|
Fluorescein Isothiocyanate
Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) is a derivative of fluorescein used in wide-ranging applications including flow cytometry. First described in 1942, FITC is the original fluorescein molecule functionalized with an isothiocyanate reactive group (−N=C=S), replacing a hydrogen atom on the bottom ring of the structure. It is typically available as a mixture of isomers, fluorescein 5-isothiocyanate (5-FITC) and fluorescein 6-isothiocyanate (6-FITC). FITC is reactive towards nucleophiles including amine and sulfhydryl groups on proteins. It was synthesized by Robert Seiwald and Joseph Burckhalter in 1958. A succinimidyl-ester functional group attached to the fluorescein core, creating "NHS-fluorescein", forms another common amine reactive derivative that has much greater specificity toward primary amines in the presence of other nucleophiles. FITC has excitation and emission spectrum peak wavelengths of approximately 495 nm and 519 nm, giving it a green color. Like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescein
Fluorescein is an organic compound and dye based on the xanthene tricyclic structural motif, formally belonging to Triarylmethane dye, triarylmethine dyes family. It is available as a dark orange/red powder slightly soluble in water and alcohol. It is used as a fluorescent Flow tracer, tracer in many applications. The color of its aqueous solutions is green by reflection and orange by transmission (its spectral properties are dependent on pH of the solution), as can be noticed in spirit level, bubble levels, for example, in which fluorescein is added as a colorant to the Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol filling the tube in order to increase the visibility of the air bubble contained within. More concentrated solutions of fluorescein can even appear red (because under these conditions nearly all incident emission is re-absorbed by the solution). It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Uses Fluorescein sodium, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excitation Wavelength
Absorption spectroscopy is spectroscopy that involves techniques that measure the absorption of electromagnetic radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. The sample absorbs energy, i.e., photons, from the radiating field. The intensity of the absorption varies as a function of frequency, and this variation is the absorption spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is performed across the electromagnetic spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is employed as an analytical chemistry tool to determine the presence of a particular substance in a sample and, in many cases, to quantify the amount of the substance present. Infrared and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy are particularly common in analytical applications. Absorption spectroscopy is also employed in studies of molecular and atomic physics, astronomical spectroscopy and remote sensing. There is a wide range of experimental approaches for measuring absorption spectra. The most common ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorone Dyes
Fluorone is a heterocyclic chemical compound. It forms the core structure for various chemicals, most notably fluorone dyes, including fluorescein, erythrosine and rhodamine. It is an isomer of xanthone, sometimes referred to as an isoxanthone. See also * Xanthene Xanthene (9''H''-xanthene, 10''H''-9-oxaanthracene) is the organic compound with the formula CH2 6H4sub>2O. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. Xanthene itself is an obscure compound, but many of its derivatives are u ... References {{Heterocyclic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzoic Acids
Benzoic acid () is a white (or colorless) solid organic compound with the formula , whose Chemical structure, structure consists of a benzene ring () with a carboxyl () substituent. The benzoyl group is often abbreviated "Bz" (not to be confused with "Bn," which is used for benzyl), thus benzoic acid is also denoted as BzOH, since the benzoyl group has the formula –. It is the simplest aromaticity, aromatic carboxylic acid. The name is derived from benzoin (resin), gum benzoin, which was for a long time its only source. Benzoic acid occurs naturally in many plants and serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of many secondary metabolites. salt (chemistry), Salts of benzoic acid are used as food preservatives. Benzoic acid is an important Precursor (chemistry), precursor for the industrial synthesis of many other organic substances. The salts and esters of benzoic acid are known as benzoates (). History Benzoic acid was discovered in the sixteenth century. The dry dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching
Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) is a method for determining the kinetics of diffusion through tissue or cells. It is capable of quantifying the two-dimensional lateral diffusion of a molecularly thin film containing fluorescently labeled probes, or to examine single cells. This technique is very useful in biological studies of cell membrane diffusion and protein binding. In addition, surface deposition of a fluorescing phospholipid bilayer (or monolayer) allows the characterization of hydrophilic (or hydrophobic) surfaces in terms of surface structure and free energy. Similar, though less well known, techniques have been developed to investigate the 3-dimensional diffusion and binding of molecules inside the cell; they are also referred to as FRAP. Experimental setup The basic apparatus comprises an optical microscope, a light source and some fluorescent probe. Fluorescent emission is contingent upon absorption of a specific optical wavelength or color which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photobleaching
In optics, photobleaching (sometimes termed fading) is the photochemical alteration of a dye or a fluorophore molecule such that it is permanently unable to fluoresce. This is caused by cleaving of covalent bonds or non-specific reactions between the fluorophore and surrounding molecules. Such irreversible modifications in covalent bonds are caused by transition from a singlet state to the triplet state of the fluorophores. The number of excitation cycles to achieve full bleaching varies. In microscopy, photobleaching may complicate the observation of fluorescent molecules, since they will eventually be destroyed by the light exposure necessary to stimulate them into fluorescing. This is especially problematic in time-lapse microscopy. However, photobleaching may also be used prior to applying the (primarily antibody-linked) fluorescent molecules, in an attempt to quench autofluorescence. This can help improve the signal-to-noise ratio. Photobleaching may also be exploited to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DyLight Fluor
The DyLight Fluor family of fluorescent dyes are produced by Dyomics in collaboration with Thermo Fisher Scientific. DyLight dyes are typically used in biotechnology and research applications as biomolecule, cell and tissue labels for fluorescence microscopy, cell biology or molecular biology. Applications Historically, fluorophores such as fluorescein, rhodamine, Cy3 and Cy5 have been used in a wide variety of applications. These dyes have limitations for use in microscopy and other applications that require exposure to an intense light source such as a laser, because they photobleach quickly (however, bleaching can be reduced at least 10 fold using oxygen scavenging). DyLight Fluors have comparable excitation and emission spectra and are claimed to be more photostable, brighter, and less pH-sensitive. The excitation and emission spectra of the DyLight Fluor series cover much of the visible spectrum and extend into the infrared region, allowing detection using most fluor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexa (fluor)
The Alexa Fluor family of fluorescence, fluorescent dyes is a series of dyes invented by Molecular Probes, now a part of Life Technologies (Thermo Fisher Scientific), Thermo Fisher Scientific, and sold under the Invitrogen brand name. Alexa Fluor dyes are frequently used as cell and tissue labels in fluorescence microscope, fluorescence microscopy and cell biology. Alexa Fluor dyes can be conjugated directly to Primary and secondary antibodies, primary antibodies or to Primary and secondary antibodies, secondary antibodies to amplify signal and sensitivity or other biomolecules. The Excited state, excitation and Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emission spectra of the Alexa Fluor series cover the visible spectrum and extend into the infrared. The individual members of the family are numbered according roughly to their excitation maxima in nanometers. History Dick Haugland, Richard and Rosaria Haugland, the founders of Molecular Probes, are well known in biology and chemis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photobleaching
In optics, photobleaching (sometimes termed fading) is the photochemical alteration of a dye or a fluorophore molecule such that it is permanently unable to fluoresce. This is caused by cleaving of covalent bonds or non-specific reactions between the fluorophore and surrounding molecules. Such irreversible modifications in covalent bonds are caused by transition from a singlet state to the triplet state of the fluorophores. The number of excitation cycles to achieve full bleaching varies. In microscopy, photobleaching may complicate the observation of fluorescent molecules, since they will eventually be destroyed by the light exposure necessary to stimulate them into fluorescing. This is especially problematic in time-lapse microscopy. However, photobleaching may also be used prior to applying the (primarily antibody-linked) fluorescent molecules, in an attempt to quench autofluorescence. This can help improve the signal-to-noise ratio. Photobleaching may also be exploited to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
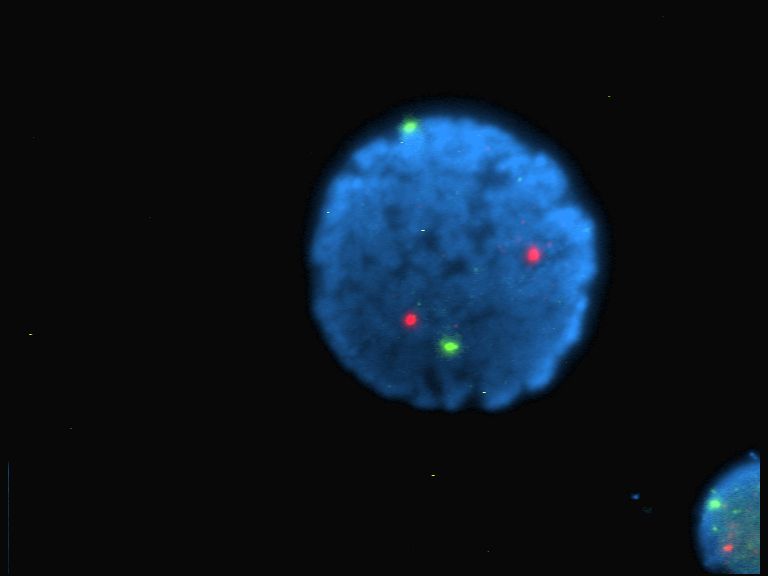
Fluorochrome
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with several π bonds. Fluorophores are sometimes used alone, as a tracer in fluids, as a dye for staining of certain structures, as a substrate of enzymes, or as a probe or indicator (when its fluorescence is affected by environmental aspects such as polarity or ions). More generally they are covalently bonded to macromolecules, serving as a markers (or dyes, or tags, or reporters) for affine or bioactive reagents (antibodies, peptides, nucleic acids). Fluorophores are notably used to stain tissues, cells, or materials in a variety of analytical methods, such as fluorescent imaging and spectroscopy. Fluorescein, via its amine-reactive isothiocyanate derivative fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), has been one of the most popular fluorophores. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emission Spectrum
The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the Spectrum (physical sciences), spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to electrons making a atomic electron transition, transition from a high energy state to a lower energy state. The photon energy of the emitted photons is equal to the energy difference between the two states. There are many possible electron transitions for each atom, and each transition has a specific energy difference. This collection of different transitions, leading to different radiated wavelengths, make up an emission spectrum. Each element's emission spectrum is unique. Therefore, spectroscopy can be used to identify elements in matter of unknown composition. Similarly, the emission spectra of molecules can be used in chemical analysis of substances. Emission In physics, emission is the process by which a higher energy quantum mechanical state of a particle becomes converted to a lower one through the emis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-Hydroxysuccinimide
''N''-Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) is an organic compound with the formula (CH2CO)2NOH. It is a white solid that is used as a reagent for preparing active esters in peptide synthesis. It can be synthesized by heating succinic anhydride with hydroxylamine or hydroxylamine hydrochloride. Activating reagent NHS is commonly found in organic chemistry or biochemistry where it is used as an activating reagent for carboxylic acids. Activated acids (carboxylates) can react with amines to form amides for example, whereas a normal carboxylic acid would just form a salt with an amine. Use A common way to synthesize an NHS-activated acid is to mix NHS with the desired carboxylic acid and a small amount of an organic base in an anhydrous solvent. A coupling reagent such as dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) or 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC) is then added to form a highly reactive activated acid intermediate. NHS reacts to create a less labile activated acid. The group is us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |