|
Flagellin
Flagellins are a family of proteins present in flagellated bacteria which arrange themselves in a hollow cylinder to form the filament in a bacterial flagellum. Flagellin has a mass on average of about 40,000 daltons. Flagellins are the principal component of bacterial flagella that have a crucial role in bacterial motility. The gene that encodes for flagellin has a different name in different bacterial species such as ''flaA'' ('' Helicobacter pylori'' for example), ''fliC'', ''fljB''. Structure The structure of flagellin is responsible for the helical shape of the flagellar filament, which is important for its proper function. It is transported through the center of the filament to the tip where it polymerases spontaneously into a part of the filament. In '' E. coli'' it is unfolded by the flagellar secretion chaperone FliS () during transport. The filament is made up of eleven smaller "protofilaments", nine of which contains flagellin in the L-type shape and the other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLS2
''FLS'' genes have been discovered to be involved in flagellin reception of bacteria. FLS1 was the original gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ... discovered shown to correspond with a specific ecotype within '' Arabidopsis thaliana''. Even so, further studies have shown a second FLS gene known as ''FLS2'' that is also associated with flagellin reception. ''FLS2'' and FLS1 are different genes with different responsibilities, but are related genetically. ''FLS2'' has a specific focus in plant defense and is involved in promoting the MAP kinase cascade. Mutations in the ''FLS2'' gene can cause bacterial infection by lack of response to flg22. Therefore, ''FLS2''’s primary focus is association with flg22 while its secondary focus is the involvement of promoting th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TLR5
Toll-like receptor 5, also known as TLR5, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''TLR5'' gene. It is a member of the toll-like receptor (TLR) family. TLR5 is known to recognize bacterial flagellin from invading mobile bacteria. It has been shown to be involved in the onset of many diseases, including Inflammatory bowel disease due to the high expression of TLR in intestinal lamina propria dendritic cells. Recent studies have also shown that malfunctioning of TLR5 is likely related to rheumatoid arthritis, osteoclastogenesis, and bone loss. Abnormal TLR5 functioning is related to the onset of gastric, cervical, endometrial and ovarian cancers. Function The TLR family plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. TLRs are highly conserved from Drosophila to humans and share structural and functional similarities. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that are expressed on infectious agents, and mediate the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabidopsis Thaliana
''Arabidopsis thaliana'', the thale cress, mouse-ear cress or arabidopsis, is a small plant from the mustard family (Brassicaceae), native to Eurasia and Africa. Commonly found along the shoulders of roads and in disturbed land, it is generally considered a weed. A winter annual with a relatively short lifecycle, ''A. thaliana'' is a popular model organism in plant biology and genetics. For a complex multicellular eukaryote, ''A. thaliana'' has a relatively small genome of around 135 Base pair#Length measurements, megabase pairs. It was the first plant to have its genome sequenced, and is an important tool for understanding the molecular biology of many plant traits, including flower development and phototropism, light sensing. Description ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' is an annual plant, annual (rarely biennial plant, biennial) plant, usually growing to 20–25 cm tall. The leaf, leaves form a rosette at the base of the plant, with a few leaves also on the flowering Plant ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toll-like Receptor
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single-pass membrane protein, single-spanning receptor (biochemistry), receptors usually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, that recognize structurally conserved molecules derived from Microorganism, microbes. Once these microbes have reached physical barriers such as the skin or intestinal tract mucosa, they are recognized by TLRs, which activate immune cell responses. The TLRs include TLR1, TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9, TLR10, TLR11, TLR12, and TLR13. Humans lack genes for TLR11, TLR12 and TLR13 and mice lack a functional gene for TLR10. The receptors TLR1, TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, and TLR10 are located on the cell membrane, whereas TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9 are located in Intracellular receptor, intracellular Vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicles (because they are sensors of nucleic acids). TLRs received their name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Flagellum
A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores (zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are known as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'', for example, uses its flagella to propel itself through the stomach to reach the mucous lining where it may colonise the epithelium and potentially cause gastritis, and ulcers – a risk factor for stomach cancer. In some swarming bacteria, the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota, the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means "whip" to describe its lash-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
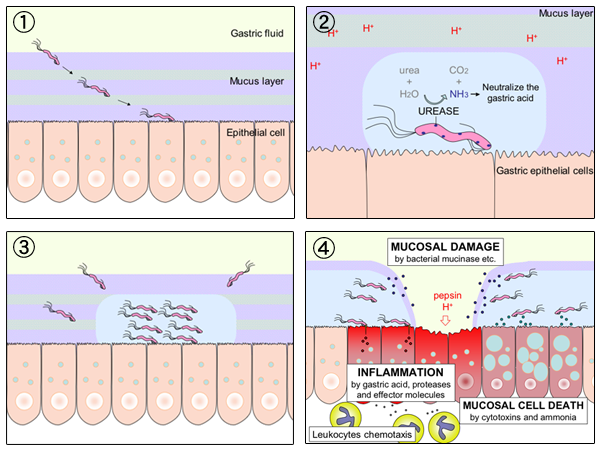
Helicobacter Pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, Flagellum#bacterial, flagellated, Bacterial cellular morphologies#Helical, helical bacterium. Mutants can have a rod or curved rod shape that exhibits less virulence. Its Helix, helical body (from which the genus name ''Helicobacter'' derives) is thought to have evolved to penetrate the gastric mucosa, mucous lining of the stomach, helped by its flagella, and thereby establish infection. While many earlier reports of an association between bacteria and the ulcers had existed, such as the works of John Lykoudis, it was only in 1983 when the bacterium was formally described for the first time in the English-language Western literature as the causal agent of peptic ulcer, gastric ulcers by Australian physician-scientists Barry Marshall and Robin Warren. In 2005, the pair was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery. Infection of the stomach with ''H. pylori'' doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TLR11
Toll-like receptor 11 (TLR11) is a protein that in mice and rats is encoded by the gene ''TLR11'', whereas in humans it is represented by a pseudogene. TLR11 belongs to the toll-like receptor (TLR) family and the interleukin-1 receptor/toll-like receptor superfamily and is found in the endosomes. In mice, TLR11 has been shown to recognise (bacterial) flagellin and (eukaryotic) profilin present on certain microbes on, it helps propagate a host immune response. TLR11 plays a fundamental role in both the innate and adaptive immune responses, through the activation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, the interleukin 12 (IL-12) response, and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) secretion. TLR11 mounts an immune response to multiple microbes, including ''Toxoplasma gondii'' (''T. gondii''), ''Salmonella'' species, and uropathogenic ''E. coli'', and likely many other species due to the highly conserved nature of flagellin and profilin. Structure and localization Proteins in the TLR family are pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Motility
Bacterial motility is the ability of bacteria to move independently using metabolic energy. Most motility mechanisms that evolved among bacteria also evolved in parallel among the archaea. Most rod-shaped bacteria can move using their own power, which allows colonization of new environments and discovery of new resources for survival. Bacterial movement depends not only on the characteristics of the medium, but also on the use of different appendages to propel. Swarming and swimming movements are both powered by rotating flagella. Whereas swarming is a multicellular 2D movement over a surface and requires the presence of surfactants, swimming is movement of individual cells in liquid environments. Other types of movement occurring on solid surfaces include twitching, gliding and sliding, which are all independent of flagella. Twitching depends on the extension, attachment to a surface, and retraction of type IV pili which pull the cell forwards in a manner similar to the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogen-associated Molecular Pattern
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are small molecular motifs conserved within a class of microbes, but not present in the host. They are recognized by toll-like receptors (TLRs) and other pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) in both plants and animals. This allows the innate immune system to recognize pathogens and thus, protect the host from infection. This initiation of the immune response consists of the secretion of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. PAMPs can initiate the maturation of immune cells, which can travel to the primary lymph node and trigger the adaptive immune system that involves the production of antibodies against specific antigens. Although the term "PAMP" is relatively new, the concept that molecules derived from microbes must be detected by receptors from multicellular organisms has been held for many decades, and references to an "endotoxin receptor" are found in much of the older literature. The recognition of PAMPs by the PRRs triggers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatic (biology)
In cellular biology, the term somatic is derived from the French somatique which comes from Ancient Greek σωματικός (sōmatikós, “bodily”), and σῶμα (sôma, “body”.) is often used to refer to the cells of the body, in contrast to the reproductive ( germline) cells, which usually give rise to the egg or sperm (or other gametes in other organisms). These somatic cells are diploid, containing two copies of each chromosome, whereas germ cells are haploid, as they only contain one copy of each chromosome (in preparation for fertilisation). Although under normal circumstances all somatic cells in an organism contain identical DNA, they develop a variety of tissue-specific characteristics. This process is called differentiation, through epigenetic and regulatory alterations. The grouping of similar cells and tissues creates the foundation for organs. Somatic mutations are changes to the genetics of a multicellular organism that are not passed on to its offspr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homologous Recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in Cell (biology), cellular organisms but may be also RNA in viruses). Homologous recombination is widely used by cells to accurately DNA repair, repair harmful DNA breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks (DSB), in a process called homologous recombinational repair (HRR). Homologous recombination also produces new combinations of DNA sequences during meiosis, the process by which eukaryotes make gamete cells, like sperm and ovum, egg cells in animals. These new combinations of DNA represent genetic variation in offspring, which in turn enables populations to Adaptation, adapt during the course of evolution. Homologous recombination is also used in horizontal gene transfer to exchange genetic material between different strains and species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UV-C
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs, Cherenkov radiation, and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. The photons of ultraviolet have greater energy than those of visible light, from about 3.1 to 12 electron volts, around the minimum energy required to ionize atoms. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack sufficient energy, it can induce chemical reactions and cause many substances to glow or fluoresce. Many practical applications, including chemical and biological effects, are derived from the way that UV radiation can interact with organic molecules. These interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |