|
Filipino Alphabet
The modern Filipino alphabet (), otherwise known as the Filipino alphabet (), is the alphabet of the Filipino language, the official national language and one of the two official languages of the Philippines. The modern Filipino alphabet is made up of 28 letters, which includes the entire 26-letter set of the ISO basic Latin alphabet, the Spanish '' Ñ'', and the '' Ng''. The Ng digraph came from the Pilipino Abakada alphabet of the Fourth Republic. Today, the modern Filipino alphabet may also be used to write all autochthonous languages of the Philippines and Chavacano, a Spanish-derived creole. In 2013, the Komisyon sa Wikang Filipino released the ''Ortograpiyang Pambansa'' ("National Orthography"), a new set of guidelines that resolved phonemic representation problems previously encountered when writing some Philippine languages and dialects. Alphabet The letters C/c, F/f, J/j, Ñ/ñ, Q/q, V/v, X/x, and Z/z are not used in most native Filipino words, but they are u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filipino Language
Filipino ( ; , ) is the national language of the Philippines, the main lingua franca, and one of the two official languages of the country, along with Philippine English, English. It is only a ''de facto'' and not a ''de jure'' standard language, standardized form of the Tagalog language, as spoken and written in Metro Manila, the National Capital Region, and in other urban centers of the archipelago. The Constitution of the Philippines, 1987 Constitution mandates that Filipino be further enriched and developed by the other languages of the Philippines. Filipino, like other Austronesian languages, commonly uses Verb–subject–object, verb-subject-object order, but can also use subject-verb-object order. Filipino follows the Symmetrical voice, trigger system of morphosyntactic alignment that is common among Philippine languages. It has Head-directionality parameter, head-initial directionality. It is an agglutinative language but can also display inflection. It is not a Tone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standard written representation for the sounds of speech. The IPA is used by linguists, lexicography, lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, speech–language pathology, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators, and translators. The IPA is designed to represent those qualities of speech that are part of lexical item, lexical (and, to a limited extent, prosodic) sounds in oral language: phone (phonetics), phones, Intonation (linguistics), intonation and the separation of syllables. To represent additional qualities of speechsuch as tooth wikt:gnash, gnashing, lisping, and sounds made with a cleft lip and cleft palate, cleft palatean extensions to the International Phonetic Alphabet, extended set of symbols may be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cebuano Language
Cebuano ( )Cebuano on Merriam-Webster.com is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language spoken in the southern Philippines by Cebuano people and other Ethnic groups in the Philippines, ethnic groups as a secondary language. It is natively, though informally, called by the generic name Bisayâ (), or Binisayâ () (both terms are translated into English as ''Visayan'', though this should not be confused with other Bisayan languages) and sometimes referred to in English sources as Cebuan ( ). It is spoken by the Visayans, Visayan ethnolinguistic groups native to the islands of Cebu, Bohol, Siquijor, the eastern half of Negros Island, Negros, the western half of Leyte, the northern coastal areas of Northern Mindanao and the eastern part of Zamboanga del Norte due to Captaincy General of the Philippines, Spanish settlements during the 18th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Alphabets
The lists and tables below summarize and compare the letter inventories of some of the Latin-script alphabets. In this article, the scope of the word "alphabet" is broadened to include letters with tone marks, and other diacritics used to represent a wide range of orthographic traditions, without regard to whether or how they are sequenced in their alphabet or the table. Parentheses indicate characters not used in modern standard orthographies of the languages, but used in obsolete and/or dialectal forms. Letters contained in the ISO basic Latin alphabet Alphabets that contain only ISO basic Latin letters Among alphabets for natural languages the English, 6/sup> Indonesian, and Malay alphabets only use the 26 letters in both cases. Among alphabets for constructed languages the Ido and Interlingua alphabets only use the 26 letters, while Toki Pona uses a 14-letter subset. Extended by ligatures * German (ß), Scandinavian (æ) Extended by diacritical marks * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippine Braille
Philippine Braille or Filipino Braille is the braille alphabet of the Philippines. Besides Filipino ( Tagalog), essentially the same alphabet is used for Ilocano, Cebuano, Hiligaynon and Bicol.The 17th edition of ''Ethnologue'' reports braille usage for Kapampangan, Pangasinan, Waray, and Chavacano as well. They use presumably the same conventions as Filipino. Philippine Braille is based on the 26 letters of the basic braille alphabet used for Grade-1 English Braille English Braille, also known as ''Grade 2 Braille'', is the braille alphabet used for English. It consists of around 250 letters ( phonograms), numerals, punctuation, formatting marks, contractions, and abbreviations (logograms). Some English ..., so the print digraph ''ng'' is written as a digraph in braille as well. The print letter ''ñ'' is rendered with the generic accent point, . These are considered part of the alphabet, which is therefore, : Numbers and punctuation are as in traditional English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suyat
Suyat (''Baybayin:'' , '' Hanunó'o:'' , '' Buhid:'' , '' Tagbanwa:'' , '' Modern Kulitan:'' '' Jawi (Arabic):'' ) is a collective name for the Brahmic scripts of Philippine ethnolinguistic groups. The term was suggested and used by cultural organizations in the Philippines to denote a unified neutral terminology for Philippine scripts. Philippine scripts Ancient Philippine scripts are various writing systems that developed and flourished in the Philippines around 300 BC. These scripts are related to other Southeast Asian systems of writing that developed from South Indian Brahmi scripts used in Asoka Inscriptions and Pallava Grantha, a type of writing used in the writing of palm leaf books called ''Grantha script'' during the ascendancy of the Pallava dynasty about the 5th century,Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filipino Orthography
Filipino orthography () specifies the correct use of the writing system of the Filipino language, the national language#Philippines, national and co-official language, official languages of the Philippines, language of the Philippines. In 2013, the Komisyon sa Wikang Filipino released the ''Ortograpiyang Pambansa'' (“National Orthography”), a new set of guidelines for writing the Filipino language. Alphabet The modern Filipino alphabet introduced since 1987 consists of 28 letters (20 if you only count native letters). Notes on Filipino orthography * C, F, J, Ñ, Q, V, X, and Z are used mostly for loanwords, regional words and proper nouns. * The vowels are A, E, I, O, and U. * Usual diacritic marks are acute accent, acute , grave accent, grave , circumflex , diaeresis (diacritic), diaeresis which are optional, and only used with the vowels. grave accent, Grave and circumflex may only appear at the end of a word ending in a vowel. Diacritics have no impact on collation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingua Franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make communication possible between groups of people who do not share a First language, native language or dialect, particularly when it is a third language that is distinct from both of the speakers' native languages. Linguae francae have developed around the world throughout human history, sometimes for commercial reasons (so-called "trade languages" facilitated trade), but also for cultural, religious, diplomatic and administrative convenience, and as a means of exchanging information between scientists and other scholars of different nationalities. The term is taken from the medieval Mediterranean Lingua Franca, a Romance languages, Romance-based pidgin language used especially by traders in the Mediterranean Basin from the 11th to the 19th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenix Loureiroi
''Phoenix loureiroi'' (commonly known as the mountain date palm, vuyavuy palm, or voyavoy palm,) is a species of flowering plant in the palm family, indigenous to southern Asia, from the Philippines, Taiwan, India, southern Bhutan, Burma, Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam, Pakistan, and China. It occurs in deciduous and evergreen forests and in clear terrain from sea level to 1,500 m altitude.Riffle, Robert L. and Craft, Paul (2003) ''An Encyclopedia of Cultivated Palms''. Portland: Timber Press. / (pages 402-403) ''Phoenix loureiroi'' is named after João de Loureiro; it was originally written by Kunth as "''loureirii''", but this is an error to be corrected to ''loureiroi'' under the provisions of the ICBN. Description ''Phoenix loureiroi'' contains solitary and clustering plants with trunks from 1–4 m high and 25 cm in width, usually covered in old leaf bases. The leaves vary to some degree but usually reach 2 m in length with leaflets wide at the base and sharply pointed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batanes
Batanes, officially the Province of Batanes (; Ilocano: ''Probinsia ti Batanes''; , ), is an archipelagic province in the Philippines, administratively part of the Cagayan Valley region. It is the northernmost province in the Philippines, and the smallest, both in population and land area. The capital is Basco, located on the island of Batan, and is also the most populous municipality in the province. The island group is located approximately north of the Luzon mainland and about south of Taiwan ( Pingtung County). Batanes is separated from the Babuyan Islands of Cagayan Province by the Balintang Channel, and from Taiwan by the Bashi Channel. Etymology The name ''Batanes'' is a Hispanicized plural form derived from the Ivatan endonym ''Batan''. History Early history The ancestors of today's Ivatans descended from Austronesians who migrated to the islands 4,000 years ago during the Neolithic period. They lived in fortified mountain areas called '' idjangs'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tilde
The tilde (, also ) is a grapheme or with a number of uses. The name of the character came into English from Spanish , which in turn came from the Latin , meaning 'title' or 'superscription'. Its primary use is as a diacritic (accent) in combination with a base letter. Its freestanding form is used in modern texts mainly to indicate approximation. History Use by medieval scribes The tilde was originally one of a variety of marks written over an omitted letter or several letters as a scribal abbreviation (a "mark of contraction"). Thus, the commonly used words ''Anno Domini'' were frequently abbreviated to ''Ao Dñi'', with an elevated terminal with a contraction mark placed over the "n". Such a mark could denote the omission of one letter or several letters. This saved on the expense of the scribe's labor and the cost of vellum and ink. Medieval European charters written in Latin are largely made up of such abbreviated words with contraction marks and other abbreviations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
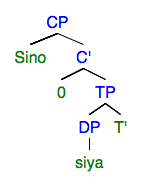
Tagalog Grammar
Tagalog grammar (Tagalog: ''Balarilà ng Tagalog'') are the rules that describe the structure of expressions in the Tagalog language, one of the languages in the Philippines. In Tagalog, there are nine parts of speech: nouns (''pangngalan''), pronouns (''panghalíp''), verbs (''pandiwà''), adverbs (''pang-abay''), adjectives (''pang-urì''), prepositions (''pang-ukol''), conjunctions (''pangatníg''), ligatures (''pang-angkóp'') and particles. Tagalog is an agglutinative yet slightly inflected language. Pronouns are inflected for number and verbs for focus/voice and aspect. Verbs Tagalog verbs are complex and are changed by taking on many affixes reflecting focus/ trigger, aspect and mood. Below is a chart of the main verbal affixes, which consist of a variety of prefixes, suffixes, infixes, and circumfixes. Conventions used in the chart: * ''CV~'' stands for reduplication of the first syllable of a root word; that is, the first consonant (if any) and the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |