Conjunctivitis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye or Madras eye, is
 Red eye, swelling of the conjunctiva, and watering of the eyes are symptoms common to all forms of conjunctivitis. However, the pupils should be normally reactive, and the visual acuity normal.
Conjunctivitis is identified by inflammation of the conjunctiva, manifested by irritation and redness. Examination using a
Red eye, swelling of the conjunctiva, and watering of the eyes are symptoms common to all forms of conjunctivitis. However, the pupils should be normally reactive, and the visual acuity normal.
Conjunctivitis is identified by inflammation of the conjunctiva, manifested by irritation and redness. Examination using a
 Approximately 80% of cases of conjunctivitis in adults and less than 20% in children are due to viruses, with 65% to 90% of these cases being attributed to adenoviruses.
Viral conjunctivitis is often associated with an infection of the upper respiratory tract, a common cold, or a sore throat. Other associated signs may include pre-auricular lymph node swelling and contact with another person with a red eye. Eye pain may be present if the cornea is also involved. Its symptoms include excessive watering and itching. The discharge in viral conjunctivitis is usually (but not always) watery in nature. The infection usually begins in one eye but may spread easily to the other eye.
Viral conjunctivitis manifests as a fine, diffuse pinkness of the conjunctiva which may be mistaken for
Approximately 80% of cases of conjunctivitis in adults and less than 20% in children are due to viruses, with 65% to 90% of these cases being attributed to adenoviruses.
Viral conjunctivitis is often associated with an infection of the upper respiratory tract, a common cold, or a sore throat. Other associated signs may include pre-auricular lymph node swelling and contact with another person with a red eye. Eye pain may be present if the cornea is also involved. Its symptoms include excessive watering and itching. The discharge in viral conjunctivitis is usually (but not always) watery in nature. The infection usually begins in one eye but may spread easily to the other eye.
Viral conjunctivitis manifests as a fine, diffuse pinkness of the conjunctiva which may be mistaken for

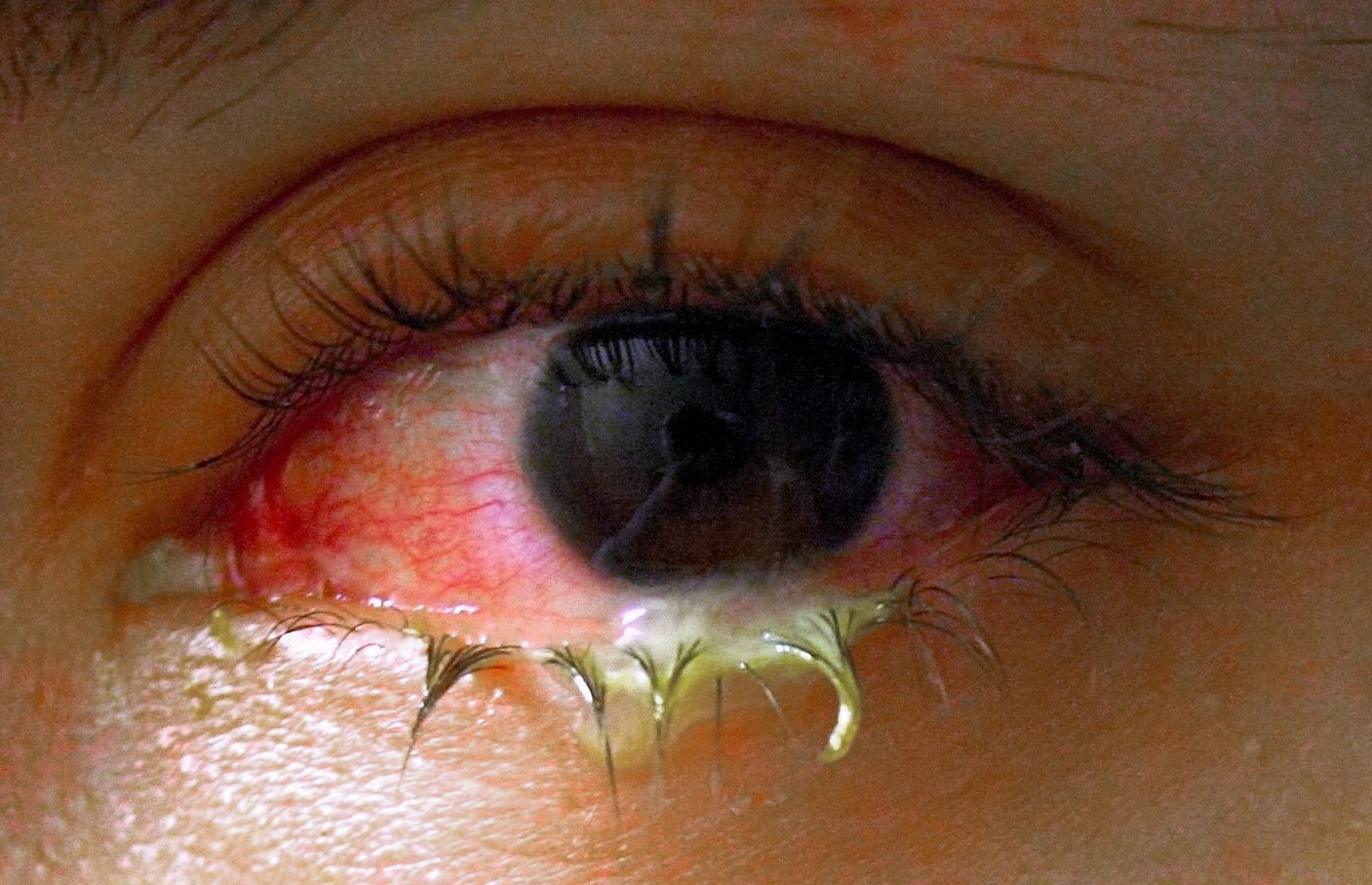 Bacteria are responsible for approximately 70% of conjunctivitis in children and less than 20% of cases in adults. Common bacteria responsible for bacterial conjunctivitis are ''
Bacteria are responsible for approximately 70% of conjunctivitis in children and less than 20% of cases in adults. Common bacteria responsible for bacterial conjunctivitis are '' Bacteria such as ''
Bacteria such as ''
 Inclusion conjunctivitis of the newborn is a conjunctivitis that may be caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and may lead to acute, purulent conjunctivitis. However, it is usually self-healing.
Inclusion conjunctivitis of the newborn is a conjunctivitis that may be caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and may lead to acute, purulent conjunctivitis. However, it is usually self-healing.
 Cultures are not often taken or needed as most cases resolve either with time or typical antibiotics. If bacterial conjunctivitis is suspected, but no response to topical antibiotics is seen, swabs for bacterial culture should be taken and tested. Viral culture may be appropriate in epidemic case clusters.
A
Cultures are not often taken or needed as most cases resolve either with time or typical antibiotics. If bacterial conjunctivitis is suspected, but no response to topical antibiotics is seen, swabs for bacterial culture should be taken and tested. Viral culture may be appropriate in epidemic case clusters.
A
inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
of the conjunctiva
In the anatomy of the eye, the conjunctiva (: conjunctivae) is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with gobl ...
, the thin, clear layer that covers the white surface of the eye and the inner eyelid. It makes the eye appear pink or reddish. Pain, burning, scratchiness, or itchiness may occur. The affected eye may have increased tears or be "stuck shut" in the morning. Swelling of the sclera
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye or, in older literature, as the tunica albuginea oculi, is the opaque, fibrous, protective outer layer of the eye containing mainly collagen and some crucial elastic fiber.
In the development of t ...
may also occur. Itching is more common in cases due to allergies. Conjunctivitis can affect one or both eyes.
The most common infectious causes in adults are viral, whereas in children bacterial causes predominate. The viral infection may occur along with other symptoms of a common cold
The common cold, or the cold, is a virus, viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the Respiratory epithelium, respiratory mucosa of the human nose, nose, throat, Paranasal sinuses, sinuses, and larynx. ...
. Both viral and bacterial cases are easily spread between people. Allergies to pollen or animal hair are also a common cause. Diagnosis is often based on signs and symptoms. Occasionally, a sample of the discharge is sent for culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
.
Prevention is partly by handwashing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap or handwash and water to remove viruses, bacteria, microorganisms, dirt, grease, and other harmful or unwanted substances stuck to the han ...
. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. In the majority of viral cases, there is no specific treatment. Most cases due to a bacterial infection also resolve without treatment; however, antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s can shorten the illness. People who wear contact lenses
Contact lenses, or simply contacts, are thin lens (optics), lenses placed directly on the surface of the Human eye, eyes. Contact lenses are ocular prosthetic devices used by over 150 million people worldwide, and they can be worn to correct ...
and those whose infection is caused by gonorrhea
Gonorrhoea or gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum.
Gonorrhea is spread through sexual c ...
or chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear, they may occur only several w ...
should be treated. Allergic cases can be treated with antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides ...
s or mast cell inhibitor drops.
About 3 to 6 million people get acute conjunctivitis each year in the United States. Typically, people get better in one or two weeks. If visual loss, significant pain, sensitivity to light or signs of herpes occur, or if symptoms do not improve after a week, further diagnosis and treatment may be required. Conjunctivitis in a newborn, known as neonatal conjunctivitis, may also require specific treatment.
Signs and symptoms
 Red eye, swelling of the conjunctiva, and watering of the eyes are symptoms common to all forms of conjunctivitis. However, the pupils should be normally reactive, and the visual acuity normal.
Conjunctivitis is identified by inflammation of the conjunctiva, manifested by irritation and redness. Examination using a
Red eye, swelling of the conjunctiva, and watering of the eyes are symptoms common to all forms of conjunctivitis. However, the pupils should be normally reactive, and the visual acuity normal.
Conjunctivitis is identified by inflammation of the conjunctiva, manifested by irritation and redness. Examination using a slit lamp
In ophthalmology and optometry, a slit lamp is an instrument consisting of a high-intensity light source that can be focused to shine a thin sheet of light into the eye. It is used in conjunction with a biomicroscope. The lamp facilitates an ...
(biomicroscope) may improve diagnostic accuracy. Examination of the palpebral conjunctiva, that overlying the inner aspects of the eyelids, is usually more diagnostic than examination of the bulbal conjunctiva, that overlying the sclera.
Viral
 Approximately 80% of cases of conjunctivitis in adults and less than 20% in children are due to viruses, with 65% to 90% of these cases being attributed to adenoviruses.
Viral conjunctivitis is often associated with an infection of the upper respiratory tract, a common cold, or a sore throat. Other associated signs may include pre-auricular lymph node swelling and contact with another person with a red eye. Eye pain may be present if the cornea is also involved. Its symptoms include excessive watering and itching. The discharge in viral conjunctivitis is usually (but not always) watery in nature. The infection usually begins in one eye but may spread easily to the other eye.
Viral conjunctivitis manifests as a fine, diffuse pinkness of the conjunctiva which may be mistaken for
Approximately 80% of cases of conjunctivitis in adults and less than 20% in children are due to viruses, with 65% to 90% of these cases being attributed to adenoviruses.
Viral conjunctivitis is often associated with an infection of the upper respiratory tract, a common cold, or a sore throat. Other associated signs may include pre-auricular lymph node swelling and contact with another person with a red eye. Eye pain may be present if the cornea is also involved. Its symptoms include excessive watering and itching. The discharge in viral conjunctivitis is usually (but not always) watery in nature. The infection usually begins in one eye but may spread easily to the other eye.
Viral conjunctivitis manifests as a fine, diffuse pinkness of the conjunctiva which may be mistaken for iritis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and i ...
, but corroborative signs on microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view subjects too small to be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical mic ...
, particularly numerous lymphoid follicles on the tarsal conjunctiva, and sometimes a punctate keratitis are seen.
Allergic

Allergic conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis (AC) is Allergic Inflammation, inflammation of the conjunctiva (the membrane covering the white part of the eye) due to allergy. Although allergens differ among patients, the most common cause is hay fever. Symptoms consist ...
is inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
of the conjunctiva due to allergy. The specific allergen
An allergen is an otherwise harmless substance that triggers an allergic reaction in sensitive individuals by stimulating an immune response.
In technical terms, an allergen is an antigen that is capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivi ...
s may differ among patients. Symptoms result from the release of histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Discovered in 19 ...
and other active substances by mast cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
s, and consist of redness (mainly due to vasodilation
Vasodilation, also known as vasorelaxation, is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. Blood vessel wa ...
of the peripheral small blood vessels), swelling of the conjunctiva, itching, and increased production of tears.
Bacterial
 Bacteria are responsible for approximately 70% of conjunctivitis in children and less than 20% of cases in adults. Common bacteria responsible for bacterial conjunctivitis are ''
Bacteria are responsible for approximately 70% of conjunctivitis in children and less than 20% of cases in adults. Common bacteria responsible for bacterial conjunctivitis are ''Staphylococcus
''Staphylococcus'', from Ancient Greek σταφυλή (''staphulḗ''), meaning "bunch of grapes", and (''kókkos''), meaning "kernel" or " Kermes", is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillale ...
'' including Staph aureus, ''Streptococcus
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs along a sing ...
'' such as strep pneumoniae, '' Haemophilus'' species and Moraxella catarrhalis. Less commonly, ''Chlamydia'' spp. and Niesseria species ( Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis) may be the cause. Infection with ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
'' may also cause conjunctivitis, particularly in the neonatal
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to Juvenile (orga ...
subtype ophthalmia neonatorum. Bacterial conjunctivitis usually causes a rapid onset of conjunctival redness, swelling of the eyelid, and a sticky discharge. Typically, symptoms develop first in one eye, but may spread to the other eye within 2–5 days. Conjunctivitis due to common pus-producing bacteria causes marked grittiness or irritation and a stringy, opaque, greyish or yellowish discharge that may cause the lids to stick together, especially after sleep. Severe crusting of the infected eye and the surrounding skin may also occur. The gritty or scratchy feeling is sometimes localized enough that patients may insist that they have a foreign body in the eye.
 Bacteria such as ''
Bacteria such as ''Chlamydia trachomatis
''Chlamydia trachomatis'' () is a Gram-negative, Anaerobic organism, anaerobic bacterium responsible for Chlamydia infection, chlamydia and trachoma. ''C. trachomatis'' exists in two forms, an extracellular infectious elementary body (EB) and an ...
'' or ''Moraxella
''Moraxella'' is a genus of gram-negative bacteria in the family Moraxellaceae. It is named after the Swiss ophthalmologist Victor Morax. The organisms are short rods, coccobacilli, or as in the case of '' Moraxella catarrhalis'', diplococci ...
'' spp. can cause a nonexudative but persistent conjunctivitis without much redness. Bacterial conjunctivitis may cause the production of membranes or pseudomembranes that cover the conjunctiva. Pseudomembranes consist of a combination of inflammatory cells and exudates and adhere loosely to the conjunctiva, while true membranes are more tightly adherent and cannot be easily peeled away. Cases of bacterial conjunctivitis that involve the production of membranes or pseudomembranes are associated with '' Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', β-hemolytic streptococci, and ''Corynebacterium diphtheriae
''Corynebacterium diphtheriae'' is a Gram-positive pathogenic bacterium that causes diphtheria. It is also known as the Klebs–Löffler bacillus because it was discovered in 1884 by German bacteriologists Edwin Klebs (1834–1912) and Friedrich ...
''. ''C. diphtheriae'' causes membrane formation in conjunctiva of unimmunized children.
Chemical
Chemical eye injury may result when anacidic
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid.
The first category of acids are the ...
or alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The a ...
ne substance gets in the eye. Alkali burns are typically worse than acidic burns. Mild burns produce conjunctivitis, while more severe burns may cause the cornea
The cornea is the transparency (optics), transparent front part of the eyeball which covers the Iris (anatomy), iris, pupil, and Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and Lens (anatomy), lens, the cornea ...
to turn white. Litmus paper
Litmus is a water-soluble mixture of different dyes extracted from lichens. It is often absorbed onto filter paper to produce one of the oldest forms of pH indicator, used to test materials for acidity. In an acidic medium, blue litmus pape ...
may be used to test for chemical causes. When a chemical cause has been confirmed, the eye or eyes should be flushed until the pH is in the range 6–8. Anaesthetic eye drops can be used to decrease the pain.
Irritant or toxic conjunctivitis is primarily marked by redness. If due to a chemical splash, it is often present in only the lower conjunctival sac. With some chemicals, above all with caustic alkalis such as sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly corrosive base (chemistry), ...
, necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who i ...
of the conjunctiva marked by a deceptively white eye due to vascular closure may occur, followed by sloughing off of the dead epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
. A slit lamp examination is likely to show evidence of anterior uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and i ...
.
Biomarkers
Omics technologies have been used to identify biomarkers that inform on the emergence and progression of conjunctivitis. For example, in chronic inflammatory cicatrizing conjunctivitis, active oxylipins, lysophospholipids,fatty acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an ...
s, and endocannabinoids alterations, from which potential biomarkers linked to inflammatory processes were identified.
Other
 Inclusion conjunctivitis of the newborn is a conjunctivitis that may be caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and may lead to acute, purulent conjunctivitis. However, it is usually self-healing.
Inclusion conjunctivitis of the newborn is a conjunctivitis that may be caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and may lead to acute, purulent conjunctivitis. However, it is usually self-healing.
Causes
Infective conjunctivitis is most commonly caused by a virus. Bacterial infections, allergies, other irritants, and dryness are also common causes. Both bacterial and viral infections are contagious, passing from person to person or spread through contaminated objects or water. Contact with contaminated fingers is a common cause of conjunctivitis. Bacteria may also reach the conjunctiva from the edges of the eyelids and the surrounding skin, from the nasopharynx, from infected eye drops or contact lenses, from the genitals or the bloodstream. Infection by human adenovirus accounts for 65% to 90% of cases of viral conjunctivitis.Viral
Adenoviruses are the most common cause of viral conjunctivitis ( adenoviral keratoconjunctivitis). Herpetic keratoconjunctivitis, caused byherpes simplex
Herpes simplex, often known simply as herpes, is a viral disease, viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Herpes infections are categorized by the area of the body that is infected. The two major types of herpes are Cold sore, ora ...
viruses, can be serious and requires treatment with aciclovir. Acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis is a highly contagious disease caused by one of two enterovirus
''Enterovirus'' is a genus of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses associated with several human and mammalian diseases. Enteroviruses are named by their transmission-route through the intestine ('enteric' meaning intestinal).
Serologic ...
es, enterovirus 70 and coxsackievirus
Coxsackieviruses are a few related enteroviruses that belong to the ''Picornaviridae'' family of viral envelope, nonenveloped, linear, positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses, as well as its genus ''Enterovirus'', which also includes poliovi ...
A24. These were first identified in an outbreak in Ghana in 1969, and have spread worldwide since then, causing several epidemics.
Bacterial
The most common causes of acute bacterial conjunctivitis are ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
'', '' Streptococcus pneumoniae'', and ''Haemophilus influenzae
''Haemophilus influenzae'' (formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or ''Bacillus influenzae'') is a Gram-negative, Motility, non-motile, Coccobacillus, coccobacillary, facultative anaerobic organism, facultatively anaerobic, Capnophile, capnophili ...
''. Though very rare, hyperacute cases are usually caused by '' Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' or '' Neisseria meningitidis''. Chronic cases of bacterial conjunctivitis are those lasting longer than 3 weeks, and are typically caused by ''S. aureus'', '' Moraxella lacunata'', or Gram-negative enteric flora.
Allergic
Conjunctivitis may also be caused by allergens such as pollen, perfumes, cosmetics, smoke, dust mites,Balsam of Peru
Balsam is the resinous exudate (or sap) which forms on certain kinds of trees and shrubs. Balsam (from Latin ''balsamum'' "gum of the balsam tree," ultimately from a Semitic source such as ) owes its name to the biblical Balm of Gilead.
Chem ...
, or eye drops. The most frequent cause of conjunctivitis is allergic conjunctivitis and it affects 15% to 40% of the population. Allergic conjunctivitis accounts for 15% of eye related primary care consultations; most including seasonal exposures in the spring and summer or perpetual conditions.
Other
* Computer vision syndrome * Dry eye syndrome * Reactive arthritis: Conjunctivitis is part of the triad of reactive arthritis, which is thought to be caused byautoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an " autoimmune disease" ...
cross-reactivity following certain bacterial infections. Reactive arthritis is highly associated with HLA-B27. Conjunctivitis is associated with the autoimmune disease relapsing polychondritis.
Diagnosis
 Cultures are not often taken or needed as most cases resolve either with time or typical antibiotics. If bacterial conjunctivitis is suspected, but no response to topical antibiotics is seen, swabs for bacterial culture should be taken and tested. Viral culture may be appropriate in epidemic case clusters.
A
Cultures are not often taken or needed as most cases resolve either with time or typical antibiotics. If bacterial conjunctivitis is suspected, but no response to topical antibiotics is seen, swabs for bacterial culture should be taken and tested. Viral culture may be appropriate in epidemic case clusters.
A patch test
A patch test is a diagnostic method used to determine which specific substances cause allergic inflammation of a patient's skin.
Patch testing helps identify which substances may be causing a delayed-type allergic reaction in a patient and ...
is used to identify the causative allergen in allergic conjunctivitis.
Although conjunctival scrapes for cytology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living an ...
can be useful in detecting chlamydial and fungal
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the tradit ...
infections, allergies, and dysplasia, they are rarely done because of the cost and the general dearth of laboratory staff experienced in handling ocular specimens. Conjunctival incisional biopsy is occasionally done when granulomatous diseases (''e.g.'', sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (; also known as Besnier–Boeck–Schaumann disease) is a disease involving abnormal collections of White blood cell, inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph n ...
) or dysplasia are suspected.
Classification
Conjunctivitis may be classified either by cause or by extent of the inflamed area.Causes
* Allergy * Bacteria * Viruses * Chemicals * Autoimmune Neonatal conjunctivitis is often grouped separately from bacterial conjunctivitis because it is caused by different bacteria than the more common cases of bacterial conjunctivitis.By extent of involvement
Blepharoconjunctivitis is the dual combination of conjunctivitis with blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids). Keratoconjunctivitis is the combination of conjunctivitis and keratitis (cornea
The cornea is the transparency (optics), transparent front part of the eyeball which covers the Iris (anatomy), iris, pupil, and Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and Lens (anatomy), lens, the cornea ...
l inflammation).
Blepharokeratoconjunctivitis is the combination of conjunctivitis with blepharitis and keratitis. It is clinically defined by changes of the lid margin, meibomian gland dysfunction, redness of the eye, conjunctival chemosis and inflammation of the cornea.
Differential diagnosis
Some more serious conditions can present with a red eye, such as infectious keratitis, angle-closure glaucoma, or iritis. These conditions require the urgent attention of an ophthalmologist. Signs of such conditions include decreased vision, significantly increased sensitivity to light, inability to keep the eye open, a pupil that does not respond to light, or a severe headache with nausea. Fluctuating blurring is common, due to tearing and mucoid discharge. Mild photophobia is common. However, if any of these symptoms is prominent, considering other diseases such asglaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to damage of the optic nerve. The optic nerve transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma may cause vision loss if left untreated. It has been called the "silent thief of ...
, uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and ...
, keratitis, and even meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, intense headache, vomiting and neck stiffness and occasion ...
or carotico-cavernous fistula is important.
A more comprehensive differential diagnosis for the red or painful eye includes:
* Corneal abrasion
Corneal abrasion is a scratch to the surface of the cornea of the eye. Symptoms include pain, redness, light sensitivity, and a feeling like a foreign body is in the eye. Most people recover completely within three days.
Most cases are due to m ...
* Subconjunctival hemorrhage
* Pinguecula
* Blepharitis
* Dacryocystitis
* Keratoconjunctivitis sicca (dry eye)
* Keratitis
* Herpes simplex
Herpes simplex, often known simply as herpes, is a viral disease, viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Herpes infections are categorized by the area of the body that is infected. The two major types of herpes are Cold sore, ora ...
* Herpes zoster
* Episcleritis – an inflammatory condition that produces a similar appearance to conjunctivitis, but without discharge or tearing
* Uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and ...
* Acute angle-closure glaucoma
* Endophthalmitis
* Orbital cellulitis
Prevention
The most effective prevention is good hygiene, especially avoiding rubbing the eyes with infected hands. Vaccination against some of the causative pathogens such as ''Haemophilus influenzae'', pneumococcus, and ''Neisseria meningitidis'' is also effective. Povidone-iodine eye solution has been found to prevent neonatal conjunctivitis. It is becoming more commonly used globally because of its low cost.Management
Conjunctivitis resolves in 65% of cases without treatment, within 2–5 days. The prescription of antibiotics is not necessary in most cases.Viral
Viral conjunctivitis usually resolves on its own and does not require any specific treatment. Antihistamines (e.g.,diphenhydramine
Diphenhydramine, sold under the brand name Benadryl among others, is an antihistamine and sedative. Although generally considered sedating, diphenhydramine can cause paradoxical central nervous system stimulation in some individuals, particula ...
) or mast cell stabilizers (e.g., cromolyn
Cromoglicic acid (International Nonproprietary Name, INN)—also referred to as cromolyn (United States Adopted Name, USAN), cromoglycate (former British Approved Name, BAN), or cromoglicate—is traditionally described as a mast cell stabilizer ...
) may be used to help with the symptoms. Povidone-iodine has been suggested as a treatment, but as of 2008, evidence to support it was poor.
Allergic
For allergic conjunctivitis, cool water poured over the face with the head inclined downward constricts capillaries, and artificial tears sometimes relieve discomfort in mild cases. In more severe cases, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications andantihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides ...
s may be prescribed. Persistent allergic conjunctivitis may also require topical steroid drops.
Bacterial
Bacterial conjunctivitis usually resolves without treatment. Topical antibiotics may be needed only if no improvement is observed after 3 days. No serious effects were noted either with or without treatment. Because antibiotics do speed healing in bacterial conjunctivitis, their use may be considered. Antibiotics are also recommended for those who wear contact lenses, areimmunocompromised
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affe ...
, have disease which is thought to be due to chlamydia or gonorrhea, have a fair bit of pain, or have copious discharge. Gonorrheal or chlamydial infections require both oral and topical antibiotics.
The choice of antibiotic varies based on the strain or suspected strain of bacteria causing the infection. Fluoroquinolones, sodium sulfacetamide, or trimethoprim/polymyxin may be used, typically for 7–10 days. Cases of meningococcal conjunctivitis can also be treated with systemic penicillin, as long as the strain is sensitive to penicillin.
When investigated as a treatment, povidone-iodine ophthalmic solution has also been observed to have some effectiveness against bacterial and chlamydial conjunctivitis, with a possible role suggested in locations where topical antibiotics are unavailable or costly.
Chemical
Conjunctivitis due to chemicals is treated viairrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
with Ringer's lactate
Ringer's lactate solution (RL), also known as sodium lactate solution, Lactated Ringer's (LR), and Hartmann's solution, is a mixture of sodium chloride, sodium lactate, potassium chloride, and calcium chloride in water. It is used for repla ...
or saline solution. Chemical injuries, particularly alkali burns, are medical emergencies, as they can lead to severe scarring and intraocular damage. People with chemically induced conjunctivitis should not touch their eyes to avoid spreading the chemical.
Epidemiology
Conjunctivitis is the most common eye disease. Rates of disease is related to the underlying cause which varies by the age as well as the time of year. Acute conjunctivitis is most frequently found in infants, school-age children and the elderly. The most common cause of infectious conjunctivitis is viral conjunctivitis. It is estimated that acute conjunctivitis affects 6 million people annually in the United States. Some seasonal trends have been observed for the occurrence of different forms of conjunctivitis. In the northern hemisphere, the occurrence of bacterial conjunctivitis peaks from December to April, viral conjunctivitis peaks in the summer months and allergic conjunctivitis is more prevalent throughout the spring and summer.History
An adenovirus was first isolated by Rowe et al. in 1953. Two years later, Jawetz et al. published on epidemic keratoconjunctivitis. "Madras eye" is a colloquial term that has been used inIndia
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
for the disease.
Outbreak in Pakistan
In September 2023, a significant outbreak of conjunctivitis occurred inPakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
. The outbreak began in Karachi
Karachi is the capital city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Sindh, Pakistan. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, largest city in Pakistan and 12th List of largest cities, largest in the world, with a popul ...
and quickly spread to Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
, Rawalpindi
Rawalpindi is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, third-largest city in the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is a commercial and industrial hub, being the list of cities in P ...
, and Islamabad
Islamabad (; , ; ) is the capital city of Pakistan. It is the country's tenth-most populous city with a population of over 1.1 million and is federally administered by the Pakistani government as part of the Islamabad Capital Territory. Bu ...
. By the end of the month, over 86,133 cases had been reported in Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
alone. The rapid spread of the disease led to the temporary closure of schools in the region. This event marked one of the largest outbreaks of Pink Eye in the country's recent history.
Society and culture
Conjunctivitis imposes economic and social burdens. The cost of treating bacterial conjunctivitis in the United States was estimated to be $377 million to $857 million per year. Approximately 1% of all primary care office visits in the United States are related to conjunctivitis. Approximately 70% of all people with acute conjunctivitis present to primary care and urgent care.See also
* Conjunctival suffusion * OphthalmiaReferences
External links
* * * {{Authority control Eye diseases Disorders of conjunctiva Inflammations Measles Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate