|
Focus-on-form Instruction
Focus on form (FonF), also called form-focused instruction, is an approach to language education in which learners are made aware of linguistic forms – such as individual words and conjugations – in the context of a communicative activity. It is contrasted with ''focus on forms'', in which forms are studied in isolation, and ''focus on meaning'', in which no attention is paid to forms at all. For instruction to qualify as ''focus on form'' and not as ''focus on forms'', the learner must be aware of the meaning and use of the language features before the form is brought to their attention. ''Focus on form'' was proposed by Michael Long in 1988.. This paper was originally presented at the European-North-American Symposium on Needed Research in Foreign Language Education, Bellagio, Italy, in 1988. Background The concept of ''focus on form'' was motivated by the lack of support for the efficacy of ''focus on forms'' on the one hand, and clear advantages demonstrated by instruct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Education
Language education refers to the processes and practices of teaching a second language, second or foreign language. Its study reflects interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary approaches, usually including some applied linguistics. There are four main learning categories for language education: communicative competencies, proficiencies, cross-cultural experiences, and multiple literacies. Need Increasing globalization has created a great need for people in the workforce who can communicate in multiple languages. Common languages are used in areas such as trade, tourism, diplomacy, technology, media, translation, interpretation and science. Many countries such as Korea (Kim Yeong-seo, 2009), Japan (Kubota, 1998) and China (Kirkpatrick & Zhichang, 2002) frame education policies to teach at least one foreign language at the primary and secondary school levels. Further, the governments of some countries more than one official language; such countries include India, Singapore, Malay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meaning (linguistics)
Semantics is the study of linguistic Meaning (philosophy), meaning. It examines what meaning is, how words get their meaning, and how the meaning of a complex expression depends on its parts. Part of this process involves the distinction between sense and reference. Sense is given by the ideas and concepts associated with an expression while reference is the object to which an expression points. Semantics contrasts with syntax, which studies the rules that dictate how to create grammatically correct sentences, and pragmatics, which investigates how people use language in communication. Lexical semantics is the branch of semantics that studies word meaning. It examines whether words have one or several meanings and in what lexical relations they stand to one another. Phrasal semantics studies the meaning of sentences by exploring the phenomenon of compositionality or how new meanings can be created by arranging words. Formal semantics (natural language), Formal semantics relies o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Long (academic)
Michael Hugh Long (1945 - February 21, 2021) was an American psycholinguist. He was a Professor of Second Language Acquisition at the University of Maryland, College Park. Long introduced the concept of ''focus on form'', which entails bringing linguistic elements (e.g., vocabulary, grammatical structures, collocations) to students’ attention within the larger context of a meaning-based lesson in order to anticipate or correct problems in comprehension or production of the target language. Long contrasted this approach with the older method of '' focus on forms'', which calls for exclusive focus on the linguistic forms when teaching a target language, often consisting of drill-type exercises such as conjugation exercises. Long is also usually credited for introducing the Interaction Hypothesis, a theory of second language acquisition which places importance on face-to-face interaction. Career He received an LL.B. (Bachelor of Laws) degree from the University of Birmingham and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequences Of Acquisition
The order of acquisition is a concept in language acquisition describing the specific order in which all language learners acquire the grammatical features of their first language (L1). This concept is based on the observation that all children acquire their first language in a fixed, universal order, regardless of the specific grammatical structure of the language they learn. Linguistic research has largely confirmed that this phenomenon is true for first-language learners; order of acquisition for second-language learners is much less consistent. It is not clear why the order differs for second-language (L2) learners, though current research suggests this variability may stem from first-language interference or general cognitive interference from nonlinguistic mental faculties. Research background Researchers have found a very consistent order in the acquisition of first-language structures by children, which has drawn interest from Second Language Acquisition (SLA) scholars. Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlanguage
An interlanguage is an idiolect developed by a learner of a second language (L2) which preserves some features of their first language (L1) and can overgeneralize some L2 writing and speaking rules. These two characteristics give an interlanguage its unique linguistic organization. It is idiosyncratically based on the learner's experiences with L2. An interlanguage can fossilize, or cease developing, in any of its developmental stages. Several factors can shape interlanguage rules, including L1 transfer, previous learning strategies, strategies of L2 acquisition, L2 communication strategies, and the overgeneralization of L2 language patterns. Interlanguage theory posits that a dormant psychological framework in the human brain is activated with study of a second language. The theory is credited to Larry Selinker, who coined the terms ''interlanguage'' and ''fossilization''. Uriel Weinreich is credited with providing the basis for Selinker's research. Selinker noted in 1972 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
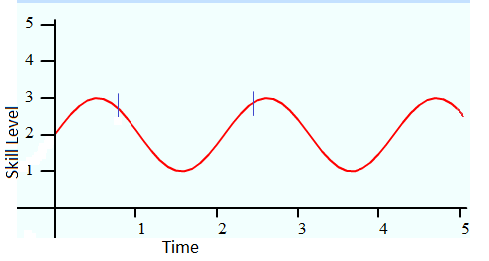
U-shaped Learning
U-shaped development, also known as U-shaped learning, is the typical pattern by which select physical, artistic, and cognitive skills are developed. It is called "U" shape development because of the shape of the letter ''U'' in correlation to a graph, skills developed in the "U-shaped" fashion begin on a high position on a graph's Y-axis. The skills start out at a high performance level and over time the skills descend to a lower position on the Y-axis. After another period of time the skill once again ascends to a higher position on the y-axis. A U-shaped time line is created of the skills development. U-shaped development can be seen in cognitive skills such as learning new words, or doing high-level algorithms in mathematics. The skill can also be artistic such as painting or playing a musical instrument, and physical skills such as walking and weight lifting. Artistic skill development This U-shaped curve is different from the other types of skill development because this sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family. Like all other Romance languages, it descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. French evolved from Northern Old Gallo-Romance, a descendant of the Latin spoken in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien language, Francien) largely supplanted. It was also substratum (linguistics), influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul and by the Germanic languages, Germanic Frankish language of the post-Roman Franks, Frankish invaders. As a result of French and Belgian colonialism from the 16th century onward, it was introduced to new territories in the Americas, Africa, and Asia, and numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole, were established. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Immersion
Language immersion, or simply immersion, is a technique used in Bilingual education, bilingual language education in which two languages are used for instruction in a variety of topics, including maths, science, or social studies. The languages used for instruction are referred to as the L1 and the L2 for each student, with L1 being the student's first language, native language and L2 being the second language to be acquired through immersion programs and techniques. There are different types of language immersion that depend on the age of the students, the classtime spent in L2, the subjects that are taught, and the level of participation by the speakers of L1. Although programs differ by country and context, most language immersion programs have the overall goal of promoting multilingualism, bilingualism between the two different sets of language-speakers. In many cases, biculturalism is also a goal for speakers of the majority language (the language spoken by the majority of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, second-largest country by total area, with the List of countries by length of coastline, world's longest coastline. Its Canada–United States border, border with the United States is the world's longest international land border. The country is characterized by a wide range of both Temperature in Canada, meteorologic and Geography of Canada, geological regions. With Population of Canada, a population of over 41million people, it has widely varying population densities, with the majority residing in List of the largest population centres in Canada, urban areas and large areas of the country being sparsely populated. Canada's capital is Ottawa and List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language-teaching Methodology
Language pedagogy is the discipline concerned with the theories and techniques of teaching language. It has been described as a type of teaching wherein the teacher draws from their own prior knowledge and actual experience in teaching language. The approach is distinguished from research-based methodologies. There are several methods in language pedagogy but they can be classified into three: structural, functional, and interactive. Each of these encompasses a number of methods that can be utilised in order to teach and learn languages. Development The development of language pedagogy came in three stages. In the late 1800s and most of the 1900s, it was usually conceived in terms of method. In 1963, the University of Michigan Linguistics Professor Edward Mason Anthony Jr. formulated a framework to describe them into three levels: ''approach, method, and technique''. It has been expanded by Richards and Rodgers in 1982 to ''approach'', ''design'', and ''procedure''. Metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |