|
Fusiform Muscle
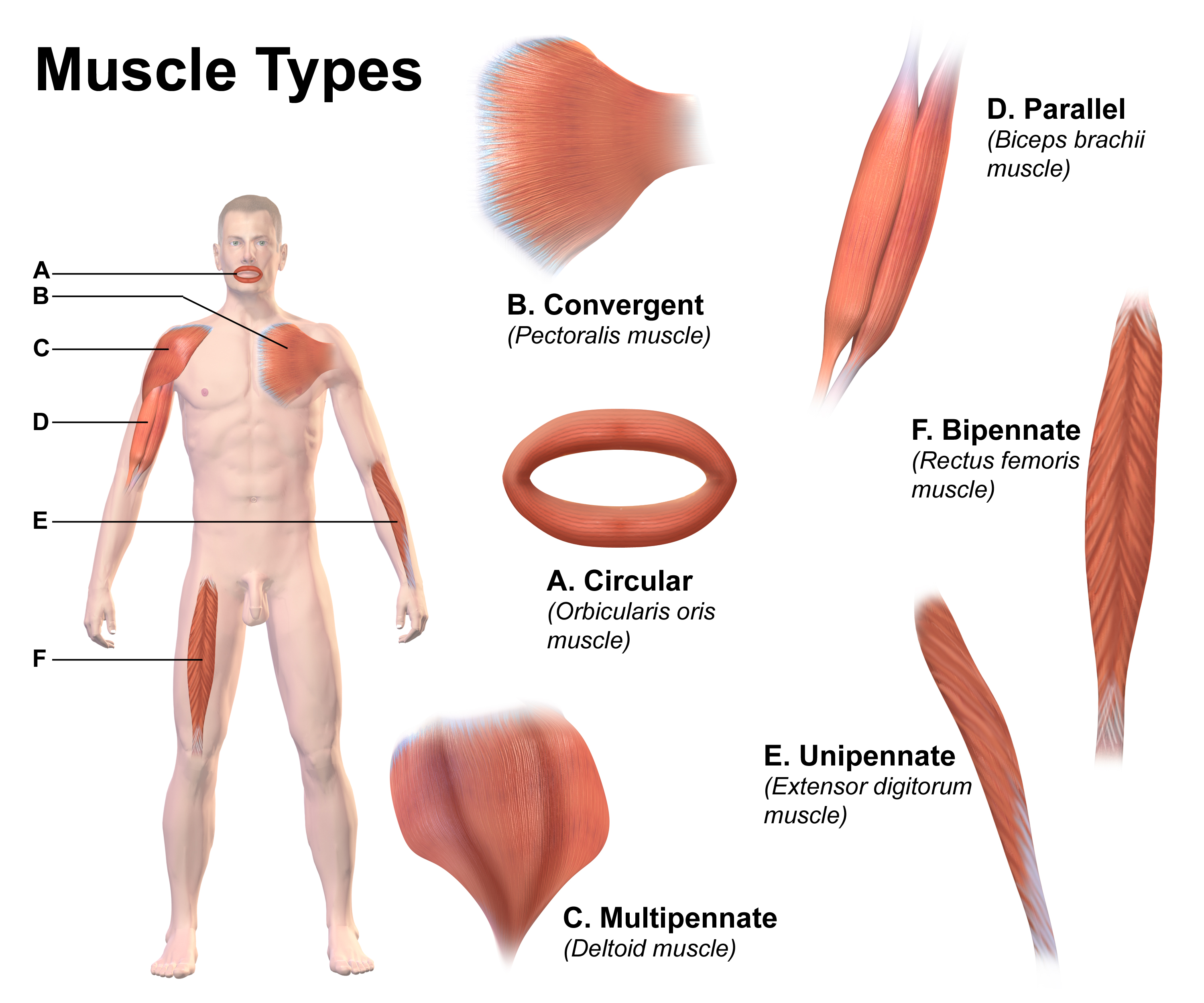
Muscle architecture is the physical arrangement of muscle fibers at the macroscopic level that determines a muscle's mechanical function. There are several different muscle architecture types including: parallel, pennate and hydrostats. Force production and gearing vary depending on the different muscle parameters such as muscle length, fiber length, pennation angle, and the physiological cross-sectional area (PCSA). Architecture types Parallel and pennate (also known as pinnate) are two main types of muscle architecture. A third subcategory, muscular hydrostats, can also be considered. Architecture type is determined by the direction in which the muscle fibers are oriented relative to the force-generating axis. The force produced by a given muscle is proportional to the cross-sectional area, or the number of parallel sarcomeres present. Parallel The parallel muscle architecture is found in muscles where the fibers are parallel to the force-generating axis. These muscles ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Fiber
A muscle cell, also known as a myocyte, is a mature contractile cell in the muscle of an animal. In humans and other vertebrates there are three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac (cardiomyocytes). A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a ''muscle fiber''. Muscle cells develop from embryonic precursor cells called myoblasts. Skeletal muscle cells form by fusion of myoblasts to produce multinucleated cells (syncytia) in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells both contain myofibrils and sarcomeres and form a striated muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle cells form the cardiac muscle in the walls of the heart chambers, and have a single central nucleus. Cardiac muscle cells are joined to neighboring cells by intercalated discs, and when joined in a visible unit they are described as a ''cardiac muscle fiber''. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular Hydrostat
A muscular hydrostat is a biological structure found in animals. It is used to manipulate items (including food) or to move its host about and consists mainly of muscles with no skeletal support. It performs its hydraulic movement without fluid in a separate compartment, as in a hydrostatic skeleton. A muscular hydrostat, like a hydrostatic skeleton, relies on the fact that water is effectively incompressible at physiological pressures. In contrast to a hydrostatic skeleton, where muscle surrounds a fluid-filled cavity, a muscular hydrostat is composed mainly of muscle tissue. Since muscle tissue itself is mainly made of water and is also effectively incompressible, similar principles apply. Muscular anatomy Muscles provide the force to move a muscular hydrostat. Since muscles are only able to produce force by contracting and becoming shorter, different groups of muscles have to work against each other, with one group relaxing and lengthening as the other group provides t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltoid Muscle
The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the shoulder, human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle is made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the # anterior or clavicular part (pars clavicularis) ( More commonly known as the front delt.) # posterior or scapular part (pars scapularis) ( More commonly known as the rear delt.) # intermediate or acromial part (pars acromialis) ( More commonly known as the side delt) The deltoid's fibres are pennate muscle. However, electromyography suggests that it consists of at least seven groups that can be independently coordinated by the nervous system. It was previously called the deltoideus (plural ''deltoidei'') and the name is still used by some anatomists. It is called so because it is in the shape of the Greek alphabet, Greek capital letter Delta (letter), delta (Δ). Deltoid is also further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectus Femoris
The rectus femoris muscle is one of the four quadriceps muscles of the human body. The others are the vastus medialis, the vastus intermedius (deep to the rectus femoris), and the vastus lateralis. All four parts of the quadriceps muscle attach to the patella (knee cap) by the quadriceps tendon. The rectus femoris is situated in the middle of the front of the thigh; it is fusiform in shape, and its superficial fibers are arranged in a bipenniform manner, the deep fibers running straight () down to the deep aponeurosis. Its functions are to flex the thigh at the hip joint and to extend the leg at the knee joint. Structure It arises by two tendons: one, the anterior or straight, from the anterior inferior iliac spine; the other, the posterior or reflected, from a groove above the rim of the acetabulum. The two unite at an acute angle and spread into an aponeurosis that is prolonged downward on the anterior surface of the muscle, and from this the muscular fibers arise. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stapedius
The stapedius is the smallest skeletal muscle in the human body. At just over one millimeter in length, its purpose is to stabilize the smallest bone in the body, the stapes or stirrup bone of the middle ear. Structure The stapedius emerges from a pinpoint foramen or opening in the apex of the pyramidal eminence (a hollow, cone-shaped prominence in the posterior wall of the tympanic cavity), and inserts into the neck of the stapes. Nerve supply The stapedius is supplied by the nerve to stapedius, a branch of the facial nerve. Function The stapedius dampens the vibrations of the stapes by pulling on the neck of that bone. As one of the muscles involved in the acoustic reflex it prevents excess movement of the stapes, helping to control the amplitude of sound, sound waves from the general external environment to the inner ear. Clinical significance Paralysis of the stapedius allows wider oscillation of the stapes, resulting in heightened reaction of the Auditory Ossicles, audit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrocnemius Muscle
The gastrocnemius muscle (plural ''gastrocnemii'') is a superficial two-headed muscle that is in the back part of the lower leg of humans. It is located superficial to the soleus in the posterior (back) compartment of the leg. It runs from its two heads just above the knee to the heel, extending across a total of three joints (knee, ankle and subtalar joints). The muscle is named via Latin, from Greek γαστήρ (''gaster'') 'belly' or 'stomach' and κνήμη (''knḗmē'') 'leg', meaning 'stomach of the leg' (referring to the bulging shape of the calf). Structure Origin/proximal attachment The lateral head originates from the lateral condyle of the femur, while the medial head originates from the medial condyle of the femur. Insertion/distal attachment Its other end forms a common tendon with the soleus muscle; this tendon is known as the calcaneal tendon or Achilles tendon and inserts onto the posterior surface of the calcaneus, or heel bone. Relations The ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennation Angle Of Fibers In Pennate Muscle
Pinnation (also called pennation) is the arrangement of feather-like or multi-divided features arising from both sides of a common Anatomical terms of location#Axes, axis. Pinnation occurs in biological morphology (biology), morphology, in Crystal, crystals, such as some forms of Ice crystals, ice or Metallic crystal, metal crystals, and in patterns of erosion or Stream bed, stream beds. The term derives from the Latin word ''pinna'' meaning "feather", "wing", or "fin". A similar concept is "pectination", which is a comb-like arrangement of parts (arising from one side of an axis only). Pinnation is commonly referred to in contrast to "palmation", in which the parts or structures radiate out from a common point. The terms "pinnation" and "pennation" are cognate, and although they are sometimes used distinctly, there is no consistent difference in the meaning or usage of the two words.Jackson, Benjamin, Daydon; ''A Glossary of Botanic Terms with their Derivation and Accent''. Geral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcomere
A sarcomere (Greek σάρξ ''sarx'' "flesh", μέρος ''meros'' "part") is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal striated muscle, Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (called muscle fibers or myofibers) which are formed during embryonic development, embryonic myogenesis. Muscle fibers contain numerous tubular myofibrils. Myofibrils are composed of repeating sections of sarcomeres, which appear under the microscope as alternating dark and light bands. Sarcomeres are composed of long, fibrous proteins as filaments that slide past each other when a muscle contracts or relaxes. The costamere is a different component that connects the sarcomere to the sarcolemma. Two of the important proteins are myosin, which forms the thick filament, and actin, which forms the thin filament. Myosin has a long fibrous tail and a globular head that binds to actin. The myosin head also binds to Adenosine triphos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biceps
The biceps or biceps brachii (, "two-headed muscle of the arm") is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join to form a single muscle belly which is attached to the upper forearm. While the long head of the biceps crosses both the shoulder and elbow joints, its main function is at the elbow where it flexes and supinates the forearm. Both these movements are used when opening a bottle with a corkscrew: first biceps screws in the cork (supination), then it pulls the cork out (flexion). Structure The biceps is one of three muscles in the anterior compartment of the upper arm, along with the brachialis muscle and the coracobrachialis muscle, with which the biceps shares a nerve supply. The biceps muscle has two heads, the short head and the long head, distinguished according to their origin at the coracoid process and supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, respectivel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the cell nucleus, nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sartorius Muscle
The sartorius muscle () is the longest muscle in the human body. It is a long, thin, superficial muscle that runs down the length of the thigh in the anterior compartment. Structure The sartorius muscle originates from the anterior superior iliac spine, and part of the notch between the anterior superior iliac spine and anterior inferior iliac spine. It runs obliquely across the upper and anterior part of the thigh in an inferomedial direction. It passes behind the medial condyle of the femur to end in a tendon. This tendon curves anteriorly to join the tendons of the gracilis and semitendinosus muscles in the pes anserinus, where it inserts into the superomedial surface of the tibia. Its upper portion forms the lateral border of the femoral triangle, and the point where it crosses adductor longus marks the apex of the triangle. Deep to sartorius and its fascia is the adductor canal, through which the saphenous nerve, femoral artery and vein, and nerve to vastus medialis pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |