U-shaped Learning on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
U-shaped development, also known as U-shaped learning, is the typical pattern by which select 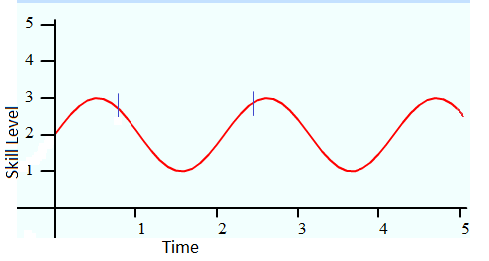
physical
Physical may refer to:
*Physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally co ...
, artistic, and cognitive
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, ...
skills are developed. It is called “U” shape development because of the shape of the letter U in correlation to a graph, skills developed in the “U shaped” fashion begin on a high position on a graph's Y-axis. The skills start out at a high performance level and over time the skills descend to a lower position on the Y-axis. After another period of time the skill once again ascends to a higher position on the y-axis. A "U" shaped time line is created of the skills development.
U-shaped development can be seen in cognitive skills such as learning new words, or doing high-level algorithms in mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
. The skill can also be artistic such as painting or playing a musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person who pl ...
, and physical skills such a walking and weight lifting.

Artistic skill development
This U-shaped curve is different from the other types of skill development because this skill has an artistic rating with it, which means there could be differences inopinion
An opinion is a judgment, viewpoint, or statement that is not conclusive, rather than facts, which are true statements.
Definition
A given opinion may deal with subjective matters in which there is no conclusive finding, or it may deal with f ...
, but in studies where children
A child ( : children) is a human being between the stages of birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. The legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor, otherwise known as a person younger ...
, adult
An adult is a human or other animal that has reached full growth. In human context, the term ''adult'' has meanings associated with social and legal concepts. In contrast to a " minor", a legal adult is a person who has attained the age of major ...
artists, and non-artist adults were all given the same directions to draw a self portrait
A self-portrait is a representation of an artist that is drawn, painted, photographed, or sculpted by that artist. Although self-portraits have been made since the earliest times, it is not until the Early Renaissance in the mid-15th century tha ...
, the children's and the artists' were the closest of the three to depicting the face when picked by an outside group. In theory, this result is because of an innate “creative
Creative may refer to:
*Creativity, phenomenon whereby something new and valuable is created
* "Creative" (song), a 2008 song by Leon Jackson
* Creative class, a proposed socioeconomic class
* Creative destruction, an economic term
* Creative dir ...
skill” in children that is either lost to age with non-artist adults or practiced by adult artists. In artists the Y-axis would be the “creative skill”, and the X-axis would be time, but in non artists the “U” shaped curve would not apply.
Physical skill development
The U-shaped development in physical skill comes from the development and recession ofmuscular strength
Physical strength is the measure of a human's exertion of force on physical objects. Increasing physical strength is the goal of strength training.
Overview
An individual's physical strength is determined by two factors: the cross-sectional are ...
, on the graph the Y-axis is muscular strength and the X-axis is time. Muscular strength develops and recedes over time because of necessity; one example of this is a baby learning to walk. The baby will gain the strength in its legs
A leg is a weight-bearing and locomotive anatomical structure, usually having a columnar shape. During locomotion, legs function as "extensible struts". The combination of movements at all joints can be modeled as a single, linear element ...
to be able to support itself and walk (which is the left top of the “U”), but it then grows larger, and the strength in its legs becomes less than required to support itself (the bottom of the “U”), but then the baby's leg strength increases again which gives it the ability to support itself again (the right top of the “U”).
Cognitive skill development
This developmentalcurve
In mathematics, a curve (also called a curved line in older texts) is an object similar to a line (geometry), line, but that does not have to be Linearity, straight.
Intuitively, a curve may be thought of as the trace left by a moving point (ge ...
reflects the progression of intuitive thinking processes as a person develops more advanced knowledge structures in a specific area. The shape of the curve reflects the variability of general intuitional availability.This means once intuition levels increase but also s/he can make more higher order intuitive connections/understandings given a corresponding increase in expertise. In this graph the axes would be availability of intuition (being th Y-axis) and level of expertise (being the X-axis), instead of the skill level (being the Y-axis) and time (being the X-axis). The “U” curve represents two different types of intuition: which are referred to as immature intuition(the top left of the "U") and mature intuition (the top right of the "U").
Other theories
There have been other human development theories in the past such as * “ cognitive theory”- Is a learning theory of psychology that explains the behavior of human throughthought
In their most common sense, the terms thought and thinking refer to conscious cognitive processes that can happen independently of sensory stimulation. Their most paradigmatic forms are judging, reasoning, concept formation, problem solving, a ...
process. The theory states that humans are logical beings
In metaphysics, ontology is the philosophical study of being, as well as related concepts such as existence, becoming, and reality.
Ontology addresses questions like how entities are grouped into categories and which of these entities exis ...
, that make the choices that make the most sense to them.
* “ social and situational theory”- Learning and development based on the person's situation and their social standing.
* “ humanist theory"- Is a theory that the behavior changes based on what education was received by the individual.
There are branch theories that relate to these theories and the theories have different notions on how environmental stimuli change a person, but none dismiss or disprove the U-shaped development theory.
See also
*Developmental psychology
Developmental psychology is the science, scientific study of how and why humans grow, change, and adapt across the course of their lives. Originally concerned with infants and children, the field has expanded to include adolescence, adult deve ...
* Kuznets curve
* Skill
* Art
* Cognition
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, ...
* Beginner's luck
Beginner's luck refers to the supposed phenomenon of novices experiencing disproportionate frequency of success or succeeding against an expert in a given activity. One would expect experts to outperform novices - when the opposite happens it is co ...
References
{{reflist, colwidth=30em Developmental psychology