|
Annobón
Annobón (; ) is a province of Equatorial Guinea. The province consists of the island of Annobón and its associated islets in the Gulf of Guinea. Annobón is the smallest province of Equatorial Guinea in both area and population. According to the 2015 census, Annobón had 5,323 inhabitants, a small population increase from the 5,008 registered by the 2001 census. The official language is Spanish but most of the inhabitants speak a creole form of Portuguese. The island's main industries are fishing and forestry. Annobón is the only island of the country located in the Southern Hemisphere of the Atlantic Ocean. The provincial capital is San Antonio de Palé on the north side of the island; the other town is Mabana, formerly known as San Pedro. The roadstead is relatively safe, and some passing vessels take advantage of it in order to obtain water and fresh provisions, of which Annobón has offered an abundant supply. However, there is no regular shipping service to the res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
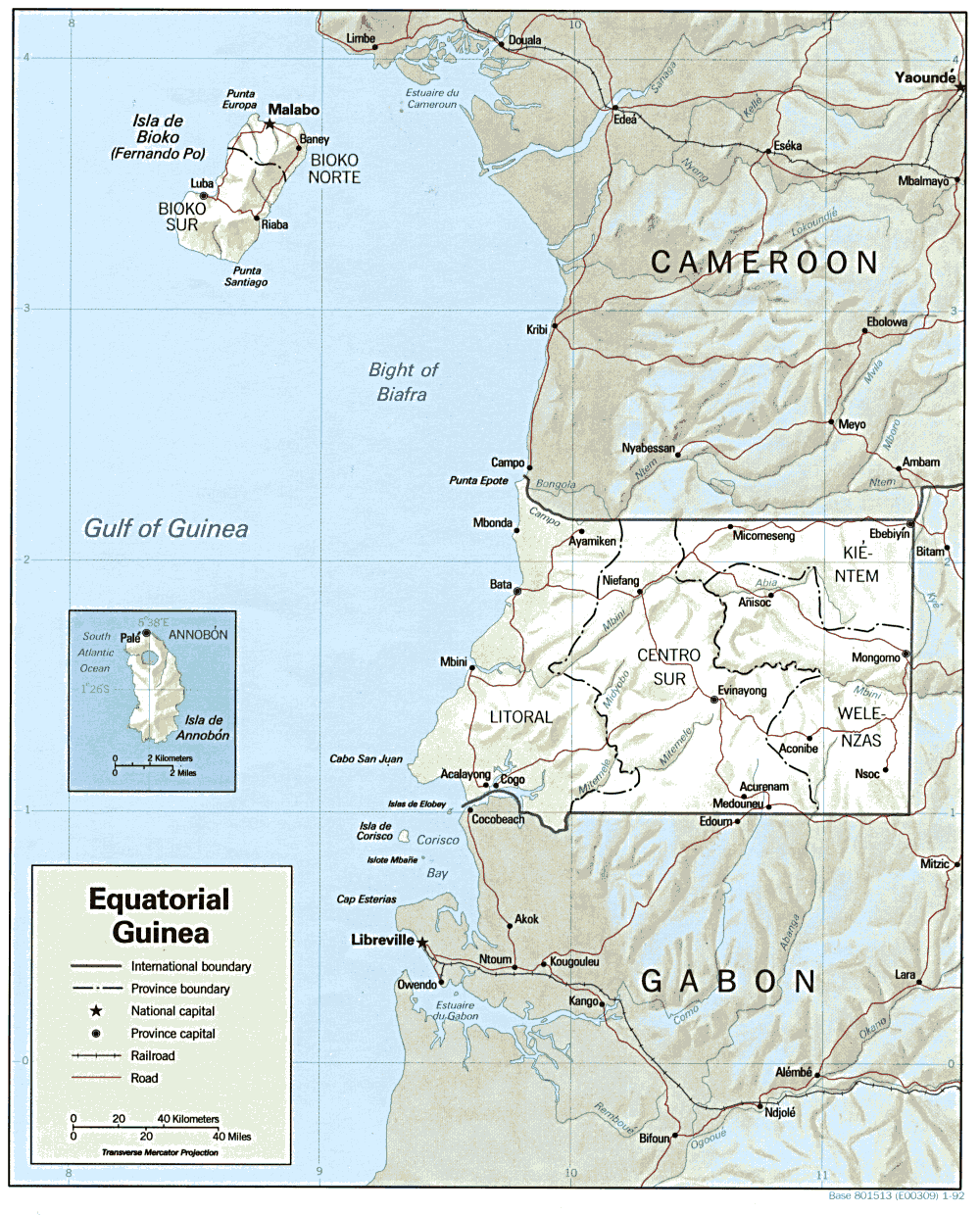
Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea, officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea, is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. It has an area of . Formerly the colony of Spanish Guinea, its post-independence name refers to its location both near the Equator and in the Guinea (region), African region of Guinea. , the country had a population of 1,795,834, over 85% of whom are members of the Fang people, the country's dominant ethnic group. The Bubi people, indigenous to Bioko, are the second largest group at approximately 6.5% of the population. Equatorial Guinea consists of two parts. The mainland region, Río Muni, is bordered by Cameroon to the north and Gabon to the south and east. It has the majority of the population and is the location of Bata, Equatorial Guinea, Bata, Equatorial Guinea's largest city, and Ciudad de la Paz, the country's planned future capital. Río Muni's small offshore islands include Corisco, Elobey Grande, and Elobey Chico. The Islands of Equatorial Guinea, ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Antonio De Palé
San Antonio de Palé, formerly known as St Antony, São Antonio de Praia and Palea, is the capital of Annobón (an island in Equatorial Guinea that was once part of the Spanish Empire in Africa). The town has 600 inhabitants, the majority of whom speak the Annobonese Creole. It is located in the extreme north of the island, which is the driest and flattest area. It is home to Annobón Airport, a dock, a hospital, a school, a lighthouse, a radio station, and a Catholic mission. History Founded by Portuguese explorers, the town served as a center of evangelization for runaway slaves from Angola Angola, officially the Republic of Angola, is a country on the west-Central Africa, central coast of Southern Africa. It is the second-largest Portuguese-speaking world, Portuguese-speaking (Lusophone) country in both total area and List of c .... Capuchin and Carmelite missionaries first made the town their base in 1580. It passed under Spanish sovereignty in 1778, along with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annobonese Creole
Annobonese Creole is a Portuguese creole known to its speakers as or (, "Annobón speech"). It is spoken on the Annobón and Bioko Islands off the coast of Equatorial Guinea, mostly by people of mixed African, Portuguese and Spanish descent. It is called or in Spanish. The attitude in Equatorial Guinea towards this language is positive. It is taught in special courses in the capital city of Malabo. History Annobonese originated sometime during the 16th century as an offshoot of Forro Creole, while this stage of Annobonese is unattested remaining linguistic traces show this. The creole language was spoken originally by the descendants of intermixing between Portuguese men and African women slaves imported from other places, especially from São Tomé and Angola, and therefore descends from Portuguese and Forro, the creole of the freed slaves of São Tomé. The government of Equatorial Guinea financed an Instituto Internacional da Língua Portuguesa (IILP) soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quioveo
Quioveo is the extinct volcanic peak at the centre of the island of Annobón, Equatorial Guinea. It rises to a height of 598 metres. accessed May 24, 2011. The island of Annobón is part of the Cameroon line of volcanoes, together with the islands of , , Bioko
Bioko (; ; ; historically known as Fernando Pó ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francisco Macías Nguema
Francisco Macías Nguema (born Mez-m Ngueme, later Africanisation, Africanised to Masie Nguema Biyogo Ñegue Ndong; 1 January 1924 – 29 September 1979), often referred to as Macías Nguema or simply Macías, was an Equatoguinean politician who served as the first president of Equatorial Guinea, president of Equatorial Guinea from the country's gaining of independence in 1968, until his overthrow in 1979. He is widely remembered as one of the most brutal dictators in history. As president, he exhibited bizarre and erratic behavior, to the point that many of his contemporaries believed he was insane. A member of the Fang people, Macías Nguema held numerous official positions under Spanish Guinea, Spanish colonial rule before 1968 Spanish Guinean general election, being elected the first president of the soon-to-be independent country in 1968. Early in his rule, he consolidated power by establishing an extreme cult of personality and a one-party state ruled by his United Nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea is divided into two regions and eight provinces (, , ). The newest province is Djibloho, created in 2017 with its headquarters at Ciudad de la Paz, the country's future capital. Regions # Insular Region (capital at Malabo) # Continental Region (capital at Bata) Provinces Annobón, Bioko Norte and Bioko Sur are in the Insular Region; the other five provinces are in the Continental Region. Subdivisions The provinces are further divided into 19 districts and 37 municipalities A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate. The term ''municipality' .... See also * * * * References {{Articles on first-level administrative divisions of African countries Subdivisions of Equatorial Guinea Equatorial Guinea 1 Equatorial Guinea geography-related lists Equatorial Guinea, Pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of El Pardo (1778)
The Treaty of El Pardo signed on 11 March 1778 sought to end conflict between Spain and Portugal in the Río de la Plata region, along the modern boundary between Argentina and Uruguay. It confirmed Spanish ownership of Colonia del Sacramento, now in Uruguay, while Portugal ceded possession of strategically important territories in Africa, now the modern state of Equatorial Guinea. In return, Spain withdrew from lands to the north, most of which are in the southern Brazilian state of Rio Grande do Sul. Background For nearly 300 years, differing interpretations of the Treaty of Tordesillas led to border disputes between Spain and Portugal over the Río de la Plata region. Portuguese encroachments in this area allowed their merchants to evade commercial restrictions imposed by Spain on the importation of goods into Spanish South America. This culminated in 1690 when Portugal established the trading post of Colonia del Sacramento, just across the river from Buenos Aires whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioko
Bioko (; ; ; historically known as Fernando Pó, ) is an island of Equatorial Guinea. It is located south of the coast of Cameroon, and northwest of the northernmost part of mainland Equatorial Guinea. Malabo, on the north coast of the island, is the capital city of Equatorial Guinea. Bioko's population was 335,048 at the 2015 census and it covers an area of . The island is part of the Cameroon line of volcanoes and is located off the Cameroon coast, in the Bight of Biafra portion of the Gulf of Guinea. Its geology is volcanic; its highest peak is Pico Basile at . Etymology Bioko's native name is ''Ëtulá a Ëri'' in the Bube language. For nearly 500 years, the island was known as ''Fernando Pó'' (; ), named for Portuguese navigator Fernão do Pó. Between 1973 and 1979 the island was named ''Macías Nguema Biyogo'' after the then-president of Equatorial Guinea. The current name, Bioko, dates from 1979 and is in honour of politician Cristino Seriche Bioko. Geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea (French language, French: ''Golfe de Guinée''; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Golfo de Guinea''; Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''Golfo da Guiné'') is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. Null Island, defined as the intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian (zero degrees latitude and longitude), is in the gulf. Among the many rivers that drain into the Gulf of Guinea are the Niger River, Niger and the Volta River, Volta. The coastline on the gulf includes the Bight of Benin and the Bight of Bonny. Name "Guinea" is thought to have originated from a local name for an area in the region, although the specifics are disputed. Bovill (1995) gives a thorough description: The name "Guinea (region), Guinea" was also previously applied to the south coast of West Africa (north of the Gulf of Guinea), which became known as "Upper Guinea", and to the west coast of Southern Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea is divided into two regions and eight provinces (, , ). The newest province is Djibloho, created in 2017 with its headquarters at Ciudad de la Paz, the country's future capital. Regions # Insular Region (capital at Malabo) # Continental Region (capital at Bata) Provinces Annobón, Bioko Norte and Bioko Sur are in the Insular Region; the other five provinces are in the Continental Region. Subdivisions The provinces are further divided into 19 districts and 37 municipalities A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate. The term ''municipality' .... See also * * * * References {{Articles on first-level administrative divisions of African countries Subdivisions of Equatorial Guinea Equatorial Guinea 1 Equatorial Guinea geography-related lists Equatorial Guinea, Pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Islands Of Africa
This is a list of islands of Africa. Sovereign island nations Indian Ocean Union of the Comoros * Grande Comore *Anjouan * Mohéli Republic of Madagascar * Île Sainte-Marie (also known as Nosy Boraha) * Nosy Be Republic of Mauritius * Mauritius island * Rodrigues island * Agaléga Islands * Saint Brandon Republic of Seychelles *Inner Islands: ** La Digue ** Félicité **Marianne ** Grande Soeur ** Petite Soeur ** Ile aux Cocos ** Ile la Fouche ** Silhouette Island ** Ile du Nord ** Les Mamelles ** Ile aux Récifs ** Frégate ** L'Ilot ** Ile aux Vaches ** Vache Marine ** Chauve Souris ** Roche Canon ** Les Trois Dames ** Cocos Dans Trou ** Bird Island **Ile Denis (Denis Island) ** Mahé **Praslin ** Sainte Anne ** Ile Ronde ** Moyenne Island ** Therese ** Roche Tortue ** Ile Du Suete ** Conception ** Ile Hodoul ** Coco Dans Milieu ** Ile Longue ** Ile Malice ** L'Islette ** Roche Bouquet ** Baleise Island ** Beacon Island ** Roche Grande Maman **Cousin ** Cousine ** Z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Guinea
Spanish Guinea () was a set of Insular Region (Equatorial Guinea), insular and Río Muni, continental territories controlled by Spain from 1778 in the Gulf of Guinea and on the Bight of Bonny, in Central Africa. It gained independence in 1968 as Equatorial Guinea. Name From the resumption of Spanish sovereignty in 1843 to 1904 the colony went by various names in official documents. The name of the colony in an 1868 Royal decree that outlined the administration of the colony was the Spanish Possessions on the Gulf of Guinea. The other name commonly used was the name Colony of Fernando Poo and Dependencies. In a royal decree in 1904 the official name became Spanish Territories on the Gulf of Guinea as many of the administrative inefficiencies in the previous decrees were rectified. This was reaffirmed in a 1935 decree. In 1956 the colony became the Province of the Gulf of Guinea, a province of Spain. History 18th–19th centuries The Spanish colony in the Guinea (region), Gui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |