Pituitary on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 The height of the pituitary gland ranges from 5.3 to 7.0 mm. The volume of the pituitary gland ranges from 200 to 440 mm3.
The height of the pituitary gland ranges from 5.3 to 7.0 mm. The volume of the pituitary gland ranges from 200 to 440 mm3.
 Some of the diseases involving the pituitary gland are:
* Central diabetes insipidus caused by a deficiency of
Some of the diseases involving the pituitary gland are:
* Central diabetes insipidus caused by a deficiency of
File:Pituitary gland.png, Location of the pituitary gland in the human brain
File:Illu pituitary pineal glands.jpg, Pituitary and pineal glands
File:Gray516.png, The arteries of the base of the brain.
File:Gray715.png, Mesal aspect of a brain sectioned in the median sagittal plane.
File:Hypophyse.png, Pituitary
File:Hypophyseal gland.jpg, Pituitary gland
File:Slide4MIR.JPG, Cerebrum.Inferior view.Deep dissection.
The Pituitary Gland, from the UMM Endocrinology Health Guide
The Pituitary Foundation
The Pituitary Network Association -- pituitary.org
{{Authority control Endocrine system Human head and neck Neuroendocrinology Human female endocrine system Articles containing video clips
 In
In vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its ...
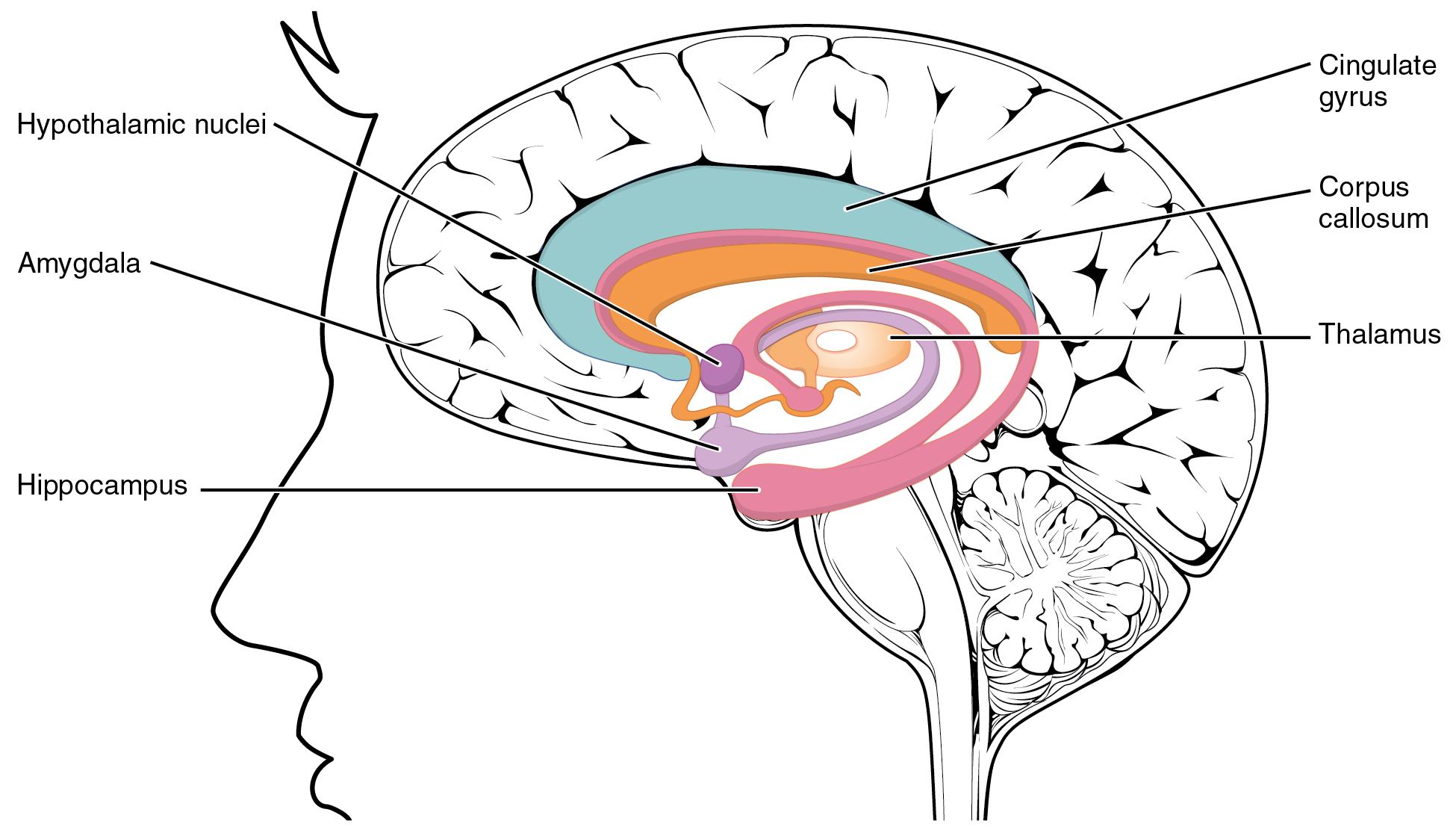
, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head ( cephalization), usually near organs for special ...
. The hypophysis rests upon the hypophyseal fossa
The sella turcica ( Latin for 'Turkish saddle') is a saddle-shaped depression in the body of the sphenoid bone of the human skull and of the skulls of other hominids including chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans. It serves as a cephalome ...
of the sphenoid bone in the center of the middle cranial fossa and is surrounded by a small bony cavity ( sella turcica) covered by a dural fold ( diaphragma sellae).
The anterior pituitary (or adenohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that regulates several physiological processes including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. The intermediate lobe
Pars intermedia is the boundary between the anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary. It contains colloid-filled cysts and two types of cells - basophils and chromophobes. The cysts are the remainder of Rathke’s pouch.
In human fetal ...
synthesizes and secretes melanocyte-stimulating hormone. The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that is functionally connected to the hypothalamus by the median eminence via a small tube called the pituitary stalk (also called the infundibular stalk or the infundibulum).
Hormones secreted from the pituitary gland help to control growth, blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressur ...
, energy management, all functions of the sex organs, thyroid glands and metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run c ...
as well as some aspects of pregnancy, childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births glo ...
, breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that bre ...
, water/salt concentration at the kidneys, temperature regulation and pain relief.
Structure
The pituitary gland, in humans, is oval in shape and is a pea-sized gland that sits in a protective bony enclosure called the sella turcica. It is composed of two lobes: anterior and posterior, with the intermediate lobe that joins the two regions. In many animals, these three lobes are distinct. The intermediate is avascular and almost absent in human beings. The intermediate lobe is present in many animal species, in particular in rodents, mice and rats, that have been used extensively to study pituitary development and function. In all animals, the fleshy, glandular anterior pituitary is distinct from the neural composition of the posterior pituitary, which is an extension of the hypothalamus. The height of the pituitary gland ranges from 5.3 to 7.0 mm. The volume of the pituitary gland ranges from 200 to 440 mm3.
The height of the pituitary gland ranges from 5.3 to 7.0 mm. The volume of the pituitary gland ranges from 200 to 440 mm3.
Anterior
The anterior pituitary arises from an invagination of the oral ectoderm ( Rathke's pouch). This contrasts with the posterior pituitary, which originates from neuroectoderm. Endocrine cells of the anterior pituitary are controlled by regulatory hormones released by parvocellular neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamic capillaries leading to infundibular blood vessels, which in turn lead to a second capillary bed in the anterior pituitary. This vascular relationship constitutes the hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system. Diffusing out of the second capillary bed, the hypothalamicreleasing hormone
Releasing hormones and inhibiting hormones are hormones whose main purpose is to control the release of other hormones, either by stimulating or inhibiting their release. They are also called liberins () and statins () (respectively), or releasing ...
s then bind to anterior pituitary endocrine cells, upregulating or downregulating their release of hormones.
The anterior lobe of the pituitary can be divided into the pars tuberalis (pars infundibularis) and pars distalis
A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is the glandular, anterior lobe that together with the posterior lobe (posterior pituitary, or the neurohypophysis) makes up the pit ...
(pars glandularis) that constitutes ~80% of the gland. The pars intermedia
Pars intermedia is the boundary between the anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary. It contains colloid-filled cysts and two types of cells - basophils and chromophobes. The cysts are the remainder of Rathke’s pouch.
In human fetal life ...
(the intermediate lobe) lies between the pars distalis and the pars tuberalis, and is rudimentary in the human, although in other species it is more developed. It develops from a depression in the dorsal wall of the pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its ...
(stomal part) known as Rathke's pouch.
The anterior pituitary contains several different types of cells that synthesize and secrete hormones. Usually there is one type of cell for each major hormone formed in anterior pituitary. With special stains attached to high-affinity antibodies that bind with distinctive hormone, at least 5 types of cells can be differentiated.
Posterior
The posterior lobe develops as an extension of the hypothalamus, from the floor of the third ventricle. The posterior pituitary hormones are synthesized by cell bodies in the hypothalamus. The magnocellular neurosecretory cells, of the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei located in the hypothalamus, project axons down the infundibulum to terminals in the posterior pituitary. This simple arrangement differs sharply from that of the adjacent anterior pituitary, which does not develop from the hypothalamus. The release of pituitary hormones by both the anterior and posterior lobes is under the control of the hypothalamus, albeit in different ways.Functions

Anterior
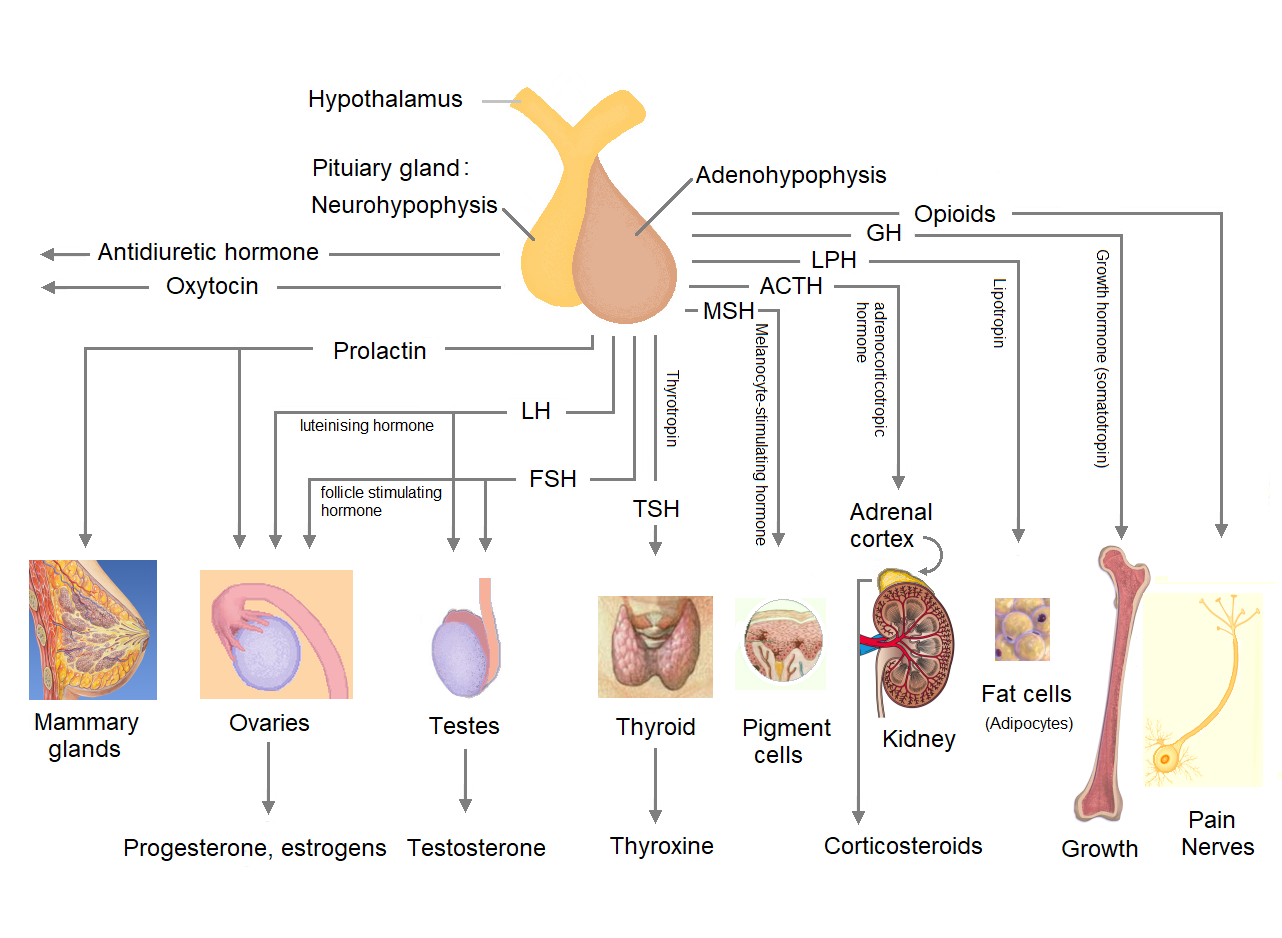
The anterior pituitary synthesizes and secretes hormones. All releasing hormones (-RH) referred to, can also be referred to as releasing factors (-RF). Somatotropes: * Human growth hormone (HGH), also referred to as 'growth hormone' (GH), and also as somatotropin, is released under the influence of hypothalamic growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), and is inhibited by hypothalamic somatostatin. Corticotropes: * Cleaved from the precursor proopiomelanocortin protein, and include adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), and beta-endorphin, and melanocyte-stimulating hormone are released under the influence of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH). Thyrotropes: *Thyroid-stimulating hormone
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (also known as thyrotropin, thyrotropic hormone, or abbreviated TSH) is a pituitary hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine (T4), and then triiodothyronine (T3) which stimulates the metabolis ...
(TSH), is released under the influence of hypothalamic thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and is inhibited by somatostatin.
Gonadotropes:
* Luteinizing hormone (LH).
* Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), both released under influence of Gonadotropin-releasing Hormone (GnRH)
Lactotropes:
* Prolactin (PRL), whose release is inconsistently stimulated by hypothalamic TRH, oxytocin, vasopressin, vasoactive intestinal peptide, angiotensin II, neuropeptide Y, galanin, substance P, bombesin-like peptides (gastrin-releasing peptide, neuromedin B and C), and neurotensin, and inhibited by hypothalamic dopamine.
These hormones are released from the anterior pituitary under the influence of the hypothalamus. Hypothalamic hormones are secreted to the anterior lobe by way of a special capillary system, called the hypothalamic-hypophysial portal system.
There is also a non-endocrine cell population called folliculostellate cell A Folliculostellate (FS) cell is a type of non- endocrine cell found in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
Histology and ultrastructure
Rinehart and Farquhar first discovered FS cells through electron microscopy of the anterior pituitary ...
s.
Intermediate
The intermediate lobe synthesizes and secretes the following important endocrine hormone: * Melanocyte–stimulating hormone (MSH). This is also produced in the anterior lobe. When produced in the intermediate lobe, MSHs are sometimes called "intermedins".Posterior
The posterior pituitary stores and secretes (but does not synthesize) the following important endocrine hormones: Magnocellular neurons: * Antidiuretic hormone (ADH, also known asvasopressin
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then ...
and arginine vasopressin AVP), the majority of which is released from the supraoptic nucleus
The supraoptic nucleus (SON) is a nucleus of magnocellular neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus of the mammalian brain. The nucleus is situated at the base of the brain, adjacent to the optic chiasm. In humans, the SON contains about 3,00 ...
in the hypothalamus.
* Oxytocin, most of which is released from the paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus. Oxytocin is one of the few hormones to create a positive feedback loop. For example, uterine contractions stimulate the release of oxytocin from the posterior pituitary, which, in turn, increases uterine contractions. This positive feedback loop continues throughout labour.
Hormones
Hormones secreted from the pituitary gland help control the following body processes: * Growth (GH) *Blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressur ...
* Some aspects of pregnancy and childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births glo ...
including stimulation of uterine contractions
Uterine contractions are muscle contractions of the uterine smooth muscle that occur during the menstrual cycle and labour. Uterine contractions occur throughout the menstrual cycle in the non-pregnant state and throughout gestation.
Throughout ...
* Breast milk production
* Sex organ functions in both sexes
* Thyroid gland function
* Metabolic
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cel ...
conversion of food into energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of hea ...
* Water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
and osmolarity regulation in the body
* Water balance via the control of reabsorption of water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
by the kidneys
* Temperature regulation
* Pain relief
Clinical significance
vasopressin
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then ...
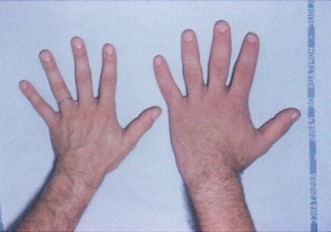
* Gigantism
Gigantism ( el, γίγας, ''gígas'', " giant", plural γίγαντες, ''gígantes''), also known as giantism, is a condition characterized by excessive growth and height significantly above average. In humans, this condition is caused by o ...
and acromegaly caused by an excess of growth hormone in childhood and adult, respectively
* Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as ...
caused by a deficiency of thyroid-stimulating hormone
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (also known as thyrotropin, thyrotropic hormone, or abbreviated TSH) is a pituitary hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine (T4), and then triiodothyronine (T3) which stimulates the metabolis ...
* Hyperpituitarism
Hyperpituitarism is a condition due to the primary hypersecretion of pituitary hormones; it typically results from a pituitary adenoma. In children with hyperpituitarism, disruption of growth regulation is rare, either because of hormone hypersec ...
, the increased (hyper) secretion of one or more of the hormones normally produced by the pituitary gland
* Hypopituitarism, the decreased (hypo) secretion of one or more of the hormones normally produced by the pituitary gland
* Panhypopituitarism a decreased secretion of most of the pituitary hormones
* Pituitary tumours
* Pituitary adenomas, noncancerous tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s that occur in the pituitary gland
All of the functions of the pituitary gland can be adversely affected by an over- or under-production of associated hormones.
The pituitary gland is important for mediating the stress response, via the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA axis) Critically, pituitary gland growth during adolescence can be altered by early life stress such as childhood maltreatment or maternal dysphoric behavior.
It has been demonstrated that, after controlling for age, sex, and BMI, larger quantities of DHEA and DHEA-S tended to be linked to larger pituitary volume. Additionally, a correlation between pituitary gland volume and Social Anxiety subscale scores was identified which provided a basis for exploring mediation. Again controlling for age, sex, and BMI, DHEA and DHEA-S have been found to be predictive of larger pituitary gland volume, which was also associated with increased ratings of social anxiety. This research provides evidence that pituitary gland volume mediates the link between higher DHEA(S) levels (associated with relatively early adrenarche) and traits associated with social anxiety. Children who experience early adrenarcheal development tend to have larger pituitary gland volume compared to children with later adrenarcheal development.
History
Etymology
Pituitary gland
The Greekphysician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through th ...
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be on ...
referred to the pituitary gland by only using the (Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
) name ἀδήν,Hyrtl, J. (1880). ''Onomatologia Anatomica. Geschichte und Kritik der anatomischen Sprache der Gegenwart.'' Wien: Wilhelm Braumüller. K.K. Hof- und Universitätsbuchhändler. ''gland''.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with the assistance of. Roderick McKenzie.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press. He described the pituitary gland as part of a series of secretory organs for the excretion of nasal mucus. Anatomist Andreas Vesalius translated ἀδήν with ''glans, in quam pituita destillat'', "gland in which slime (''pituita''Lewis, C.T. & Short, C. (1879). ''A Latin dictionary founded on Andrews' edition of Freund's Latin dictionary.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.) drips".Schreger, C.H.Th.(1805). ''Synonymia anatomica. Synonymik der anatomischen Nomenclatur.'' Fürth: im Bureau für Literatur. Besides this 'descriptive' name, Vesalius used ''glandula pituitaria'', from which the English name ''pituitary gland''Anderson, D.M. (2000). ''Dorland’s illustrated medical dictionary'' (29th edition). Philadelphia/London/Toronto/Montreal/Sydney/Tokyo: W.B. Saunders Company. is ultimately derived.
The expression ''glandula pituitaria'' is still used as official synonym beside ''hypophysis'' in the official Latin nomenclature '' Terminologia Anatomica''.Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology (FCAT) (1998). ''Terminologia Anatomica''. Stuttgart: Thieme In the seventeenth century the supposed function of the pituitary gland to produce nasal mucus was debunked. The expression ''glandula pituitaria'' and its English equivalent ''pituitary gland'' can only be justified from a historical point of view.Triepel, H. (1927). ''Die anatomischen Namen. Ihre Ableitung und Aussprache. Anhang: Biographische Notizen.''(Elfte Auflage). München: Verlag J.F. Bergmann. The inclusion of this synonym is merely justified by noting that the main term ''hypophysis'' is a much less popular term.International Anatomical Nomenclature Committee (1966). ''Nomina Anatomica''. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica Foundation, p. 62
Hypophysis
Note: ''hypophysial'' (or ''hypophyseal'') means "related to the hypophysis (pituitary gland)". The anatomist Samuel Thomas von Sömmerring coined the name ''hypophysis''. This name consists of ὑπό ('under') and φύειν ('to grow'). In later Greek ὑπόφυσις is used differently by Greek physicians as ''outgrowth''. Sömmering also used the equivalent expression ''appendix cerebri'', with ''appendix'' as ''appendage''. In various languages, ''Hirnanhang'' in German and ''hersenaanhangsel''Pinkhof, H. (1923). ''Vertalend en verklarend woordenboek van uitheemsche geneeskundige termen.'' Haarlem: De Erven F. Bohn. in Dutch, the terms are derived from ''appendix cerebri''.Other animals
The pituitary gland is found in all vertebrates, but its structure varies among different groups. The division of the pituitary described above is typical of mammals, and is also true, to varying degrees, of all tetrapods. However, only in mammals does the posterior pituitary have a compact shape. In lungfish, it is a relatively flat sheet of tissue lying above the anterior pituitary, but in amphibians, reptiles, andbird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s, it becomes increasingly well developed. The intermediate lobe is, in general, not well developed in any species and is entirely absent in birds.
The structure of the pituitary in fish, apart from the lungfish, is generally different from that in other animals. In general, the intermediate lobe tends to be well developed, and may equal the remainder of the anterior pituitary in size. The posterior lobe typically forms a sheet of tissue at the base of the pituitary stalk, and in most cases sends irregular finger-like projection into the tissue of the anterior pituitary, which lies directly beneath it. The anterior pituitary is typically divided into two regions, a more anterior ''rostral'' portion and a posterior ''proximal'' portion, but the boundary between the two is often not clearly marked. In elasmobranchs there is an additional, ''ventral lobe'' beneath the anterior pituitary proper.
The arrangement in lampreys, which are among the most primitive of all fish, may indicate how the pituitary originally evolved in ancestral vertebrates. Here, the posterior pituitary is a simple flat sheet of tissue at the base of the brain, and there is no pituitary stalk. Rathke's pouch remains open to the outside, close to the nasal openings. Closely associated with the pouch are three distinct clusters of glandular tissue, corresponding to the intermediate lobe, and the rostral and proximal portions of the anterior pituitary. These various parts are separated by meningial membranes, suggesting that the pituitary of other vertebrates may have formed from the fusion of a pair of separate, but associated, glands.
Most armadillos also possess a neural secretory gland very similar in form to the posterior pituitary, but located in the tail and associated with the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spin ...
. This may have a function in osmoregulation.
There is a structure analogous to the pituitary in the octopus brain.
Intermediate lobe
Although rudimentary in humans (and often considered part of the anterior pituitary), theintermediate lobe
Pars intermedia is the boundary between the anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary. It contains colloid-filled cysts and two types of cells - basophils and chromophobes. The cysts are the remainder of Rathke’s pouch.
In human fetal ...
located between the anterior and posterior pituitary is important to many animals. For instance, in fish, it is believed to control physiological color change. In adult humans, it is just a thin layer of cells between the anterior and posterior pituitary. The intermediate lobe produces melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH), although this function is often (imprecisely) attributed to the anterior pituitary.
The intermediate lobe is, in general, not well developed in tetrapods, and is entirely absent in birds.
See also
* Head and neck anatomy * MelanotrophReferences
External links
* *The Pituitary Gland, from the UMM Endocrinology Health Guide
The Pituitary Foundation
The Pituitary Network Association -- pituitary.org
{{Authority control Endocrine system Human head and neck Neuroendocrinology Human female endocrine system Articles containing video clips