|
Fernando Po Creole English
Pichinglis, commonly referred to by its speakers as ''Pichi'' and formally known as Fernando Po Creole English (''Fernandino''), is an Atlantic English-lexicon creole language spoken on the island of Bioko, Equatorial Guinea. It is an offshoot of the Krio language of Sierra Leone, and was brought to Bioko by Krios who immigrated to the island during the colonial era in the 19th century. Pichi is the most widely spoken language of the capital Malabo, next to Spanish, and it serves as a primary language to probably the majority of the capital's inhabitants. Pichi is also used as a primary language in a number of villages and towns along the Coast of Bioko – amongst them Sampaca, Fiston, Basupú, Barrio las Palmas and Luba, and is spoken as a lingua franca throughout Bioko. It is also spoken by a sizable community of people originating from Bioko in Bata, the largest town on the continental part of the country. Size of speaker community Pichi is believed to have derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
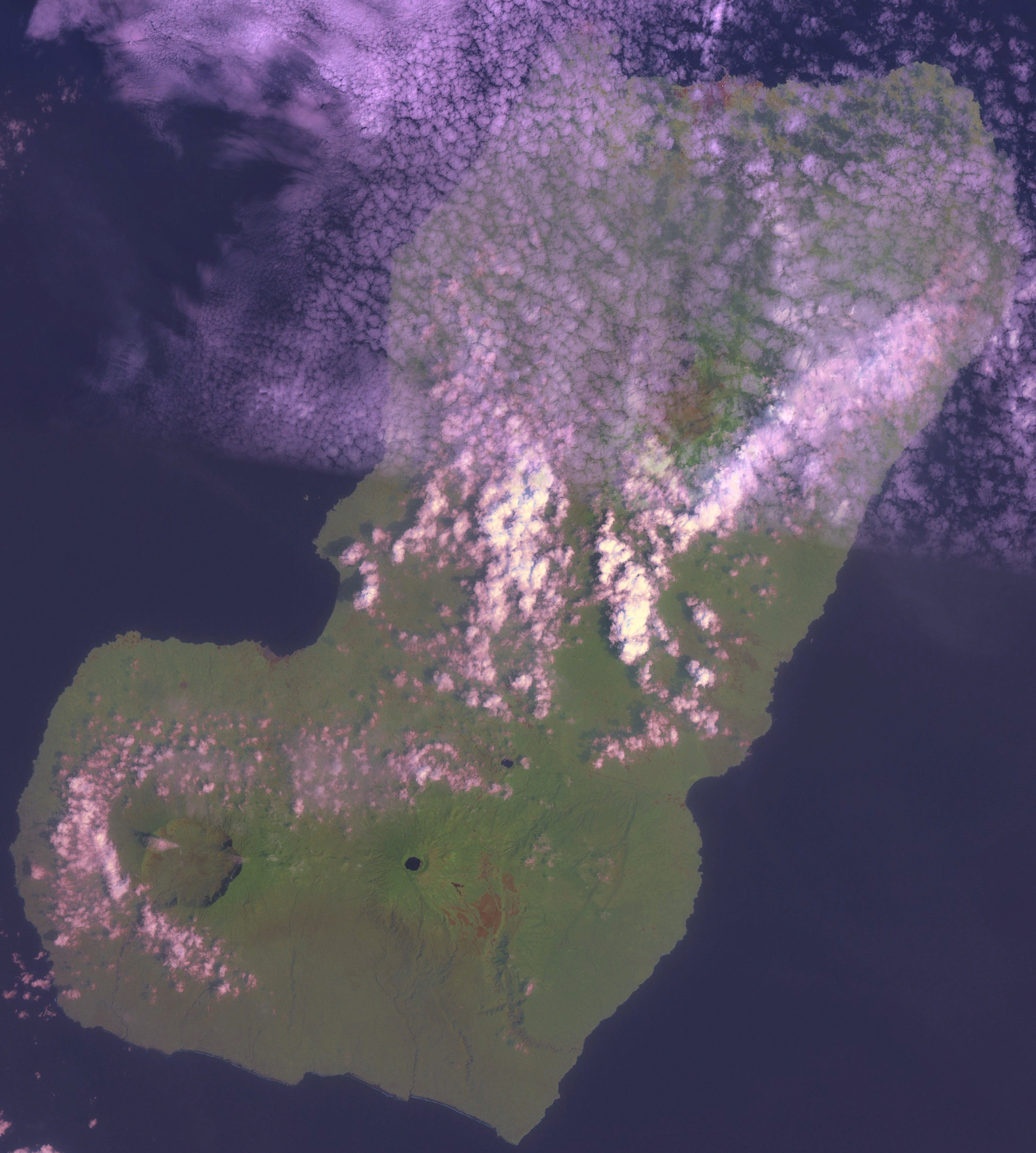
Bioko
Bioko (; ; ; historically known as Fernando Pó, ) is an island of Equatorial Guinea. It is located south of the coast of Cameroon, and northwest of the northernmost part of mainland Equatorial Guinea. Malabo, on the north coast of the island, is the capital city of Equatorial Guinea. Bioko's population was 335,048 at the 2015 census and it covers an area of . The island is part of the Cameroon line of volcanoes and is located off the Cameroon coast, in the Bight of Biafra portion of the Gulf of Guinea. Its geology is volcanic; its highest peak is Pico Basile at . Etymology Bioko's native name is ''Ëtulá a Ëri'' in the Bube language. For nearly 500 years, the island was known as ''Fernando Pó'' (; ), named for Portuguese navigator Fernão do Pó. Between 1973 and 1979 the island was named ''Macías Nguema Biyogo'' after the then-president of Equatorial Guinea. The current name, Bioko, dates from 1979 and is in honour of politician Cristino Seriche Bioko. Geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bata, Equatorial Guinea
Bata () is a port city in the Litoral (Equatorial Guinea), Litoral Provinces of Equatorial Guinea, province of Equatorial Guinea. With a 2005 estimated population of 173,046, it is the most populous city in Equatorial Guinea. It lies on the Atlantic Ocean coast of Río Muni. Bata was formerly capital of Equatorial Guinea and is a transport hub and port, from which ferry, ferries sail to Malabo and Douala, while aircraft can land at Bata Airport. Bata is also known for its Nightlife (activity), nightlife and Market (place), market. History After the anti-Spanish riots of 1969, the European population declined in Bata, and severe economic stagnation affected Bata in the 1970s and early 1980s.BritannicaBata britannica.com, USA, accessed on July 7, 2019 An oil boom of the country boosted the development of the city in the late 1980s and 1990s. On 7 March 2021, the city was struck by 2021 Bata explosions, a series of explosions which resulted in the death of at least 105 people a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantu Language
The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu language, Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀), or Ntu languages are a language family of about 600 languages of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern, East Africa, Eastern and Southeast Africa, Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages. The total number of Bantu languages is estimated at between 440 and 680 distinct languages, depending on the definition of Dialect#Dialect or language, "language" versus "dialect"."Guthrie (1967–71) names some 440 Bantu 'varieties', Grimes (2000) has 501 (minus a few 'extinct' or 'almost extinct'), Bastin ''et al.'' (1999) have 542, Maho (this volume) has some 660, and Mann ''et al.'' (1987) have ''c.'' 680." Derek Nurse, 2006, "Bantu Languages", in the ''Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics'', p. 2:Ethnologue report for Southern Bantoid" lists a total of 535 languages. The count includes 13 Mbam languages, which are not always included under "Narrow Bantu". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
São Tomé Island
São Tomé Island, at , is the largest island of São Tomé and Príncipe and is home in May 2018 to about 193,380 or 96% of the nation's population. The island is divided into six districts of São Tomé and Príncipe, districts. It is located 2 km (1¼ miles) north of the equator. Geography São Tomé Island is about long (north-south) by wide (east-west). It rises to at Pico de São Tomé and includes the capital city, São Tomé, on the northeast coast. It is situated in the Gulf of Guinea, off the western equatorial coast of Africa. The nearest city on mainland Africa is the port city of Port Gentil in Gabon located to the east. The island is surrounded by a number of small islands, including Ilhéu das Rolas, Ilhéu das Cabras and Ilhéu Gabado. Languages The main language is Portuguese language, Portuguese, but there are many speakers of Forro language, Forro and Angolar language, Angolar (Ngola), two Portuguese-based creole languages. The name "" is Portuguese for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angolar
Angolar Creole () is a Portuguese-based creole language of São Tomé and Príncipe, spoken in the southernmost towns of São Tomé Island and sparsely along the coast, especially by Angolar people. It is also called ''n'golá'' by its native speakers. It is a creole language with a majority Portuguese lexicon and a heavy substrate of a dialect of Kimbundu (port. Quimbundo), a Bantu language from inland Angola, where many had come from prior to being enslaved. It is rather different from Sãotomense, the other creole language spoken on the island. Description It is a Portuguese-based creole language different from other Portuguese-based creole languages in Africa. The main difference is the substrate form Kimbundu and Kikongo from Angola. History In the middle of the 16th century, a slave ship from Angola sunk before the southern coast of São Tomé. The surviving people aboard settled the coast as free fishermen. Their language was different from other creole language on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lungwa Santome
Lungwa, also known as Longwa, is a Konyak Naga village located in India and Myanmar (Burma) that straddles both sides in the Mon District of the Indian state of Nagaland and the Naga Self-Administered Zone of the Sagaing Region of Myanmar. The Lungwa Angh's house is situated in the middle of the border of India and Myanmar. One half of the Angh's house falls within Indian territory, whereas the other half lies under Myanmar control. However, the whole village is controlled by the Angh. He has 60 wives and he rules over 60 villages of the Konyaks extending up to Myanmar and Arunachal Pradesh. Transportation The village has a road connecting it to Loji Village in Myanmar's Sagaing Division, that also provides access to the larger Tatmadaw military towns of Lahe and Yengjong in Myanmar. See also * India–Myanmar border References {{DEFAULTSORT:Lungwa India–Myanmar border The India–Myanmar border is the international border between India and Myanmar (former ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annobón
Annobón (; ) is a province of Equatorial Guinea. The province consists of the island of Annobón and its associated islets in the Gulf of Guinea. Annobón is the smallest province of Equatorial Guinea in both area and population. According to the 2015 census, Annobón had 5,323 inhabitants, a small population increase from the 5,008 registered by the 2001 census. The official language is Spanish but most of the inhabitants speak a creole form of Portuguese. The island's main industries are fishing and forestry. Annobón is the only island of the country located in the Southern Hemisphere of the Atlantic Ocean. The provincial capital is San Antonio de Palé on the north side of the island; the other town is Mabana, formerly known as San Pedro. The roadstead is relatively safe, and some passing vessels take advantage of it in order to obtain water and fresh provisions, of which Annobón has offered an abundant supply. However, there is no regular shipping service to the res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubi Language
The Bube language or Bubi, Bohobé, Bube–Benga or Fernandian (Bobe) is a Bantu language spoken predominately by the Bubi, a Bantu people native to, and once the primary inhabitants of Bioko Island in Equatorial Guinea. The language was brought to Bioko from continental Africa more than three thousand years ago when the Bubi began settling on the island. It has around 50,000 speakers, with three variants: North, South and Central-East. It is noted for its tonal character and the divergence of words by gender. The language is also spoken by the Bubi native to Gabon and Cameroon. The Bube language is divided into six different dialects that vary in the northern and southern regions of Bioko Island. For example, in the North, people speak ''Rebola'' and its variations: ''Basile'', ''Banapa'' and ''Basupa''. However, in the North-East, ''Bakake'' is spoken. Bube is also spoken in a small area on the mainland closest to the island, where speakers are shifting to Wumboko. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |