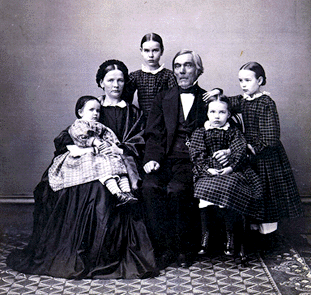|
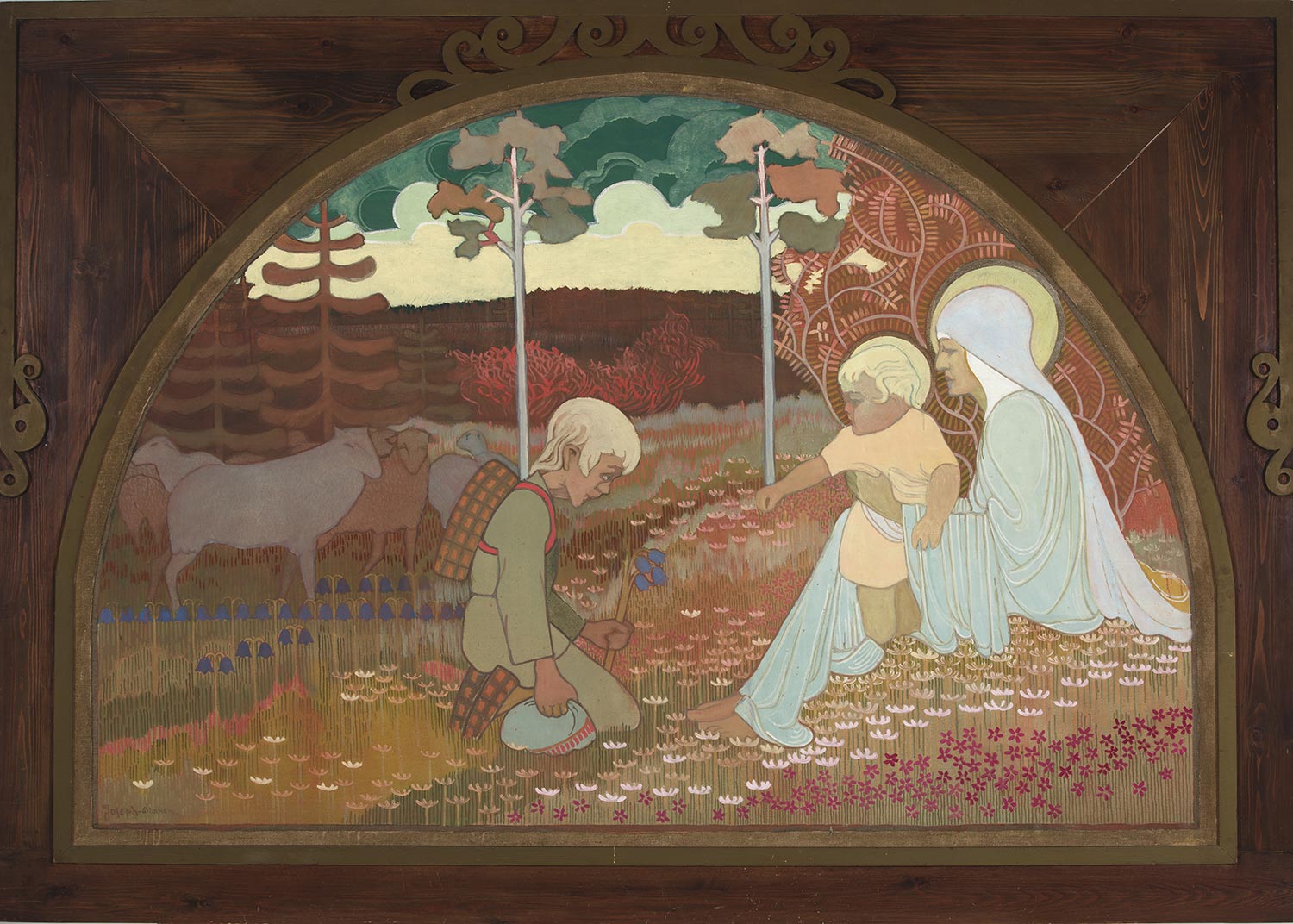
Finnish Mythology
Finnish mythology commonly refers of the folklore of Finnish paganism, of which a Finnish Neopaganism, modern revival is practiced by a small percentage of the Finnish people. It has many shared features with Estonian mythology, Estonian and other Baltic Finns, Finnic mythologies, but also with neighbouring Baltic mythology, Baltic, slavic mythology, Slavic and, to a lesser extent, Norse mythology, Norse mythologies. Finnish mythology survived within an oral tradition of mythical poem-singing and folklore well into the 19th century. Of the animals, the most sacred was the bear, whose real name was never uttered out loud, which was thought to be unfavorable to the hunt. The bear ("karhu" in Finnish) was seen as the embodiment of the forefathers, and for this reason it was called by many circumlocutions: ''mesikämmen'' ("mead-paw"), ''otso'' ("browed one"), ''kontio'' ("dweller of the land"), ''metsän kultaomena'' ("the golden apple of the forest"). It was not strictly seen as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelia
Karelia (; Karelian language, Karelian and ; , historically Коре́ла, ''Korela'' []; ) is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia (including the Soviet Union, Soviet era), Finland, and Sweden. It is currently divided between northwestern Russia (the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast) and Finland (the Regions of Finland, regions of South Karelia, North Karelia, and the eastern portion of Kymenlaakso). Use of name Various regions may be called Karelia. Finnish Karelia is a historical province of Finland and is now divided between Finland and Russia, often called just ''Karjala'' in Finnish. The eastern part of this chiefly Lutheran area was ceded to Russia after the Winter War of 1939–40. The Republic of Karelia is a Russian federal subject, including East Karelia, with a chiefly Russian Orthodox population. Within present-day Finland, ''Karjala'' refers to the Regions of Finland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanteletar
''Kanteletar'' is a collection of Finnish folk poetry compiled by 19th-century Finnish linguist Elias Lönnrot. It is considered to be a sister collection to the Finnish national epic ''Kalevala''. The poems of ''Kanteletar'' are based on the trochaic tetrameter, generally referred to as "Kalevala metre". The name consists of the base word ''kantele'' (a Finnish zither-like instrument) and the feminising morpheme ''-tar'' and can be roughly interpreted as "maiden of the kantele" or "zither-daughter", a kind of muse. History ''Kanteletar'' was published in 1840 under the name ''Kanteletar taikka Suomen Kansan Wanhoja Lauluja ja Wirsiä'' (''"Kanteletar or Old Songs and Hymns of the Finnish People"''). Lönnrot got the foundation for the collection on his journeys in 1838 after he met rune singer Mateli Kuivalatar on the banks of the Koitere. The poems sung by Kuivalatar were recorded in Lönnrot's notes. ''Kanteletar'' consists of three books. The first book includes 238 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalevala
The ''Kalevala'' () is a 19th-century compilation of epic poetry, compiled by Elias Lönnrot from Karelian and Finnish oral folklore and mythology, telling a story about the Creation of the Earth, describing the controversies and retaliatory voyages between the peoples of the land of Kalevala called Väinölä and the land of Pohjola and their various protagonists and antagonists, as well as the construction and robbery of the mythical wealth-making machine Sampo. The ''Kalevala'' is regarded as the national epic of Karelia and Finland, and is one of the most significant works of Finnish literature along with J. L. Runeberg's ''The Tales of Ensign Stål'' and Aleksis Kivi's '' The Seven Brothers''. The ''Kalevala'' was instrumental in the development of the Finnish national identity and the intensification of Finland's language strife that ultimately led to Finland's independence from Russia in 1917. The work is known internationally and has partly influenced, for exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synty
''Synty'' ('origin, birth, aetiology', pl. ''synnyt'') is an important concept in Finnish mythology. ''Syntysanat'' ('origin-words') or ''syntyloitsut'' ('origin-charms') provide an explanatory, mythical account of the origin of a phenomenon (such as an illness), material (such as iron), or species (such as a bear), and were an important part of traditional Finno-Karelian culture, particularly in healing rituals. Although much in the Finnish traditional charms is paralleled elsewhere, 'the role of etiological, aetiological and creation myth, cosmogonic myths' in Finnic tradition 'appears exceptional in Eurasia'. The major study remains that by Kaarle Krohn, published in 1917. Meanings of ''synty'' The term ''synty'' is used in this article and in a range of scholarship as a genre-label, but it had a wide variety of meanings. ''Synty'' transparently derives from ''syntyä'' (‘come into existence, be born’) and means ‘birth’, ‘origin’, ‘aetiology’, and so forth. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tietäjä
Tietäjä (, pl. ''tietäjät'', 'seer', 'wise man', literally 'knower') is a magically powerful figure in traditional Finnic culture, whose supernatural powers arise from his great knowledge. Roles The activities of a ''tietäjä'' were primarily healing and preventing illness, but also included helping with farming, fishing and hunting; dealing with witchcraft; supporting approved marriages and disrupting disapproved liaisons; identifying thieves; and bringing success to ventures such as journeys or building. Their incantations might call on helpers such as the dead, '' väki'', Ukko, Jesus Christ, the Virgin Mary, or animal spirits. Many ''tietäjät'' knew '' Kalevala''-metre poems, as well as mythical stories, spells, and healing charms. One of the key branches of the ''tietäjäs knowledge concerned aetiologies ('' synnyt'', s. ''synty'') of natural phenomena. It was believed that beings and phenomena could be controlled if their origin was known. For example, disease cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folk Poetry
Folk poetry (sometimes referred to as ''poetry in action'') is poetry that is part of a society's folklore, usually part of their oral tradition. When sung, folk poetry becomes a folk song. Description Folk poetry in general has several characteristics. It may be informal and unofficial, generally lacks an owner and may "belong" to the society, and its telling may be an implicitly social activity. The term can refer to poems of an oral tradition that may date back many years; that is, it is information that has been transmitted over time (between generations) ''only'' in spoken (and non-written) form. Thus as an oral tradition folk poetry requires a performer to promulgate it over generations. The definition can also be extended to include not just oral epics, but latrinalia, many forms of childlore (skipping-rope rhymes, the words of counting-out games etc.), and limericks; as well as including anonymous or improvised poems. Narrative folk poetry is often characterized by repetit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Europaeus
David Emanuel Daniel (Taneli) Europaeus (1820–1884) was a Finnish linguist and folklore collector. He was born to Pietari Aadolf Europaeus and Sofia Peijo. During the period 1845–54, he made several trips to Finnish and Russian Karelia. Of his large and valuable collections, Elias Lönnrot received, among other things, the entire Kullervo section for the expanded second edition of the Kalevala in 1849. Europaeus also collected Sámi traditions. As a linguist, he was primarily interested in the early history of the Finnish language and the Finnish people. He is considered the founder of onomastics in Finland. Europaeus was enrolled at the Imperial Alexander University, now the University of Helsinki, for 12 years but did not graduate. He published a Swedish-Finnish dictionary (1852-53) and ''Suomalaisten puustavein äännöskuvat'' (1857). Europaeus was also involved in founding the newspaper "Suometar" in 1846 and served as its editor from 1847 to 1850. Europaeus conducted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthias Castrén
Matthias Alexander Castrén (2 December 1813 – 7 May 1852) was a Finnish Swedish ethnologist and philologist who was a pioneer in the study of the Uralic languages. He was an educator, author and linguist at the University of Helsinki. Castrén is known for his research in the linguistics and ethnography of the Northern Eurasian peoples. Early life Castrén was born at Tervola, in northern Finland. His father, Christian Castrén, the parish priest and vicar in Rovaniemi, died in 1825. Castrén passed under the protection of his uncle, Matthias Castrén. At the age of twelve, he was sent to school at Oulu. On entering the Alexander University in Helsinki (now the University of Helsinki) in 1828, he first devoted himself to Greek and Hebrew with the intention of entering the church, but his interest was soon excited by the Finnish language, and even before his course was completed, he began to lay the foundations of a work on Finnish mythology. He received his bachelor's degr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johan Cajan
Juhana "Johan" Fredrik Cajan (13 September 1815 – 28 February 1887) was a Finnish clergyman and historian, the author of the first history of Finland written in Finnish.Charles Dudley Warner, ed., ''Library of the world's best literature'', vol. 43, 1896p.295/ref> Cajan was born in Sotkamo, Finland and died in Piippola, Finland. Cajan's parents were Johann Cajan and Eva Elfving. After his exam he traveled to Lapland. During his studies, he got to know Elias Lönnrot Elias Lönnrot (; 9 April 1802 – 19 March 1884) was a Finnish polymath, physician, philosopher, poet, musician, linguist, journalist, philologist and collector of traditional Finnish language, Finnish Oral literature, oral poetry. He is best k ..., and he collected folklore with him. Cajan wrote about Finland's history (in the Finnish language) in the publication ''Mehiläinen'' 1839-40. He used writing names as J. F. Kainonen and J. F. Kajaani. His magnum opus is ''Suomen Historia, koetteeksi kerrottu lyhyk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elias Lönnrot
Elias Lönnrot (; 9 April 1802 – 19 March 1884) was a Finnish polymath, physician, philosopher, poet, musician, linguist, journalist, philologist and collector of traditional Finnish language, Finnish Oral literature, oral poetry. He is best known for synthesizing the Finnish national epic, ''Kalevala'' (1835, enlarged 1849) from short ballads and lyric poetry, lyric poems he gathered from Finnish folklore, Finnish oral tradition during several field expeditions in Finland, Russian Karelia, the Kola Peninsula and Baltic countries. In botany, he is remembered as the author of the 1860 ''Flora Fennica'', the first scientific text written in Finnish rather than in Latin. Education and early life Lönnrot was born in Sammatti, in the province of Uusimaa, Finland, which was then Finland under Swedish rule, part of Sweden. From 1814 to 1815, he attended the school of Tammisaari Pedagogio. He studied at Katedralskolan i Åbo, Turku Cathedral School from 5April1816 until he droppe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |