|
GWR 3521 Class
The 3521 Class were forty tank locomotives designed by William Dean to haul passenger trains on the Great Western Railway. They were introduced as locomotives in 1887, but were quickly altered to become s to improve their running. Following two serious accidents they were further altered from 1899 to run as tender locomotives, in which form the last was withdrawn in 1934. Locomotives 0-4-2T standard gauge The first twenty locomotives were turned out in 1887 as locomotives for services on the lines. * 3521 * 3522 * 3523 * 3524 * 3525 * 3526 * 3527 * 3528 * 3529 * 3530 * 3531 * 3532 * 3533 * 3534 * 3535 * 3536 * 3537 * 3538 * 3539 * 3540 0-4-2ST broad gauge In 1888 a further batch of twenty were ordered as s for the broad gauge lines in Devon and Cornwall. * 3541 (1888 - 1890) * 3542 (1888 - 1891) * 3543 (1888 - 1891) * 3544 (1888 - 1890) * 3545 (1888 - 1891) * 3546 (1888 - 1890) * 3547 (1888 - 1891) * 3548 (1888 - 1891) * 3549 (1888 - 1891) * 3550 (1888 - 1890) * 3551 (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Dean (engineer)
William Dean (8 January 1840 – 24 September 1905) was an English railway engineer. He was the second son of Henry Dean, who was the manager of the Hawes Soap Factory in New Cross, London. William was educated at the Haberdashers' Company School. He became the Chief Locomotive Engineer for the Great Western Railway from 1877, when he succeeded Joseph Armstrong. He retired from the post in 1902 and was replaced by George Jackson Churchward. He designed famous steam locomotive classes such as the Duke Class, the Bulldog Class and the long-lived 2301 Class. Apprenticeship He was apprenticed at the age of fifteen to Joseph Armstrong at the Great Western Railway's Wolverhampton Stafford Road Works. During his eight-year apprenticeship he attended Wolverhampton Working Men's College in the evening, excelling in mathematics and engineering. Upon completion of his apprentice years in 1863 he was made Joseph Armstrong's chief assistant. Posts with GWR A year later, Joseph Arms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
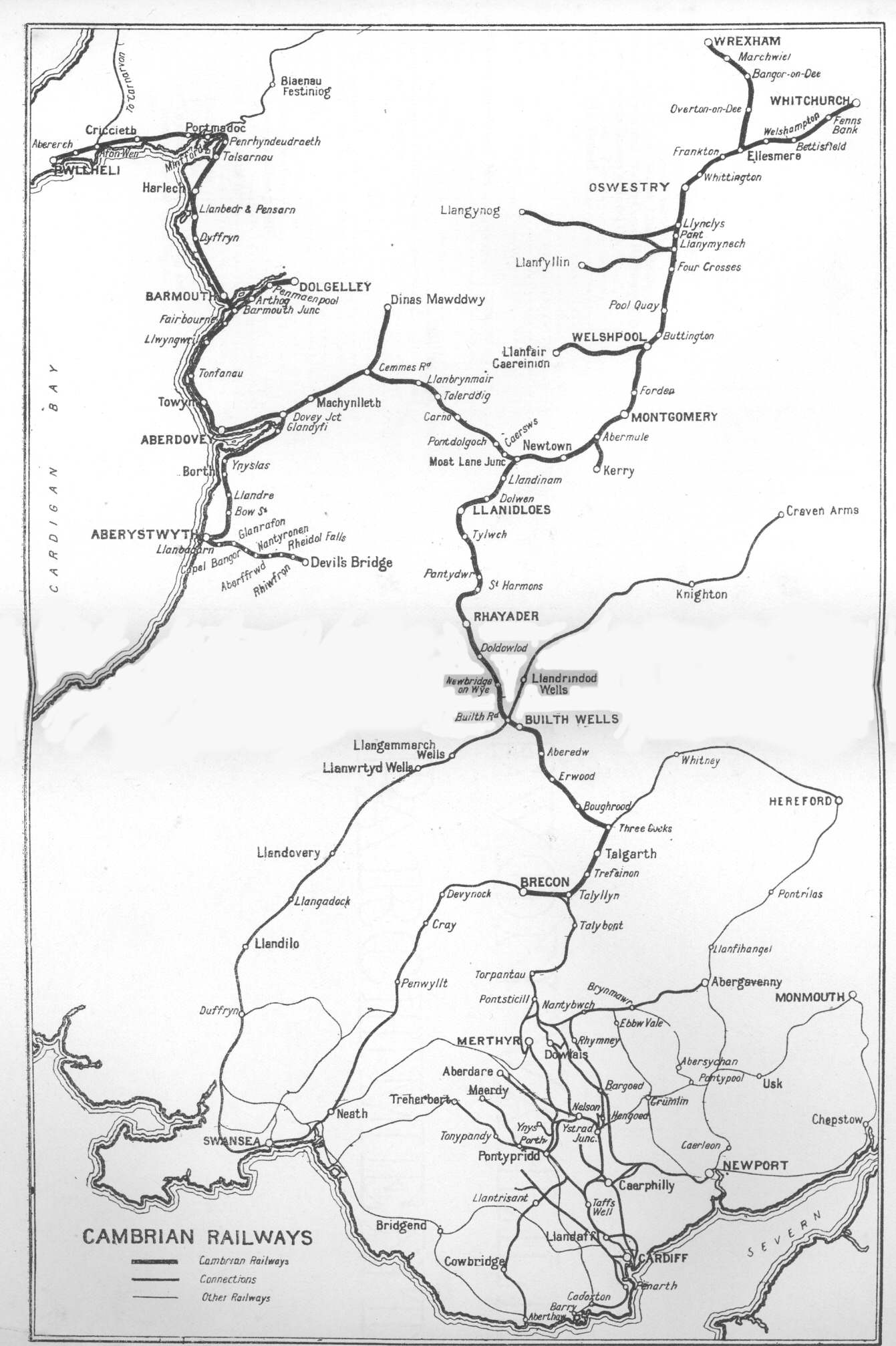
Cambrian Railways
The Cambrian Railways owned of Railway track, track over a large area of mid Wales. The system was an amalgamation of a number of railways that were incorporated in 1864, 1865 and 1904. The Cambrian connected with two larger railways with connections to the northwest of England via the London and North Western Railway, and the Great Western Railway for connections between London and Wales. The Cambrian Railways amalgamated with the Great Western Railway on 1 January 1922 as a result of the Railways Act 1921. The name is continued today in the route known as the Cambrian Line. History Creation of the Cambrian Railways: 1864 The Cambrian Railways Company was created on 25 July 1864 when the (27 & 28 Vict. c. cclxii) received royal assent. The company was formed by amalgamating most of the railway companies in mid Wales: the Oswestry and Newtown Railway, the Llanidloes and Newtown Railway, the Newtown and Machynlleth Railway and the Oswestry, Ellesmere and Whitchurch Rai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard-gauge Steam Locomotives Of Great Britain
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the most widely used track gauge around the world, with about 55% of the lines in the world using it. All high-speed rail lines use standard gauge except those in Russia, Finland, Uzbekistan, and some line sections in High-speed rail in Spain, Spain. The distance between the inside edges of the heads of the rails is defined to be 1,435 mm except in the United States, Canada, and on some heritage British lines, where it is defined in Imperial and US customary measurement systems, U.S. customary/Imperial units, British Imperial units as exactly "four feet eight and one half inches", which is equivalent to 1,435.1mm. History As railways developed and expanded, one of the key issues was the track gauge (the distance, or width, between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Locomotives Introduced In 1887
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of land transport, next to road transport. It is used for about 8% of passenger and freight transport globally, thanks to its energy efficiency and potentially high speed.Rolling stock on rails generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, allowing rail cars to be coupled into longer trains. Power is usually provided by diesel or electric locomotives. While railway transport is capital-intensive and less flexible than road transport, it can carry heavy loads of passengers and cargo with greater energy efficiency and safety. Precursors of railways driven by human or animal power have existed since antiquity, but modern rail transport began with the invention of the steam locomotive in the United Kingdom at the beginning of the 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad Gauge (7 Feet) Railway Locomotives
A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge (the distance between the rails) broader than the used by standard-gauge railways. Broad gauge of , more known as Russian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in former Soviet Union countries ( CIS states, Baltic states, Georgia, Ukraine) and Mongolia. Broad gauge of , commonly known as five foot gauge, is mainly used in Finland. Broad gauge of , commonly known as Irish gauge, is the dominant track gauge in Ireland, the Australian state of Victoria and Adelaide in South Australia and passenger trains of Brazil. Broad gauge of , commonly known as Iberian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in Spain and Portugal. Broad gauge of , commonly known as Indian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Argentina, Chile, and on BART (Bay Area Rapid Transit) in the San Francisco Bay Area. This is the widest gauge in common use anywhere in the world. It is possible for trains on both Iberian gauge and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Western Railway Locomotives
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements * Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size * Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent People * List of people known as "the Great" * Artel Great (born 1981), American actor * Great Osobor (born 2002), Spanish-born British basketball player Other uses * ''Great'' (1975 film), a British animated short about Isambard Kingdom Brunel * ''Great'' (2013 film), a German short film * Great (supermarket), a supermarket in Hong Kong * GReAT, Graph Rewriting and Transformation, a Model Transformation Language * Gang Resistance Education and Training Gang Resistance Education And Training, abbreviated G.R.E.A.T., provides a school-based, police officer-instructed program in America that includes classroom instruction and a variety of learning activities. The program was originally adminis ..., or GREAT, a school-based and police officer-instructed program * Global Research and Analysis Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodmin Parkway Railway Station
Bodmin Parkway railway station () is on the Cornish Main Line that serves the nearby town of Bodmin and other parts of mid-Cornwall, England. It is situated south-east of the town of Bodmin in the civil parish of St Winnow, from measured via and . Network Rail’s National Rail Timetable dated May 2023 records the distance from London Paddington to Bodmin Parkway as 252.50 miles. Great Western Railway (train operating company), Great Western Railway manages the station and operates most of the train services, although CrossCountry operates some long-distance services. The Bodmin and Wenford Railway operates a heritage service on the branch to the town on certain days. History Drawings held by Network Rail show that the Liskeard Contract section of Cornwall Railway’s Plymouth to Falmouth scheme, within which Bodmin Road Station was eventually situated, had reached the detailed design stage by June 1854. Original proposals to build a branch to Bodmin, then the most important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian Railways 4-4-0 Locomotives
The Cambrian Railways 4-4-0 locomotives consisted of five tender locomotive classes introduced between 1878 and 1921. Three of them were designed for the Cambrian Railways and supplied new, the fourth class was rebuilt from 4-4-0 tank locomotives, and the fifth consisted of secondhand purchases. Altogether 37 locomotives were owned by the Cambrian at one time or another, of which 35 passed to the Great Western Railway (GWR) at the start of 1922. The last was withdrawn in 1933. In addition there was a class of six 4-4-0 tank locomotives introduced in 1905, four of which were not rebuilt as tender locomotives. They all passed to the GWR, and the last were withdrawn in 1923. None of these locomotives were preserved, but another locomotive from the same class as the six 4-4-0 tank locomotives was preserved. Small Bogie Passenger class, or 16 class This class comprised six locomotives, built in pairs by Sharp, Stewart and Company between 1878 and 1891. The first two were named: no. 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |