|
Felypressin
Felypressin is a non-catecholamine vasoconstrictor that is chemically related to vasopressin, the posterior pituitary hormone. It is added to some local anaesthetics such as prilocaine in a concentration of 0.03 IU/ml. Felypressin is a Vasopressin 1 agonist, and will thus have effects at all Arginine vasopressin receptor 1As. It will, however, have its main physiological effects on vascular SMC's due to the form in which it is administered. V1 receptors are found in various sites around the body. The major points include the CNS, Liver, Anterior Pituitary, Muscle (both vascular and non-vascular smooth muscle), and Platelets (CLAMP). Another example of a V1 agonist is terlipressin - which is used in oesophageal varices Esophageal varices are extremely dilated sub-mucosal veins in the lower third of the esophagus. They are most often a consequence of portal hypertension, commonly due to cirrhosis. People with esophageal varices have a strong tendency to develo .... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
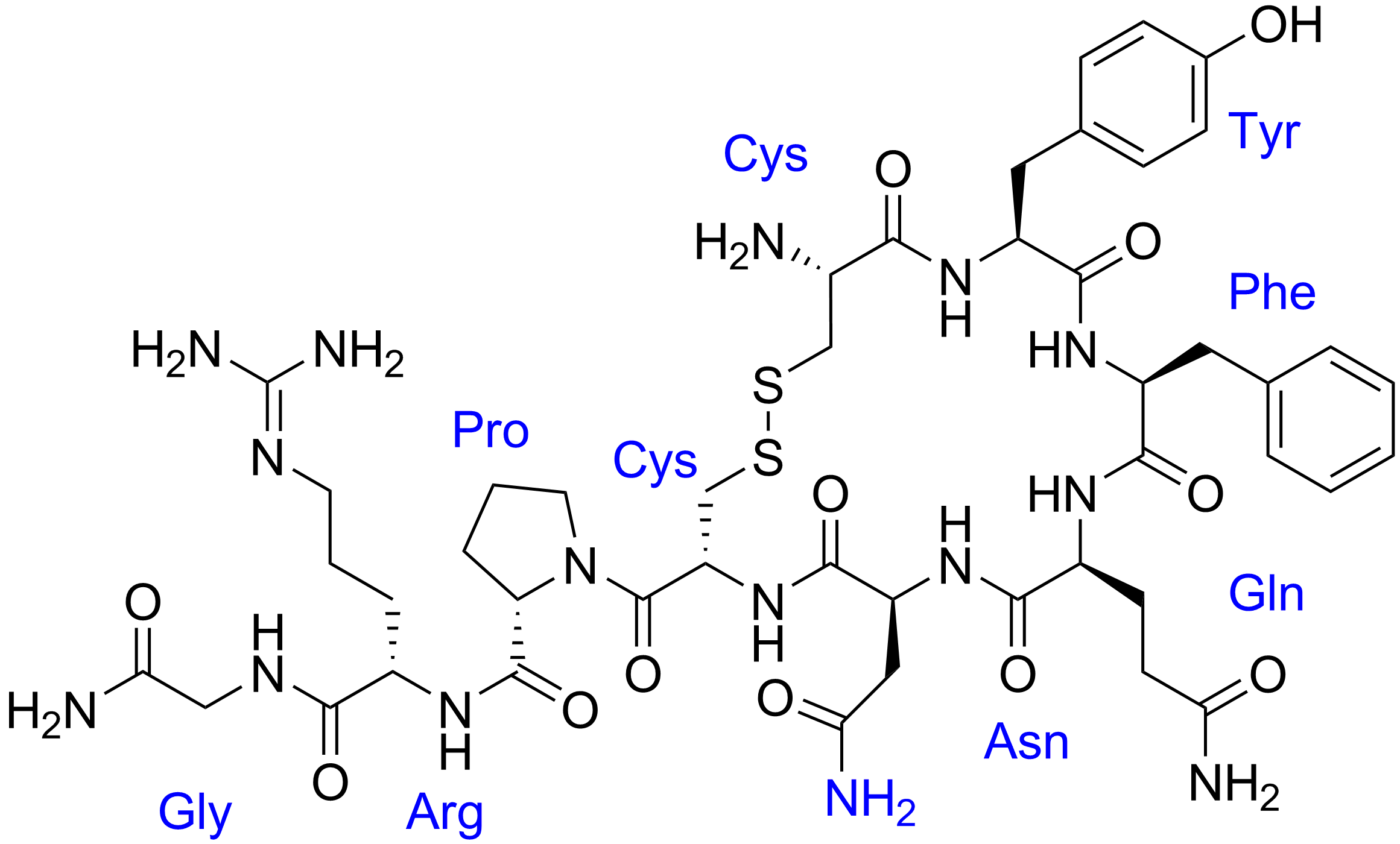
Vasopressin
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travels down the axon terminating in the posterior pituitary, and is released from vesicles into the circulation in response to extracellular fluid hypertonicity ( hyperosmolality). AVP has two primary functions. First, it increases the amount of solute-free water reabsorbed back into the circulation from the filtrate in the kidney tubules of the nephrons. Second, AVP constricts arterioles, which increases peripheral vascular resistance and raises arterial blood pressure. A third function is possible. Some AVP may be released directly into the brain from the hypothalamus, and may play an important role in social behavior, sexual motivation and pair bonding, and maternal responses to stress. Vasopressin induces differentiation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catecholamine
A catecholamine (; abbreviated CA) is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol ( benzene with two hydroxyl side groups next to each other) and a side-chain amine. Catechol can be either a free molecule or a substituent of a larger molecule, where it represents a 1,2-dihydroxybenzene group. Catecholamines are derived from the amino acid tyrosine, which is derived from dietary sources as well as synthesis from phenylalanine. Catecholamines are water-soluble and are 50% bound to plasma proteins in circulation. Included among catecholamines are epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and dopamine. Release of the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine from the adrenal medulla of the adrenal glands is part of the fight-or-flight response. Tyrosine is created from phenylalanine by hydroxylation by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase. Tyrosine is also ingested directly from dietary protein. Catecholamine-secreting cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasoconstrictor
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, in particular the large arteries and small arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels. The process is particularly important in controlling hemorrhage and reducing acute blood loss. When blood vessels constrict, the flow of blood is restricted or decreased, thus retaining body heat or increasing vascular resistance. This makes the skin turn paler because less blood reaches the surface, reducing the radiation of heat. On a larger level, vasoconstriction is one mechanism by which the body regulates and maintains mean arterial pressure. Medications causing vasoconstriction, also known as vasoconstrictors, are one type of medicine used to raise blood pressure. Generalized vasoconstriction usually results in an increase in systemic blood pressure, but it may also occur in specific tissues, causing a localized reduction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
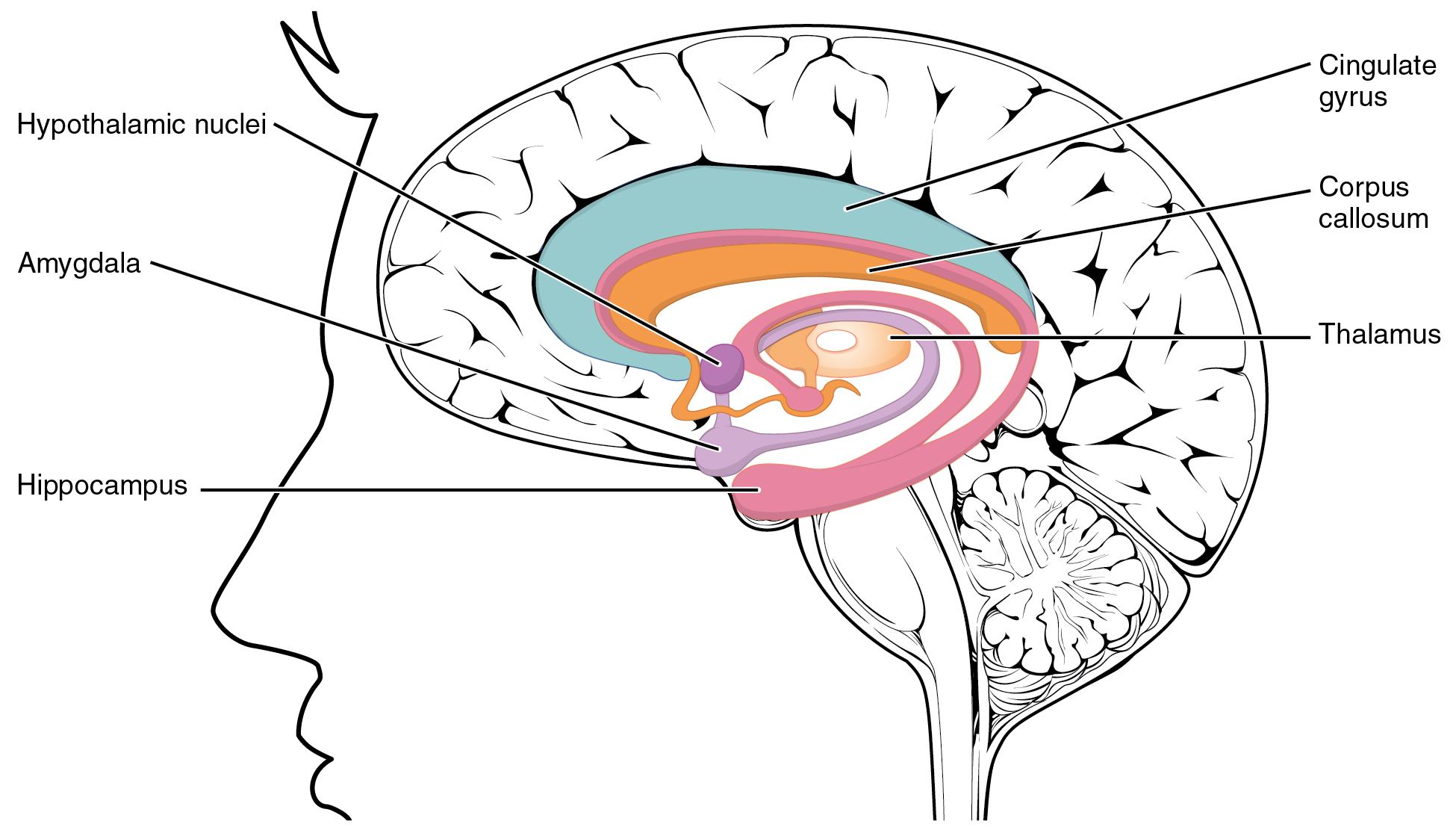
Pituitary
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypophysis rests upon the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone in the center of the middle cranial fossa and is surrounded by a small bony cavity ( sella turcica) covered by a dural fold ( diaphragma sellae). The anterior pituitary (or adenohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that regulates several physiological processes including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. The intermediate lobe synthesizes and secretes melanocyte-stimulating hormone. The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that is functionally connected to the hypothalamus by the median eminence via a small tube called the pituitary stalk (also called the infundibular stalk or the infundibulum). Hormones secreted from the pituitary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the correct development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organs and tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating a variety of physiological processes and behavioral activities such as diges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Anaesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of pain sensation. In the context of surgery, a local anesthetic creates an absence of pain in a specific location of the body without a loss of consciousness, as opposed to a general anesthetic. When it is used on specific nerve pathways ( local anesthetic nerve block), paralysis (loss of muscle power) also can be achieved. Examples Short Duration & Low Potency Procaine Chloroprocaine Medium Duration & Potency Lidocaine Prilocaine High Duration & Potency Tetracaine Bupivacaine Cinchocaine Ropivacaine Clinical LAs belong to one of two classes: aminoamide and aminoester local anesthetics. Synthetic LAs are structurally related to cocaine. They differ from cocaine mainly in that they have a very low abuse potential and do not produce hypertension or (with few exceptions) vasoconstriction. They are used in various techniques of local anesthesia such as: * Topical anesthesia (surface) * Topical a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prilocaine
Prilocaine () is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type first prepared by Claes Tegner and Nils Löfgren. In its injectable form (trade name Citanest), it is often used in dentistry. It is also often combined with lidocaine as a topical preparation for dermal anesthesia ( lidocaine/prilocaine or EMLA), for treatment of conditions like paresthesia. As it has low cardiac toxicity, it is commonly used for intravenous regional anaesthesia (IVRA). Contraindications In some patients, ortho-toluidine, a metabolite of prilocaine, may cause methemoglobinemia, which may be treated with methylene blue. Prilocaine may also be contraindicated in people with sickle cell anemia, anemia, or symptomatic hypoxia. Combinations It is given as a combination with the vasoconstrictor epinephrine under the trade name ''Citanest Forte''. It is used as a eutectic mixture with lidocaine, 50% w/w, as lidocaine/prilocaine. The mixture is an oil with a melting point of . A 5% emulsion pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arginine Vasopressin Receptor 1A
Vasopressin receptor 1A (V1AR), or arginine vasopressin receptor 1A (officially called AVPR1A) is one of the three major receptor types for vasopressin ( AVPR1B and AVPR2 being the others), and is present throughout the brain, as well as in the periphery in the liver, kidney, and vasculature. V1AR is also known as: * V1a vasopressin receptor * antidiuretic hormone receptor 1A * SCCL vasopressin subtype 1a receptor * V1-vascular vasopressin receptor AVPR1A * vascular/hepatic-type arginine vasopressin receptor Structure and function Human AVPR1A cDNA is 1472 bp long and encodes a 418 amino-acid long polypeptide which shares 72%, 36%, 37%, and 45% sequence identity with rat Avpr1a, human AVPR2, rat Avpr2, and human oxytocin receptor (OXTR), respectively. AVPR1A is a G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) with 7 transmembrane domains that couples to Gaq/11 GTP binding proteins, which along with Gbl, activate phospholipase C activity. Clinically, the V1A receptor is related to vasoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terlipressin
Terlipressin, sold under the brand name Terlivaz among others, is an analogue of vasopressin used as a vasoactive drug in the management of low blood pressure. It has been found to be effective when norepinephrine does not help. Terlipressin is a vasopressin receptor agonist. Terlipressin was approved for medical use in the United States in 2022. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication. Medical uses Terlipressin is indicated to improve kidney function in adults with hepatorenal syndrome with rapid reduction in kidney function. Indications for use include norepinephrine-resistant septic shock and hepatorenal syndrome. In addition, it is used to treat bleeding esophageal varices Esophageal varices are extremely dilated sub-mucosal veins in the lower third of the esophagus. They are most often a consequence of portal hypertension, commonly due to cirrhosis. People with esophageal varices have a strong tendency to develop .. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oesophageal Varices
Esophageal varices are extremely dilated sub-mucosal veins in the lower third of the esophagus. They are most often a consequence of portal hypertension, commonly due to cirrhosis. People with esophageal varices have a strong tendency to develop severe bleeding which left untreated can be fatal. Esophageal varices are typically diagnosed through an esophagogastroduodenoscopy. Pathogenesis The upper two thirds of the esophagus are drained via the esophageal veins, which carry deoxygenated blood from the esophagus to the azygos vein, which in turn drains directly into the superior vena cava. These veins have no part in the development of esophageal varices. The lower one third of the esophagus is drained into the superficial veins lining the esophageal mucosa, which drain into the left gastric vein, which in turn drains directly into the portal vein. These superficial veins (normally only approximately 1 mm in diameter) become distended up to 1–2 cm in diamet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasoconstrictors
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, in particular the large arteries and small arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels. The process is particularly important in controlling hemorrhage and reducing acute blood loss. When blood vessels constrict, the flow of blood is restricted or decreased, thus retaining body heat or increasing vascular resistance. This makes the skin turn paler because less blood reaches the surface, reducing the radiation of heat. On a larger level, vasoconstriction is one mechanism by which the body regulates and maintains mean arterial pressure. Medications causing vasoconstriction, also known as vasoconstrictors, are one type of medicine used to raise blood pressure. Generalized vasoconstriction usually results in an increase in systemic blood pressure, but it may also occur in specific tissues, causing a localized reduction in bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptides
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Hence, peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. A polypeptide that contains more than approximately 50 amino acids is known as a protein. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, or to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic pept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |