|
Ferromagnetic Superconductor
Ferromagnetic superconductors are materials that display intrinsic coexistence of ferromagnetism and superconductivity. They include UGe2, URhGe, and UCoGe. Evidence of ferromagnetic superconductivity was also reported for ZrZn2 in 2001, but later reports question these findings. These materials exhibit superconductivity in proximity to a magnetic quantum critical point. The nature of the superconducting state in ferromagnetic superconductors is currently under debate. Early investigations studied the coexistence of conventional ''s''-wave superconductivity with itinerant ferromagnetism. However, the scenario of spin-Triplet state, triplet pairing soon gained the upper hand. A mean-field model for coexistence of spin-triplet pairing and ferromagnetism was developed in 2005. These models consider uniform coexistence of ferromagnetism and superconductivity, i.e. the same electrons which are both ferromagnetic and superconducting at the same time. Another scenario where there is an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferromagnetism
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron) that results in a significant, observable magnetic permeability, and in many cases, a significant magnetic coercivity, allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagnetic materials are noticeably attracted to a magnet, which is a consequence of their substantial magnetic permeability. Magnetic permeability describes the induced magnetization of a material due to the presence of an external magnetic field. For example, this temporary magnetization inside a steel plate accounts for the plate's attraction to a magnet. Whether or not that steel plate then acquires permanent magnetization depends on both the strength of the applied field and on the coercivity of that particular piece of steel (which varies with the steel's chemical composition and any heat treatment it may have undergone). In physics, multiple types of material magnetism have been distinguished. Ferromagnetism (along with the similar effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in superconductors: materials where Electrical resistance and conductance, electrical resistance vanishes and Magnetic field, magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Unlike an ordinary metallic Electrical conductor, conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered, even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic Phase transition, critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source. The superconductivity phenomenon was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Like ferromagnetism and Atomic spectral line, atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete cancellation of the magnetic field in the interior of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triplet State
In quantum mechanics, a triplet state, or spin triplet, is the quantum state of an object such as an electron, atom, or molecule, having a quantum spin ''S'' = 1. It has three allowed values of the spin's projection along a given axis ''m''S = −1, 0, or +1, giving the name "triplet". Spin, in the context of quantum mechanics, is not a mechanical rotation but a more abstract concept that characterizes a particle's intrinsic angular momentum. It is particularly important for systems at atomic length scales, such as individual atoms, protons, or electrons. A triplet state occurs in cases where the spins of two unpaired electrons, each having spin ''s'' = , align to give ''S'' = 1, in contrast to the more common case of two electrons aligning oppositely to give ''S'' = 0, a spin singlet. Most molecules encountered in daily life exist in a singlet state because all of their electrons are paired, but molecular oxygen is an exception. At room temperature, O2 exists in a triplet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
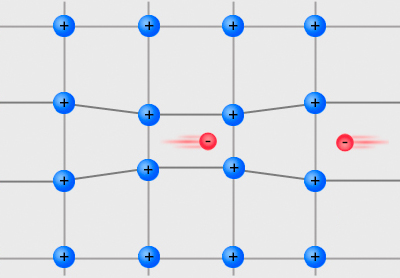
Cooper Pair
In condensed matter physics, a Cooper pair or BCS pair (Bardeen–Cooper–Schrieffer pair) is a pair of electrons (or other fermions) bound together at low temperatures in a certain manner first described in 1956 by American physicist Leon Cooper. Description Cooper showed that an arbitrarily small attraction between electrons in a metal can cause a paired state of electrons to have a lower energy than the Fermi energy, which implies that the pair is bound. In conventional superconductors, this attraction is due to the electron–phonon interaction. The Cooper pair state is responsible for superconductivity, as described in the BCS theory developed by John Bardeen, Leon Cooper, and John Schrieffer for which they shared the 1972 Nobel Prize in Physics. Although Cooper pairing is a quantum effect, the reason for the pairing can be seen from a simplified classical explanation. An electron in a metal normally behaves as a free particle. The electron is repelled from other electrons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bean's Critical State Model
Bean's critical state model, introduced by C. P. Bean in 1962, gives a macroscopic explanation of the irreversible magnetization behavior (hysteresis) of hard Type-II superconductors. Assumptions Hard superconductors often exhibit hysteresis in magnetization measurements. C. P. Bean postulated for the Shubnikov phase an extraordinary shielding process due to the microscopic structure of the materials. He assumed lossless transport with a critical current density ''Jc(B)'' ''(Jc(B→0) = const.'' and ''Jc(B→∞) = 0)''. An external magnetic field is shielded in the Meissner phase (''H < Hc1'') in the same way as in a soft superconductor. In the Shubnikov phase ''(Hc1 < H < Hc2)'', the critical current flows below the surface within a depth necessary to reduce the field in the inside of the superconductor to ''Hc1''. Explanation of the irreversible magnetization To understand the origin of the irreversible magnetiza ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twistronics
Twistronics (from ''twist'' and ''electronics'') is the study of how the angle (the twist) between layers of two-dimensional materials can change their electrical properties. Materials such as bilayer graphene have been shown to have vastly different electronic behavior, ranging from non-conductive to superconductive, that depends sensitively on the angle between the layers. The term was first introduced by the research group of Efthimios Kaxiras at Harvard University in their theoretical treatment of graphene superlattices. Pablo Jarillo-Herrero, Allan H. MacDonald and Rafi Bistritzer were awarded the 2020 Wolf Prize in Physics for their theoretical and experimental work on twisted bilayer graphene. History In 2007, National University of Singapore physicist Antonio H. Castro Neto hypothesized that pressing two misaligned graphene sheets together might yield new electrical properties, and separately proposed that graphene might offer a route to superconductivity, but he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reentrant Superconductivity
In physics, reentrant superconductivity is an effect observed in systems that lie close to the boundary between ferromagnetic and superconducting. By its very nature (normal) superconductivity (condensation of electrons into the BCS ground state) cannot exist together with ferromagnetism (condensation of electrons into the same spin state, all pointing in the same direction). Reentrance is when while changing a continuous parameter, superconductivity is first observed, then destroyed by the ferromagnetic order, and later reappears. An example is the changing of the thickness of the ferromagnetic layer in a bilayer of a superconductor and a ferromagnet. At a certain thickness superconductivity is destroyed by the Andreev reflected electrons in the ferromagnet, but if the thickness increases, this effect disappears again. Another example are materials with a Curie temperature In physics and materials science, the Curie temperature (''T''C), or Curie point, is the temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in superconductors: materials where Electrical resistance and conductance, electrical resistance vanishes and Magnetic field, magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Unlike an ordinary metallic Electrical conductor, conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered, even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic Phase transition, critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source. The superconductivity phenomenon was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Like ferromagnetism and Atomic spectral line, atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete cancellation of the magnetic field in the interior of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |