|
French Frigate Sibylle (1792)
''Sibylle'' was a 38-gun of the French Navy. She was launched in 1791 at the dockyards in Toulon and placed in service in 1792. After the 50-gun Fourth-rate, fourth rate captured her in 1794, the British took her into service as HMS ''Sybille''. She served in the Royal Navy until disposed of in 1833. While in British service, ''Sybille'' participated in three notable single-ship actions, in each case capturing a French vessel. On anti-slavery duties off West Africa from July 1827 to June 1830, ''Sybille'' captured many slavers and freed some 3,500 slaves. She was finally sold in 1833 in Portsmouth. French service From 23 April 1790 to October–December 1792, ''Sibylle'' escorted a convoy and transferred funds from Toulon to Smyrna, first under Capitaine de vaisseau (CV) Grasse-Briançon and then CV de Venel. From March 1793 to January 1794, under CV Rondeau, she escorted convoys between Toulon and Marseilles and then she moved to the Levant station. She cruised the Aegean S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
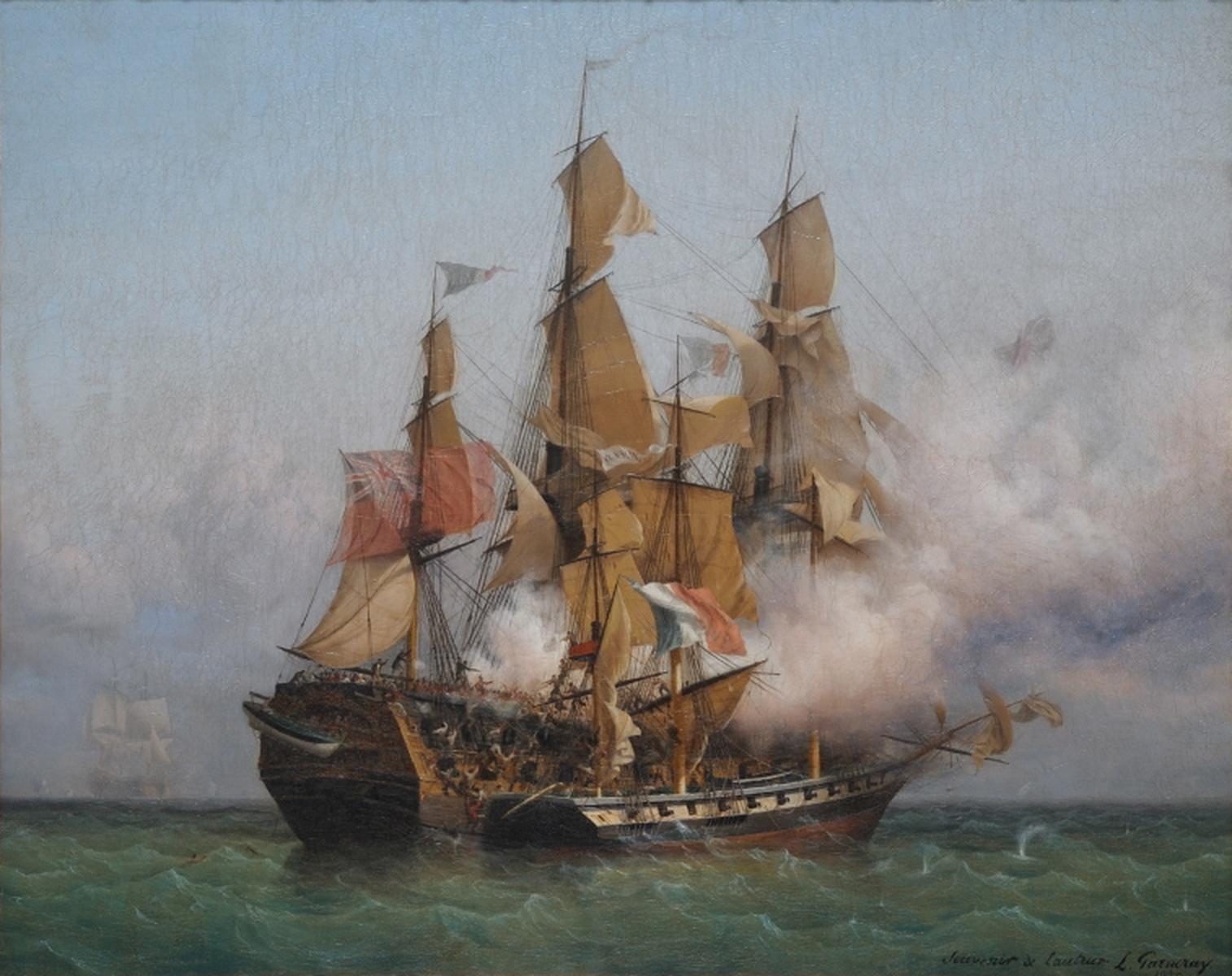
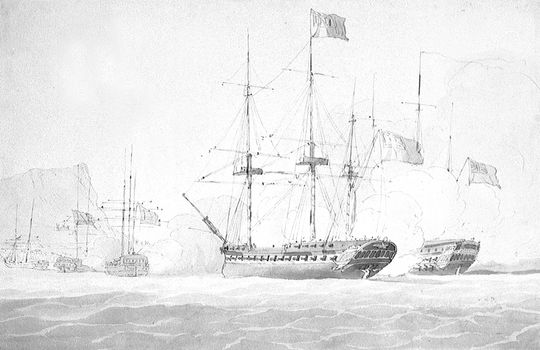
Battle Of Mykonos
The Battle of Mykonos was a minor naval engagement fought in the main harbour of the Cycladic island of Mykonos on 17 June 1794 during the French Revolutionary Wars. A Royal Navy squadron led by fourth rate ship HMS ''Romney'' was escorting a convoy of eight merchant ships westwards through the Aegean Sea to Smyrna when the French frigate ''Sibylle'' was sighted at anchor in the harbour of Mykonos town with three French merchant ships. Ordering the convoy to continue with the rest of the squadron, Captain William Paget diverted the 50-gun ''Romney'' to the port and demanded the surrender of the 40-gun French ship and its convoy. French Commodore Jacques-Mélanie Rondeau refused Paget's demands, and prepared to defend his ship. After some manoeuvring to ensure that the town was not within his firing arc, Paget brought ''Romney'' alongside the French frigate and for an hour and ten minutes the two vessels exchanged broadsides at close range. The engagement was hard fought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heraklion
Heraklion or Herakleion ( ; , , ), sometimes Iraklion, is the largest city and the administrative capital city, capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion (regional unit), Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a municipal population of 179,302 (2021) and 211,370 in its wider metropolitan area, according to the 2011 census. The greater area of Heraklion has been continuously inhabited since at least 7000 BCE, making it one of the oldest inhabited regions in Europe. It is also home to the ancient Knossos Palace, a major center of the Minoan civilization dating back to approximately 2000-1350 BCE, often considered Europe's oldest city. The palace is one of the most significant archaeological sites in Greece, second only to the Parthenon in terms of visitor numbers. Heraklion was Europe's fastest growing tourism destination for 2017, according to Euromonitor, with an 11.2% growth in international arrivals. According to the ranking, Herakl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, department of the Government of the United Kingdom that was responsible for the command of the Royal Navy. Historically, its titular head was the Lord High Admiral of the United Kingdom, Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of its history, from the early Admiralty in the 18th century, 18th century until its abolition, the role of the Lord High Admiral was almost invariably put "in commission" and exercised by the Lords Commissioner of the Admiralty, who sat on the governing Board of Admiralty, rather than by a single person. The Admiralty was replaced by the Admiralty Board (United Kingdom), Admiralty Board in 1964, as part of the reforms that created the Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), Ministry of Defence and its Navy Department (Ministry of Defence), Navy Department (later Navy Command (Ministry of Defence), Navy Command). Before the Acts of Union 1707, the Office of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an Anglican church in the City of Westminster, London, England. Since 1066, it has been the location of the coronations of 40 English and British monarchs and a burial site for 18 English, Scottish, and British monarchs. At least 16 royal weddings have taken place at the abbey since 1100. Although the origins of the church are obscure, an abbey housing Benedictine monks was on the site by the mid-10th century. The church got its first large building from the 1040s, commissioned by King Edward the Confessor, who is buried inside. Construction of the present church began in 1245 on the orders of Henry III. The monastery was dissolved in 1559, and the church was made a royal peculiar – a Church of England church, accountable directly to the sovereign – by Elizabeth I. The abbey, the Palace of Westminster and St Margaret's Church became a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1987 becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South Asia and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company gained Company rule in India, control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent and British Hong Kong, Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world by various measures and had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British Army at certain times. Originally Chartered company, chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies," the company rose to account for half of the world's trade during the mid-1700s and early 1800s, particularly in basic commodities including cotton, silk, indigo dye, sugar, salt, spices, Potass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Of 28 February 1799
The action of 28 February 1799 was a minor naval engagement of the French Revolutionary Wars, fought off the mouth of the Hooghly River in the Bay of Bengal between the French frigate ''Forte'' and the Royal Navy frigate HMS ''Sybille''. ''Forte'' was an exceptionally large and powerful ship engaged on a commerce raiding operation against British merchant shipping off the port of Calcutta in British India. To eliminate this threat, ''Sybille'' was sent from Madras in pursuit. Acting on information from released prisoners, Edward Cooke, captain of ''Sybille'', was sailing off Balasore when distant gunfire alerted him to the presence of ''Forte'' on the evening of 28 February. The French frigate was discovered at anchor in the sandbanks at the mouth of the Hooghly with two recently captured British merchant ships. For unclear reasons the French captain Hubert Le Loup de Beaulieu did not properly prepare ''Forte'' to receive the attack from Cooke's frigate and he was consequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balasore Roads
Balasore Roads is a roadstead (a sheltered anchorage), on the Indian coast near Balasore. It was the location of the Bengal Pilot Service pilot boarding station (see chart). It was considered to be a generally safe anchorage, with depths varying from 5 to 15 fathoms, and with the sea bottom consisting of mud and sand. The entrance to the Hooghly River was considered to be the most difficult of any river in India, and the river pilot station was located in close proximity to the mouth of the river. During the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars French privateer captains such as Jean-François Hodoul and Robert Surcouf would cruise the mouth of the Hooghly River hoping to capture vessels anchored in the Roads, or proceeding to or from Calcutta. The French captured both pilot vessels such as , and large East Indiamen such as . See also * roadstead in wiktionary Wiktionary (, ; , ; rhyming with "dictionary") is a multilingual, web-based project to create a free content ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubert Le Loup De Beaulieu
Hubert Le Loup de Beaulieu,Papers from the ships Iris (Captain Pinatel) and Carnate (Captain Le Loup de Beaulieu).… National Archives often written Beaulieu-Leloup, ( ? — ''Forte'', Gulf of Bengal, 1 March 1799) was a and later Navy officer. He was a cousin to . |
Capture Of La Forte
Capture may refer to: Arts and entertainment * "Capture", a song by Simon Townshend * Capture (band), an Australian electronicore band previously known as Capture the Crown * ''Capture'' (TV series), a reality show Television episodes * "Chapter One: Capture", ''Zastrozzi, A Romance'' episode 1 (1986) * "Capture", ''Adam-12'' season 6, episode 9 (1973) * "Capture", ''Argevollen'' episode 22 (2014) * "Capture", ''G.I. Joe: Sigma 6'' season 1, episode 3 (2005) * "Capture", ''Invasion America'' episode 7 (1998) * "Capture", ''Logan's Run'' episode 3 (1977) * "Capture", ''Richard the Lionheart'' episode 28 (1963) * "Capture", ''Special Forces: World's Toughest Test'' season 2, episode 8 (2023) Science * Gravitational capture, where an astronomical object enters into a stable orbit around another body ** Asteroid capture, when an asteroid is gravitationally captured *Electron capture, a nuclear reaction *Stream capture, a geomorphological phenomenon occurring when a stream or r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Surcouf
Robert Surcouf (; 12 December 1773 – 8 July 1827) was a French privateer, businessman and slave trader who operated in the Indian Ocean from 1789 to 1808 during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. Capturing over 40 prizes, he later amassed a large fortune from a variety of commercial activities, such as ship-owning, privateering, slave trading and owning land.Alain Roman; summary oRobert Surcouf, www.netmarine.net Surcouf started his maritime career as an officer on the ships ''Aurore'', ''Courrier d'Afrique'' and ''Navigateur''. Having risen to the rank of captain, he illegally engaged in slave trading onboard the slave ship ''Créole''. Surcouf then captained the merchantman ''Émilie'', on which he engaged in commerce raiding despite lacking a letter of marque. He preyed on British shipping, capturing several merchantmen including the East Indiaman '' Triton'', before returning to the Isle de France where his prizes were confiscated. Surcouf then retur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privateer
A privateer is a private person or vessel which engages in commerce raiding under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or delegated authority issued commissions, also referred to as letters of marque, during wartime. The commission empowered the holder to carry on all forms of hostility permissible at sea by the usages of war. This included attacking foreign vessels and taking them as prizes and taking crews prisoner for exchange. Captured ships were subject to condemnation and sale under prize law, with the proceeds divided by percentage between the privateer's sponsors, shipowners, captains and crew. A percentage share usually went to the issuer of the commission (i.e. the sovereign). Most colonial powers, as well as other countries, engaged in privateering. Privateering allowed sovereigns to multiply their naval forces at relatively low cost by mobilizi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raid On Manila (1798)
The raid on Manila of January 1798 was a Royal Navy false flag military operation during the French Revolutionary Wars intended to scout the strength of the defences of Manila, capital of the Spanish Philippines, capture a Manila galleon and assess the condition of the Spanish Navy squadron maintained in the port. Spain had transformed from an ally of Great Britain in the War of the First Coalition into an enemy in 1796. Thus, the presence of a powerful Spanish squadron at Manila posed a threat to the China Fleet, an annual convoy of East Indiaman merchant ships from Macau in Qing Dynasty China to Britain, which was of vital economic importance to Britain. So severe was this threat that a major invasion of the Spanish Philippines had been planned from British India during 1797, but had been called off following the Treaty of Campo Formio in Europe and the possibility of a major war in India between the British East India Company and the Kingdom of Mysore. To ensure the safety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |