|
Fringe Physics
Fringe science refers to ideas whose attributes include being highly speculative or relying on premises already Objection (argument), refuted. The chance of ideas rejected by editors and published outside the mainstream being correct is remote. When the general public does not distinguish between science and imitators, it risks exploitation, and in some cases, a "yearning to believe or a generalized suspicion of experts is a very potent incentive to accepting some pseudoscientific claims". The term "fringe science" covers everything from novel hypotheses, which can be tested utilizing the scientific method, to wild ad hoc hypotheses and Mumbo jumbo (phrase), mumbo jumbo. This has resulted in a tendency to dismiss all fringe science as the domain of Pseudoscience, pseudoscientists, hobbyists, and Quackery, quacks. A concept that was once accepted by the mainstream scientific community may become fringe science because of a later evaluation of previous research. For example, focal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Objection (argument)
In argumentation theory, argumentation, an objection is a reason argument, arguing against a premise, argument, or conclusion of law, conclusion. Definitions of objection vary in whether an objection is always an argument (or counterargument) or may include other moves such as questioning. An objection to an objection is sometimes known as a counterargument, rebuttal. An objection can be issued against an argument retroactively from the point of reference of that argument. This form of objection – invented by the presocratic philosopher Parmenides – is commonly referred to as a retroactive refutation. Inference objection An inference objection is an objection to an argument based not on any of its stated premises, but rather on the ''relationship'' between a premise (or set of premises) and main contention. For a given simple argument, if the assumption is made that its premises are correct, fault may be found in the progression from these to the conclusion of the argument. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Drift
Continental drift is a highly supported scientific theory, originating in the early 20th century, that Earth's continents move or drift relative to each other over geologic time. The theory of continental drift has since been validated and incorporated into the science of plate tectonics, which studies the movement of the continents as they ride on plates of the Earth's lithosphere. The speculation that continents might have "drifted" was first put forward by Abraham Ortelius in 1596. A pioneer of the modern view of mobilism was the Austrian geologist Otto Ampferer. The concept was independently and more fully developed by Alfred Wegener in his 1915 publication, "The Origin of Continents and Oceans". However, at that time his hypothesis was rejected by many for lack of any motive mechanism. In 1931, the English geologist Arthur Holmes proposed mantle convection for that mechanism. History Early history Abraham Ortelius , Theodor Christoph Lilienthal (1756), Alexan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therapy
A therapy or medical treatment is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis. Both words, ''treatment'' and ''therapy'', are often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx. As a rule, each therapy has indications and contraindications. There are many different types of therapy. Not all therapies are effective. Many therapies can produce unwanted adverse effects. ''Treatment'' and ''therapy'' are often synonymous, especially in the usage of health professionals. However, in the context of mental health, the term ''therapy'' may refer specifically to psychotherapy. Semantic field The words ''care'', ''therapy'', ''treatment'', and ''intervention'' overlap in a semantic field, and thus they can be synonymous depending on context. Moving rightward through that order, the connotative level of holism decreases and the level of specificity (to concrete instances) increases. Thus, in health-care contexts (where its senses are always nonc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigenetics
In biology, epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that happen without changes to the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix ''epi-'' (ἐπι- "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in addition to" the traditional (DNA sequence based) genetic mechanism of inheritance. Epigenetics usually involves a change that is not erased by cell division, and affects the regulation of gene expression. Such effects on cellular and physiological traits may result from environmental factors, or be part of normal development. The term also refers to the mechanism of changes: functionally relevant alterations to the genome that do not involve mutation of the nucleotide sequence. Examples of mechanisms that produce such changes are DNA methylation and histone modification, each of which alters how genes are expressed without altering the underlying DNA sequence. Further, non-coding RNA sequences have been shown to play a key role in the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategies For Engineered Negligible Senescence
Strategies for engineered negligible senescence (SENS) is a range of proposed regenerative medical therapies, either planned or currently in development, for the periodic repair of all age-related damage to human tissue. These therapies have the ultimate aim of maintaining a state of negligible senescence in patients and postponing age-associated disease.de Grey, Aubrey; Rae, Michael (September 2007). ''Ending Aging: The Rejuvenation Breakthroughs that Could Reverse Human Aging in Our Lifetime''. New York, NY: St. Martin's Press, 416 pp. . SENS was first defined by British biogerontologist Aubrey de Grey. Many mainstream scientists believe that it is a fringe theory. De Grey later highlighted similarities and differences of SENS to subsequent categorization systems of the biology of aging, such as the highly influential ''Hallmarks of Aging'' published in 2013. While some biogerontologists support the SENS program, others contend that the ultimate goals of de Grey's programme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longevity
Longevity may refer to especially long-lived members of a population, whereas ''life expectancy'' is defined Statistics, statistically as the average number of years remaining at a given age. For example, a population's life expectancy at birth is the same as the average age at death for all people born in the same year (in the case of Cohort (statistics), cohorts). Longevity studies may involve putative methods to extend life. Longevity has been a topic not only for the scientific community but also for writers of Hyperborei, travel, science fiction, and utopian novels. The legendary fountain of youth appeared in the work of the Ancient Greek historian Herodotus. There are difficulties in authenticating the longest human maximum life span, life span, owing to inaccurate or incomplete birth statistics. Fiction, legend, and folklore have proposed or claimed life spans in the past or future vastly longer than those verified by modern standards, and longevity narratives and unverif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
60 Minutes
''60 Minutes'' is an American television news magazine broadcast on the CBS television network. Debuting in 1968, the program was created by Don Hewitt and Bill Leonard, who distinguished it from other news programs by using a unique style of reporter-centered investigation. In 2002, ''60 Minutes'' was ranked number six on ''TV Guide''s list of the " 50 Greatest TV Shows of All Time", and in 2013, it was ranked number 24 on the magazine's list of the "60 Best Series of All Time". In 2023, '' Variety'' ranked ''60 Minutes'' as the twentieth-greatest TV show of all time. ''The New York Times'' has called it "one of the most esteemed news magazines on American television". The program began in 1968 as a bi-weekly television show hosted by Mike Wallace and Harry Reasoner. The two sat on opposite sides of the cream-colored set, though the set's color was later changed to black, the color still in use. The show used a large stopwatch during transition periods and highlighted its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aubrey De Grey
Aubrey David Nicholas Jasper de Grey (; born 20 April 1963) is an English biomedical gerontologist. He is the author of ''The Mitochondrial Free Radical Theory of Aging'' (1999) and co-author of '' Ending Aging'' (2007). De Grey is known for his view that medical technology may enable human beings alive today not to die from age-related causes. As an amateur mathematician, he has contributed to the study of the Hadwiger–Nelson problem in geometric graph theory, making the first progress on the problem in over 60 years. De Grey is an international adjunct professor of the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. In August 2021, he was removed as the Chief Science Officer of the SENS Research Foundation after he had allegedly attempted to interfere in a probe investigating sexual harassment allegations against him. In September 2021, an independent investigation concluded that he had made offensive remarks to two women. Early life and education De Grey was born on 20 Apr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clovis Culture
The Clovis culture is an archaeological culture from the Paleoindian period of North America, spanning around 13,050 to 12,750 years Before Present (BP). The type site is Blackwater Draw locality No. 1 near Clovis, New Mexico, where stone tools were found alongside the remains of Columbian mammoths in 1929. Clovis sites have been found across North America. The most distinctive part of the Clovis culture toolkit are Clovis points, which are projectile points with a fluted, lanceolate shape.Fluted: Having a flake removed from the base, either on one or both sides.Lanceolate: Tapering to a point at one end, like the head of a lance. Clovis points are typically large, sometimes exceeding in length. These points were multifunctional, also serving as cutting tools. Other stone tools used by the Clovis culture include knives, scrapers, and bifacial tools, with bone tools including beveled rods and shaft wrenches, with possible ivory points also being identified. Hides, wood, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fringe Theory
A fringe theory is an idea or a viewpoint that differs significantly from the accepted scholarship of the time within its field. Fringe theories include the models and proposals of fringe science, as well as similar ideas in other areas of scholarship, such as the humanities. In a narrower sense, the term ''fringe theory'' is commonly used as a pejorative, roughly synonymous with the terms pseudo-scholarship and conspiracy theory. Precise definitions distinguishing widely held viewpoints and unaccepted theories are difficult to construct. Issues of false balance or false equivalence can occur when fringe theories are presented as being equal to widely accepted theories. Definitions Fringe theories are ideas which depart significantly from a prevailing or mainstream theory. A fringe theory is neither a majority opinion nor that of a respected minority. In general, the term ''fringe theory'' is closer to the popular understanding of the word ''theory''—a hypothesis or a gue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Extraction
A dental extraction (also referred to as tooth extraction, exodontia, exodontics, or informally, tooth pulling) is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, but most commonly to remove teeth which have become unrestorable through tooth decay, periodontal disease, or dental trauma, especially when they are associated with toothache. Sometimes impacted wisdom teeth (wisdom teeth that are stuck and unable to grow normally into the mouth) cause recurrent infections of the gum ( pericoronitis), and may be removed when other conservative treatments have failed (cleaning, antibiotics and operculectomy). In orthodontics, if the teeth are crowded, healthy teeth may be extracted (often bicuspids) to create space so the rest of the teeth can be straightened. Procedure Extractions could be categorized into non-surgical (simple) and surgical, depending on the type of tooth to be removed and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
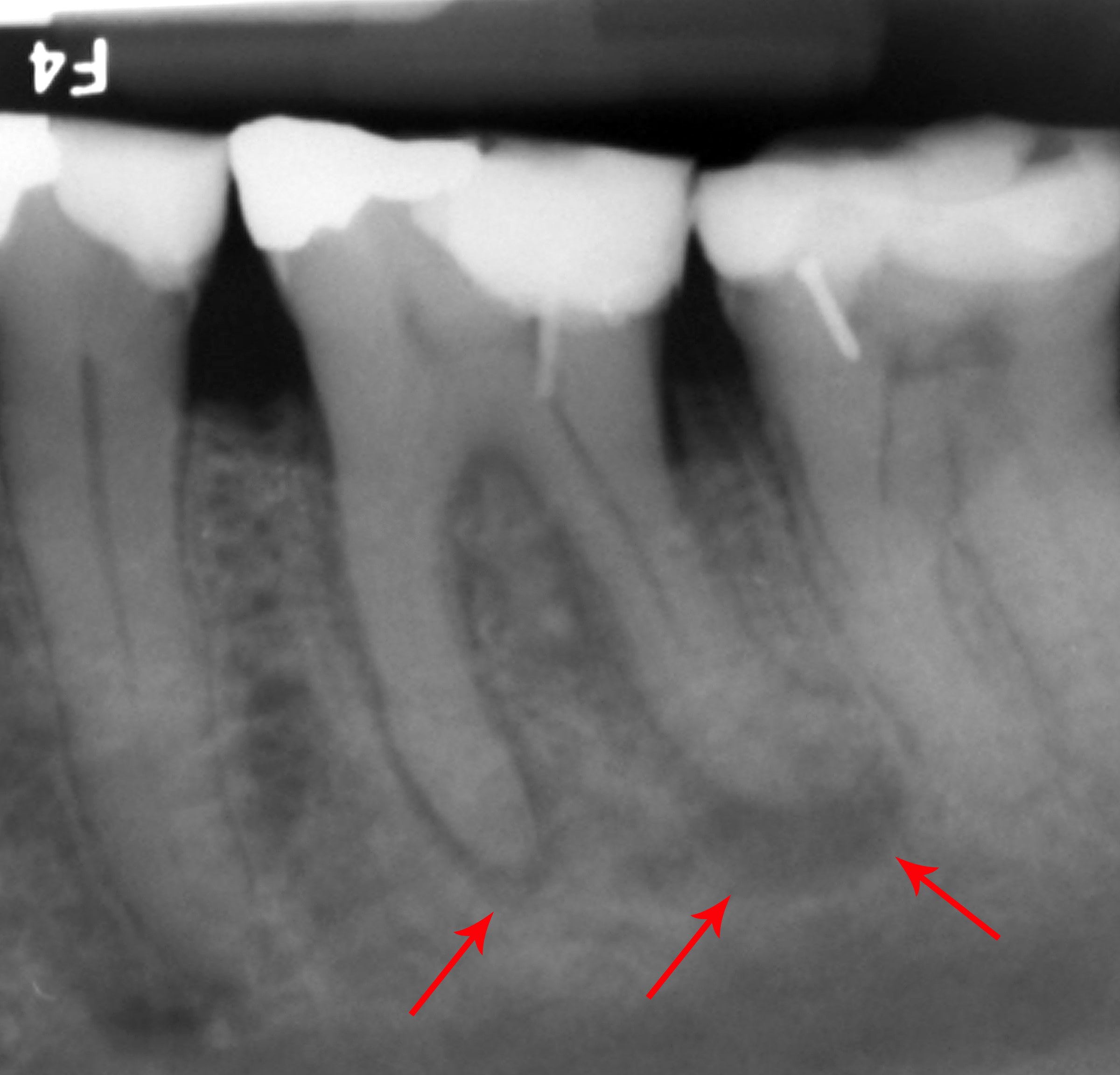
Focal Infection Theory
Focal infection theory is the historical concept that many chronic diseases, including systemic disease, systemic and common ones, are caused by focal infections. A focal infection is a localized infection, often asymptomatic, that causes disease elsewhere in the host, but the present medical consensus is that focal infections are fairly infrequent and mostly limited to fairly uncommon diseases. (Distant injury is focal infection's key principle, whereas in ordinary infectious disease, the infection itself is systemic, as in measles, or the initially infected site is readily identifiable and invasion progresses contiguously, as in gangrene.)J Craig Baumgartner, José F Siqueira Jr, Christine M Sedgley & Anil Kishen, ch 7 "Microbiology of endodontic disease", in John I Ingle, Leif K Bakland & J Craig Baumgartner, eds, ''Ingle's Endodontics'', 6th edn (Hamilton Ontario: BC Decker, 2008)p 221–24 Historical focal infection theory, rather, so explained virtually all diseases, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |