Antoku, Antoku (himself the grandson of the powerful ''Kugyō'' Taira no Kiyomori) and had effectively dominated the Imperial capital of Heian-kyō, Heian. However, they were opposed by their rivals the Minamoto clan (the Genji), which culminated in the Genpei War (1180–1185 AD). The five-year-long war concluded with a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minamoto No Yoshitsune
was a commander of the Minamoto clan of Japan in the late Heian period, Heian and early Kamakura period, Kamakura periods. During the Genpei War, he led a series of battles that toppled the Ise-Heishi branch of the Taira clan, helping his half-brother Minamoto no Yoritomo, Yoritomo consolidate power. He is considered one of the greatest and the most popular warriors of his era, and one of the most famous samurai in the history of Japan. Yoshitsune perished after being betrayed by the son of a trusted ally and was labelled as a tragic hero. Early life Yoshitsune was the ninth son of Minamoto no Yoshitomo, and the third and final son and child that Yoshitomo would father with Tokiwa Gozen. Yoshitsune's older half-brother Minamoto no Yoritomo (the third son of Yoshitomo) would go on to establish the Kamakura shogunate. Yoshitsune's name in childhood was or ''young bull'' (). He was born just before the Heiji Rebellion in 1160 in which his father and two oldest brothers were kil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benkei
, popularly known by the mononym Benkei (), was a Japanese warrior monk (''sōhei'') who lived in the latter years of the Heian Period (794–1185). Benkei led a varied life, first becoming a monk, then a mountain ascetic, and then a rogue warrior. He later came to respect and serve the famous warrior Minamoto no Yoshitsune, also known as Ushiwakamaru. He is commonly depicted as a man of great strength and loyalty, and a popular subject of Japanese folklore showcased in many ancient and modern literature and productions. The earliest records of Benkei are in the '' Azuma Kagami'', ''The Tale of the Heike'', and the '' Genpei Jōsuiki''—all sources from around a century or more after Benkei's life. These sources generally only indicate Benkei was one of Yoshitsune's retainers and was a thin monk, although they do indicate Yoshitsune was aided and protected by a band of rogueish ''sōhei'' (warrior-monks) near Mount Hiei after he fled the capital—perhaps the historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |