|
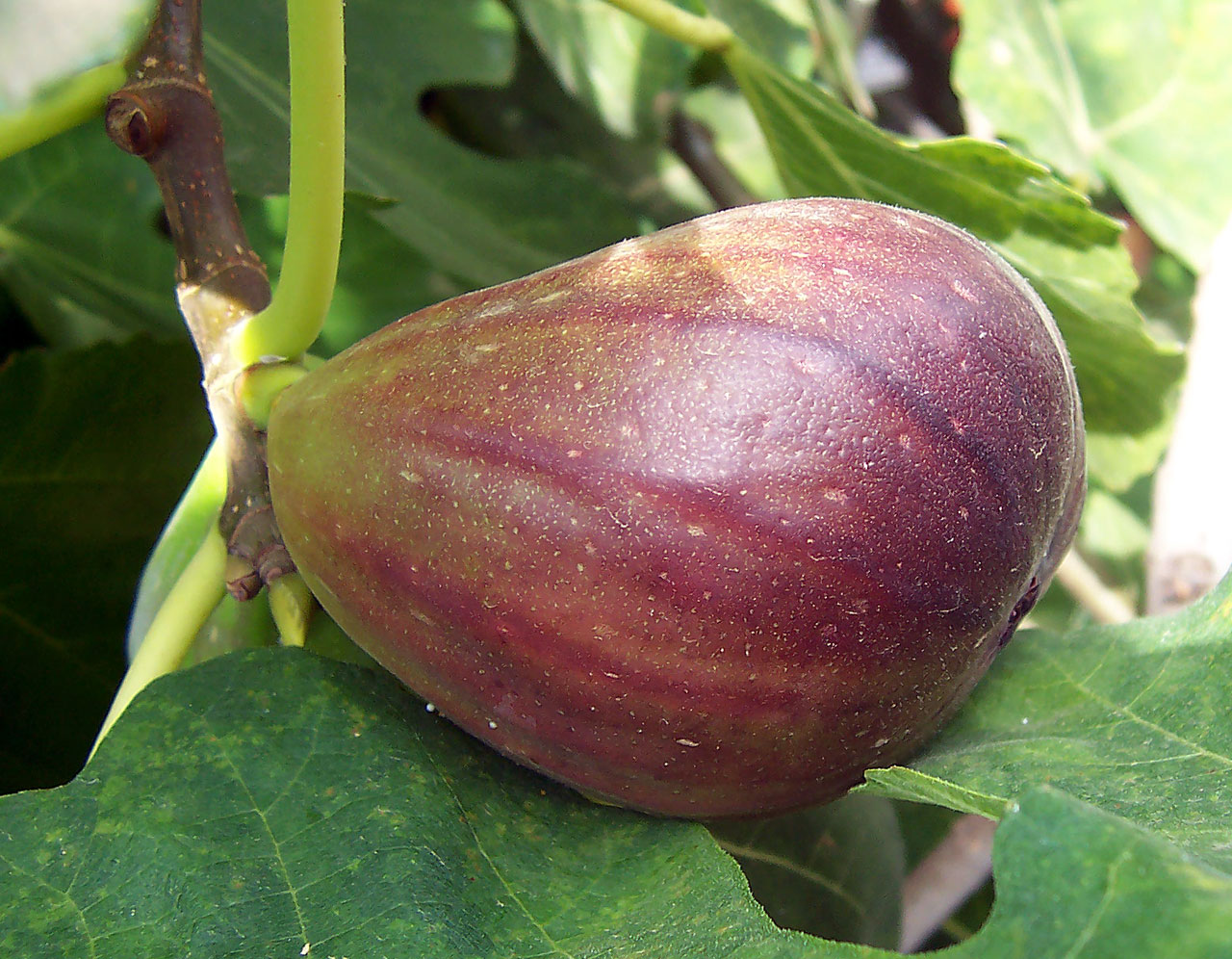
Ficus Neriifolia
''Ficus neriifolia'' is a species of fig (''Ficus''). It is native to Asia, including Bhutan, Burma, China, India, and Nepal.''Ficus neriifolia''. Flora of China. Description ''Ficus neriifolia'' grows as a tree up to 15 m (50 ft) tall with smooth, dark grey bark on its trunk. The hairless, leathery oval to lanceolate (spear-shaped) leaves are up to long by wide, and often asymmetrical in shape. The diameter figs are rounded, oval, or cylindrical and grow in pairs off older branches.Taxonomy James Edward Smith described ''Ficus neriifolia'' in 1810. In 1965, E.H.Corner regarded the species as having three valid va ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Edward Smith (botanist)
Sir James Edward Smith (2 December 1759 – 17 March 1828) was an English botanist and founder of the Linnean Society. Early life and education Smith was born in Norwich in 1759, the son of a wealthy wool merchant. He started studying botanical science when he was eighteen. In 1781 he enrolled in the medical course at the University of Edinburgh, where he studied chemistry under Joseph Black, natural history under John Walker, and botany under John Hope, an early teacher of Linnaean taxonomy. He moved to London in 1783 to continue his studies and became a friend of Sir Joseph Banks, who was offered the entire collection of books, manuscripts and specimens of the Swedish natural historian and botanist Carl Linnaeus following the death of his son Carolus Linnaeus the Younger. Banks declined the purchase, but Smith borrowed money from his father and bought the collection for the price of £1,000 in 1784. Smith was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1785. Academic ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Hoolock Gibbon
The eastern hoolock gibbon (''Hoolock leuconedys'') is a primate from the gibbon family, Hylobatidae. It is one of three species of hoolock gibbon. This species is found in east of the Chindwin River, such as the Mahamyaing Wildlife Sanctuary, and in south west Yunnan of China. Recent study published in April, 2021, in International Journal of Primatology confirmed that this species is not found in India as it was thought to be. Taxonomy Mootnick and Groves stated that hoolock gibbons do not belong in the genus ''Bunopithecus'', and placed them in a new genus, ''Hoolock''. This genus was argued to contain two distinct species which were previously thought to be subspecies: '' Hoolock hoolock'' and ''Hoolock leuconedys''. The ranges of the two species are unclear and may overlap, and intermediates may occur. Habitat and ecology The eastern hoolock gibbon is a forest-dwelling primate that prefers a continuous canopy, which makes them vulnerable to loss of habitat. They can be foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trees Of China
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated Plant stem, stem, or trunk (botany), trunk, usually supporting Branch, branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only Bark (botany), woody plants with secondary growth, only plants that are usable as lumber, or only plants above a specified height. But wider definitions include taller Arecaceae, palms, Cyatheales, tree ferns, Musa (genus), bananas, and bamboos. Trees are not a Monophyletic group, monophyletic taxonomic group but consist of a wide variety of plant species that Convergent evolution, have independently evolved a trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. The majority of tree species are angiosperms or hardwoods; of the rest, many are gymnosperms or softwoods. Trees tend to be long-lived, some trees reaching several thousand years old. Trees evolved around 400 million years ago, and it is estimated that there are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trees Of Myanmar
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only plants that are usable as lumber, or only plants above a specified height. But wider definitions include taller palms, tree ferns, bananas, and bamboos. Trees are not a monophyletic taxonomic group but consist of a wide variety of plant species that have independently evolved a trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. The majority of tree species are angiosperms or hardwoods; of the rest, many are gymnosperms or softwoods. Trees tend to be long-lived, some trees reaching several thousand years old. Trees evolved around 400 million years ago, and it is estimated that there are around three trillion mature trees in the world currently. A tree typically has many secondary branches supported clear of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of The Indian Subcontinent
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring ( indigenous) native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora as in the terms ''gut flora'' or ''skin flora'' for purposes of specificity. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ficus
''Ficus'' ( or ) is a genus of about 850 species of woody trees, shrubs, vines, epiphytes and hemiepiphytes in the family (biology), family Moraceae. Collectively known as fig trees or figs, they are native throughout the tropics with a few species extending into the semi-warm temperate zone. The common fig (''F. carica'') is a temperate species native to southwest Asia and the Mediterranean region (from Afghanistan to Portugal), which has been widely cultivated from ancient times for its fruit, also referred to as figs. The fruit of most other species are also edible though they are usually of only local economic importance or eaten as bushfood. However, they are extremely important food resources for wildlife. Figs are also of considerable cultural importance throughout the tropics, both as objects of worship and for their many practical uses. Description ''Ficus'' is a pantropical genus of trees, shrubs, and vines occupying a wide variety of ecological niches; most a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
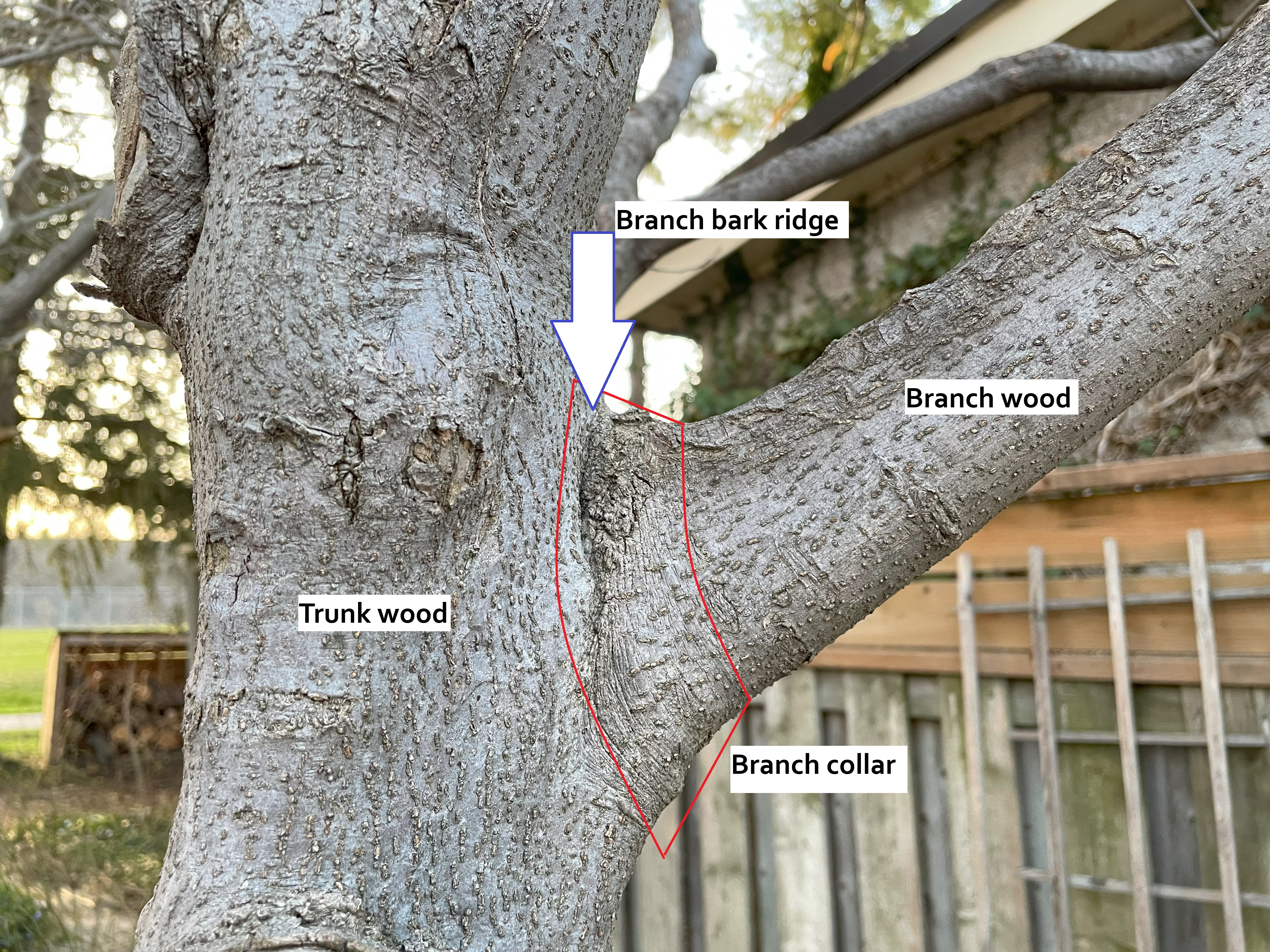
Pruning
Pruning is the selective removal of certain parts of a plant, such as branches, buds, or roots. It is practiced in horticulture (especially fruit tree pruning), arboriculture, and silviculture. The practice entails the targeted removal of diseased, damaged, dead, non-productive, structurally unsound, or otherwise unwanted plant material from crop and landscape plants. In general, the smaller the branch that is cut, the easier it is for a woody plant to compartmentalize the wound and thus limit the potential for pathogen intrusion and decay. It is therefore preferable to make any necessary formative structural pruning cuts to young plants, rather than removing large, poorly placed branches from mature plants. Woody plants may undergo a process referred to as ''self-pruning'', where they will drop twigs or branches which are no longer producing more energy than they require. It is theorized that this process can also occur in response to lack of water, in order to reduce the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indoor Bonsai
Indoor bonsai are bonsai cultivated for the indoor environment. Traditionally, bonsai are temperate climate trees grown outdoors in containers. Tropical and sub-tropical tree species can be cultivated to grow and thrive indoors, with some suited to bonsai aesthetics shaped as traditional outdoor or wild bonsai. Bonsai and related practices, like ''penjing'', Hòn Non Bộ, ''hòn non bộ'', and ''saikei'', involve the long-term cultivation of small trees and landscapes in containers. The term ''bonsai'' is generally used in English as an umbrella term for all miniature trees in containers or pots. Indoor vs. traditional bonsai Indoor bonsai is the cultivation of an attractive, healthy plant in the artificial environment of indoors rather than using an outdoor climate, as may occur in traditional bonsai. Indoor penjing is the cultivation of miniature landscapes in a pot or tray, possibly with rocks, bonsai trees, and ground covers, and sometimes with small objects or figurines. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye or Madras eye, is inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin, clear layer that covers the white surface of the eye and the inner eyelid. It makes the eye appear pink or reddish. Pain, burning, scratchiness, or itchiness may occur. The affected eye may have increased tears or be "stuck shut" in the morning. Swelling of the sclera may also occur. Itching is more common in cases due to allergies. Conjunctivitis can affect one or both eyes. The most common infectious causes in adults are viral, whereas in children bacterial causes predominate. The viral infection may occur along with other symptoms of a common cold. Both viral and bacterial cases are easily spread between people. Allergies to pollen or animal hair are also a common cause. Diagnosis is often based on signs and symptoms. Occasionally, a sample of the discharge is sent for microbial culture, culture. Prevention is partly by handwashing. Treatment depends on the underlying cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ficus Neriifolia Bonsai
''Ficus'' ( or ) is a genus of about 850 species of woody trees, shrubs, vines, epiphytes and hemiepiphytes in the family Moraceae. Collectively known as fig trees or figs, they are native throughout the tropics with a few species extending into the semi-warm temperate zone. The common fig (''F. carica'') is a temperate species native to southwest Asia and the Mediterranean region (from Afghanistan to Portugal), which has been widely cultivated from ancient times for its fruit, also referred to as figs. The fruit of most other species are also edible though they are usually of only local economic importance or eaten as bushfood. However, they are extremely important food resources for wildlife. Figs are also of considerable cultural importance throughout the tropics, both as objects of worship and for their many practical uses. Description ''Ficus'' is a pantropical genus of trees, shrubs, and vines occupying a wide variety of ecological niches; most are evergreen, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Crested Gibbon
The black crested gibbon (''Nomascus concolor'') is a Critically Endangered species of gibbon found in China, Laos, and northern Vietnam, with four subspecies. Taxonomy The taxonomy of the species is confused. Previously grouped in the genus '' Hylobates'', currently four subspecies are recognized. * Central Yunnan black crested gibbon (''Nomascus concolor jingdongensis''), Yunnan province, China * West Yunnan black crested gibbon (''N. c. furvogaster''), Yunnan province, China * Laotian black crested gibbon (''N. c. lu''), Laos * Tonkin black crested gibbon (''N. c. concolor''), northern Vietnam, Yunnan province, China. Description The length from the head to the end of body is and it weighs from . The species exhibits sexual dichromatism, the male is completely black, while the female is a golden or buff colour with variable black patches, including a black streak on the head. Behavior Gibbons are forest dwellers and are well known for their habit of swinging be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ficus
''Ficus'' ( or ) is a genus of about 850 species of woody trees, shrubs, vines, epiphytes and hemiepiphytes in the family (biology), family Moraceae. Collectively known as fig trees or figs, they are native throughout the tropics with a few species extending into the semi-warm temperate zone. The common fig (''F. carica'') is a temperate species native to southwest Asia and the Mediterranean region (from Afghanistan to Portugal), which has been widely cultivated from ancient times for its fruit, also referred to as figs. The fruit of most other species are also edible though they are usually of only local economic importance or eaten as bushfood. However, they are extremely important food resources for wildlife. Figs are also of considerable cultural importance throughout the tropics, both as objects of worship and for their many practical uses. Description ''Ficus'' is a pantropical genus of trees, shrubs, and vines occupying a wide variety of ecological niches; most a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |