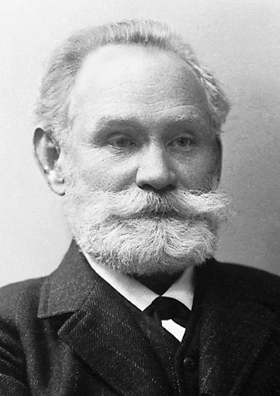|
Stimulus (psychology)
In psychology, a stimulus is any object or event that elicits a sensory or behavioral response in an organism. In this context, a distinction is made between the ''distal stimulus'' (the external, perceived object) and the ''proximal stimulus'' (the stimulation of sensory organs). *In perceptual psychology, a stimulus is an energy change (e.g., light or sound) which is registered by the senses (e.g., vision, hearing, taste, etc.) and constitutes the basis for perception. *In behavioral psychology (i.e., classical conditioning, classical and operant conditioning, operant conditioning), a stimulus constitutes the basis for behavior. The stimulus–response model emphasizes the relation between stimulus and behavior rather than an animal's internal processes (i.e., in the nervous system). *In experimental psychology, a stimulus is the event or object to which a response is measured. Thus, not everything that is presented to participants qualifies as stimulus. For example, a cross mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulus–response Model
The stimulus–response model is a conceptual framework in psychology that describes how individuals react to external Stimulus_(psychology), stimuli. According to this model, an external stimulus triggers a reaction in an organism, often without the need for conscious thought. This model emphasizes the mechanistic aspects of behavior, suggesting that behavior can often be predicted and controlled by understanding and manipulating the stimuli that trigger responses. Fields of application Stimulus–response models are applied in international relations, :en:Neuropsychological test, psychology, risk assessment, :en:Neuroscience, neuroscience, neurally-inspired system design, and many other fields. Pharmacological dose response relationships are an application of stimulus-response models. Another field this model can be applied to is psychological problems/disorders such as Tourette syndrome. Research shows Gilles de la Tourette syndrome (GTS) can be characterized by enhanced c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feelings, and motivation, motives. Psychology is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the Natural science, natural and social sciences. Biological psychologists seek an understanding of the Emergence, emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as Behavioural sciences, behavioral or Cognitive science, cognitive scientists. Some psychologists attempt to understand the role of mental functions in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensation (psychology)
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the surroundings through the detection of stimuli. Although, in some cultures, five human senses were traditionally identified as such (namely sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing), many more are now recognized. Senses used by non-human organisms are even greater in variety and number. During sensation, sense organs collect various stimuli (such as a sound or smell) for transduction, meaning transformation into a form that can be understood by the brain. Sensation and perception are fundamental to nearly every aspect of an organism's cognition, behavior and thought. In organisms, a sensory organ consists of a group of interrelated sensory cells that respond to a specific type of physical stimulus. Via cranial and spinal nerves (nerves of the central and peripheral nervous systems that relay sensory information to and from the brain and body), the different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioral Concepts
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions of individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as well as the inanimate physical environment. It is the computed response of the system or organism to various stimuli or inputs, whether internal or external, conscious or subconscious, overt or covert, and voluntary or involuntary. While some behavior is produced in response to an organism's environment (extrinsic motivation), behavior can also be the product of intrinsic motivation, also referred to as "agency" or "free will". Taking a behavior informatics perspective, a behavior consists of actor, operation, interactions, and their properties. This can be represented as a behavior vector. Models Biology Definition Behavior may be defined as "the internally coordinated responses (actions or inactions) of whole living organisms (individuals or groups) to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulation
Stimulation is the encouragement of development or the cause of activity in general. For example, "The press provides stimulation of political discourse." An interesting or fun activity can be described as "stimulating", regardless of its physical effects on senses. ''Stimulate'' means to act as a stimulus to; ''stimulus'' means something that rouses the recipient to activity; ''stimuli'' is the plural of ''stimulus''. A particular use of the term is physiological stimulation, which refers to sensory excitation, the action of various agents or forms of energy (Stimulus (physiology), stimuli) on receptors that generate Action potential, impulses that travel through nerves to the brain (afferents). There are sensory receptors on or near the surface of the body, such as photoreceptors in the retina of the eye, hair cells in the cochlea of the ear, touch receptors in the skin and chemical receptors in the mouth and nasal cavity. There are also sensory receptors in the muscles, joints ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Cue
In perceptual psychology, a sensory cue is a statistic or signal that can be extracted from the Sense, sensory input by a perceiver, that indicates the state of some property of the world that the perceiver is interested in perceiving. A ''cue'' is some organization of the data present in the signal which allows for meaningful extrapolation. For example, sensory cues include Visual system, visual cues, Auditory system, auditory cues, Haptic perception, haptic cues, Sense of smell, olfactory cues and Environmental psychology, environmental cues. Sensory cues are a fundamental part of theories of perception, especially theories of appearance (how things look). Concept There are two primary theory sets used to describe the roles of sensory cues in perception. One set of theories are based on the constructivist theory of perception, while the others are based on the ecological theory. Basing his views on the constructivist theory of perception, Helmholtz (1821–1894) held that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appleton-Century-Crofts
Appleton-Century-Crofts, Inc. was a division of the Meredith Publishing Company. It was a result of the merger of Appleton-Century Company with F.S. Crofts Co. in 1948. Prior to that The Century Company had merged with D. Appleton & Company in 1933. The Century Company and its subsequent incarnations published the '' New Century Dictionary''. Eventually Meredith sold the majority of the company and the Appleton name to Prentice-Hall in 1973. Part of the company became part of Hawthorn Books and New Win Publishing. Timeline * 1948 Appleton-Century Company, founded in 1933, merged with F. S. Crofts Co., founded in 1924, to form Appleton-Century-Crofts. * 1960 Purchased by Meredith Publishing Company * 1969 Meredith trade books division sold to Hawthorn Books * 1973 Appleton textbook division purchased by Prentice Hall; the medical division retains the Appleton name * 1974 New Century division sold to Charles Walther, and was later renamed New Win Publishing * 1998 Prenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Publishers
International Publishers is a book publishing company based in New York City, specializing in Marxism, Marxist works of economics, political science, and history. Company history Establishment International Publishers Company, Inc., was founded in 1924 with funds given the project by Abraham A. Heller. Heller was the radical son of a wealthy jeweler doing business in Paris.Trachtenberg, Testimony to the House Special Committee, September 13, 1939, pg. 4882. He expanded his fortune as head of the International Oxygen Company, a welding supply company that operated a trade concession in Soviet Russia during the time of the New Economic Policy in the early 1920s. A lifelong socialist, Heller had previously been a heavy financial donor to the ''New York Call,'' the Socialist Party's New York daily newspaper. He had been instrumental in funding the purchase of the headquarters building for the Rand School of Social Science. The company began with a capital stock of $50,000, paid i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Pavlov
Ivan Petrovich Pavlov (, ; 27 February 1936) was a Russian and Soviet experimental neurologist and physiologist known for his discovery of classical conditioning through his experiments with dogs. Pavlov also conducted significant research on the physiology of digestion, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1904. Education and early life Pavlov was born the first of ten children, in Ryazan, Russian Empire. His father, Peter Dmitrievich Pavlov (1823–1899), was a village Russian Orthodox priest. His mother, Varvara Ivanovna Uspenskaya (1826–1890), was a homemaker. As a child, Pavlov willingly participated in house duties such as doing the dishes and taking care of his siblings. He loved to garden, ride his bicycle, row, swim, and play gorodki; he devoted his summer vacations to these activities. Although able to read by the age of seven, Pavlov did not begin formal schooling until he was 11 years old, due to serious injuries he had sustained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behaviorism
Behaviorism is a systematic approach to understand the behavior of humans and other animals. It assumes that behavior is either a reflex elicited by the pairing of certain antecedent stimuli in the environment, or a consequence of that individual's history, including especially reinforcement and punishment contingencies, together with the individual's current motivational state and controlling stimuli. Although behaviorists generally accept the important role of heredity in determining behavior, deriving from Skinner's two levels of selection: phylogeny and ontogeny. they focus primarily on environmental events. The cognitive revolution of the late 20th century largely replaced behaviorism as an explanatory theory with cognitive psychology, which unlike behaviorism views internal mental states as explanations for observable behavior. Behaviorism emerged in the early 1900s as a reaction to depth psychology and other traditional forms of psychology, which often had diffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |