|
Fairy Fort
Fairy forts (also known as ''lios'' or ''raths'' from the Irish language, Irish, referring to an earthen mound) are the remains of stone circles, ringforts, hillforts, or other circular prehistoric dwellings in Ireland. From possibly the late Iron Age to early Christian times, people built circular structures with earth banks or ditches. These were sometimes topped with wooden palisades and wooden framed buildings. As the dwellings were not durable, only vague circular marks often remained in the landscape. The remains of these structures, in conjunction with the vegetation around them, are associated with local traditions and folklore, perhaps involving fairy, fairies or other supposed supernatural entities, who would "defend" the structures from destruction by builders or farmers. As of 1991, there were between thirty and forty thousand identifiable fairy forts in Ireland's countryside, the oldest of them possibly dating back as early as 600 BCE. Interpretation Tradition cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort In Knocknagranshy
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ("strong") and ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley Civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large cyclopean stone walls fitted without mortar had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae. A Greek ''Towns of ancient Greece#Military settlements, phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the ancient Roman, Roman castellum or fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leprechaun
A leprechaun () is a diminutive supernatural being in Irish folklore, classed by some as a type of solitary fairy. They are usually depicted as little bearded men, wearing a coat and hat, who partake in mischief. In later times, they have been depicted as shoe-makers who have a hidden pot of gold at the end of the rainbow. Leprechaun-like creatures rarely appear in Irish mythology and only became prominent in later folklore. Etymology The Anglo-Irish (Hiberno-English) word ''leprechaun'' is descended from Old Irish ''luchorpán or lupracán'', via various (Middle Irish) forms such as ''luchrapán, lupraccán'', (or var. ''luchrupán''). Modern forms The current spelling is used throughout Ireland, but there are numerous regional variants. John O'Donovan's supplement to O'Reilly's ''Irish-English Dictionary'' defines as "a sprite, a pigmy; a fairy of a diminutive size, who always carries a purse containing a shilling".O'Donovan in O'Reilly (1817)''Irish Dict''. Suppl., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N22 Road (Ireland)
The N22 road is a national primary road in Ireland which goes through counties Kerry and Cork, from Tralee in the west through Killarney, Macroom and Ballincollig to Cork City Centre in the east. Improvements Sections of the N22 were upgraded in the late 20th and early 21st century. During the 1980s and 1990s, a section between Killarney and the border with County Cork was rebuilt and widened. An auxiliary climbing lane has been provided on the steep grade sections. The late 1980s saw a bypass of Killarney. In 2004, the Ballincollig bypass in the west of Cork city was completed. This is an dual carriageway road built to motorway standards that connects with the N40 Cork South Ring Road. In 2005, of the road between Tralee and Farranfore was upgraded. This added to a section opened in 2002. In August 2013, a new section of road was added as part of the Tralee N22/ N69 bypass project at Ballingrelagh replacing the section of road where the N22 originally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danny Healy-Rae
Daniel Healy-Rae (born 16 July 1954) is an Irish independent politician who has been a Teachta Dála (TD) for the Kerry constituency since the 2016 general election. He is part of the Healy-Rae family. He is a son of Jackie Healy-Rae and brother of fellow constituency TD Michael Healy-Rae. He has worked in plant hire and owns a pub in Kilgarvan, businesses associated with the Healy-Rae family. Prior to entering national politics, he was a member of Kerry County Council from 2003 to 2016 for the Killarney local electoral area. His daughter, Maura and son, Johnny are both elected members of Kerry County Council for the Killarney and Kenmare local electoral areas respectively. Political career Healy-Rae was co-opted on to Kerry County Council in 2003 representing the Killarney Local electoral area. He replaced his father, Jackie Healy-Rae, who was forced to resign his seat following the end of the dual mandate. He was re-elected to the council in the 2004, 2009 and 2014 Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John DeLorean
John Zachary DeLorean ( ; January 6, 1925 – March 19, 2005) was an American engineer, inventor, and executive in the U.S. automobile industry. He is widely known as founder of the DeLorean Motor Company, as well as for his work at General Motors. DeLorean managed the development of several vehicles throughout his career, including the Pontiac GTO, Pontiac Firebird, Pontiac Grand Prix, Chevrolet Cosworth Vega, and DMC DeLorean, which was featured in the 1985 film ''Back to the Future''. He was the youngest division chief in General Motors history, then left to start the DeLorean Motor Company (DMC) in 1973. Production delays meant that DMC's first car did not reach the consumer market until 1981, when a depressed buying market was compounded by lukewarm reviews from critics and the public. After a year, the DeLorean had failed to recover its $175 million investment costs, unsold cars accumulated, and the company was in financial trouble. In October 1982, DeLorean was charged wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seán Quinn
John Ignatius Quinn, commonly known as Seán Quinn (born 5 December 1947), is an Irish businessman and conglomerateur. In 2008 he was the richest person in the Republic of Ireland, but in 2012 he was declared bankrupt. The ''Sunday Times Rich List'' in 2008 estimated his personal worth to be €4.722 billion or £3.73 billion, thereby making him the richest person in Ireland. ''Forbes'' magazine's 2008 Rich List listed him again as the richest person in Ireland, in 164th place amongst the wealthiest individuals in the world. His net worth, as of February 2008, was estimated at $6.0 billion, approximately £3.084 billion. In November 2005 the Quinn Group, which was then privately owned by the Quinn family, was elsewhere estimated to be worth between €4 billion and €5 billion. In 2007 the group made a pre-tax profit of £439m. In April 2011 Kieran Wallace of KPMG was appointed as share receiver to Anglo Irish Bank (to which the Quinn Group owe over €2.8 billion) and took c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Wexford
County Wexford () is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and is part of the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. Named after the town of Wexford, it was based on the historic Gaelic Ireland, Gaelic territory of Uí Ceinnselaig, Hy Kinsella (''Uí Ceinnsealaigh''), whose capital was Ferns, County Wexford, Ferns. Wexford County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority for the county. The population of the county was 163,527 at the 2022 census. History The county is rich in evidence of early human habitation.Stout, Geraldine. "Essay 1: Wexford in Prehistory 5000 B.C. to 300 AD" in ''Wexford: History and Society'', pp 1 – 39. ''Portal tombs'' (sometimes called dolmens) exist at Ballybrittas (on Bree Hill) and at Newbawn – and date from the Neolithic period or earlier. Remains from the Bronze Age period are far more widespread. Early Irish tribes formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monamolin
Monamolin or Monamoling () is a small rural village in County Wexford, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, about south of the town of Gorey. Monamolin (in the Civil parishes in Ireland, civil parish of the same name), Retrieved: 9 September 2010. has a population of 661. Villages nearby include Kilmuckridge, Oulart, Boolavogue, Ballycanew and Ballygarrett. Name In 1685 in Ireland, 1685 Sir William Petty's map spells it Monemoling (a pronunciation which has survived to the present day). By 1837 the spelling had changed to Monemolin according to Samuel Lewis's ''Topographical Dictionary of Ireland''. In 1851 The Index of Irish Townlands records it as Monomolin. However, Monamolin is the standardised spelling today. The various English language, English versions of the name all come from the Irish language, Irish ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
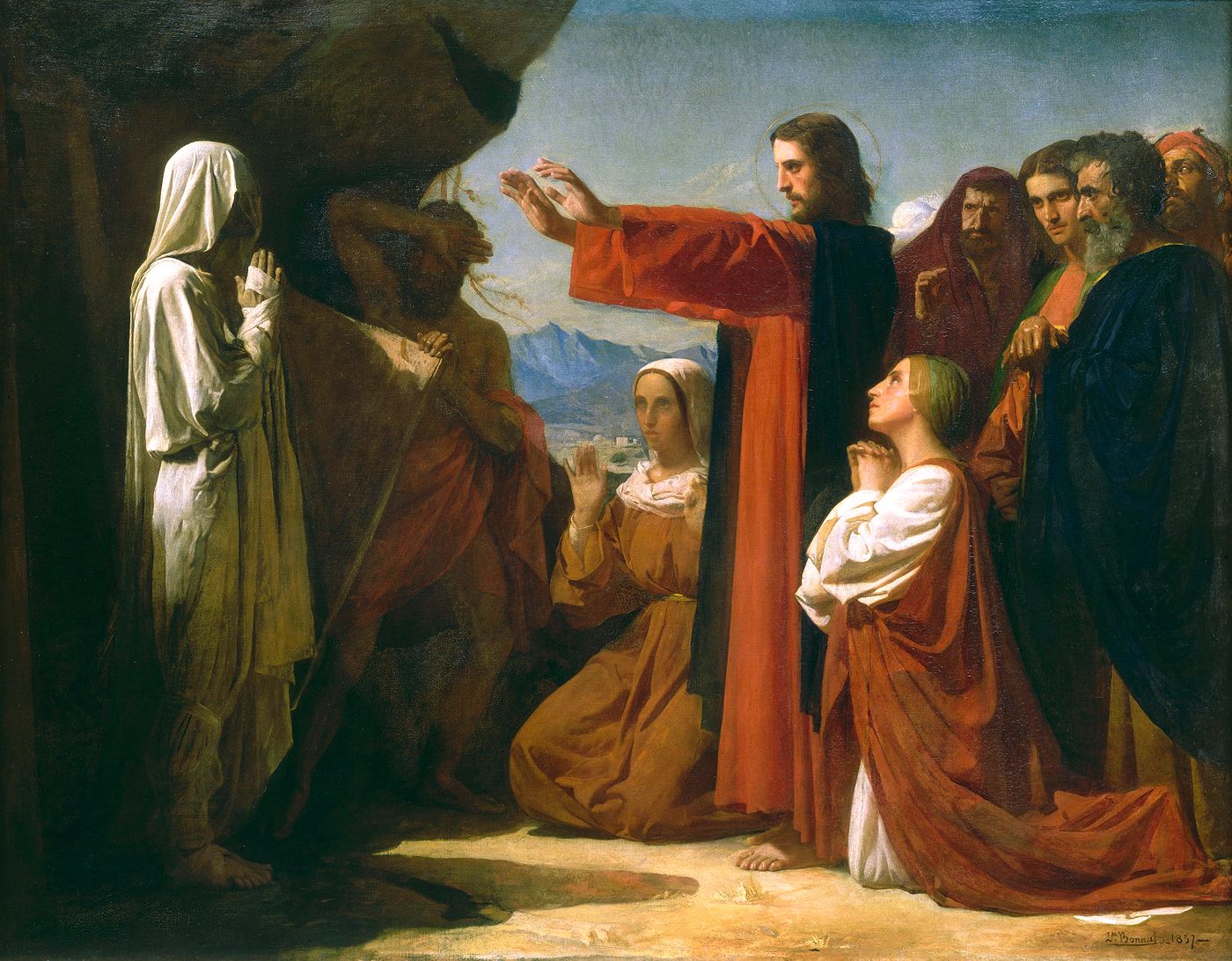
Resurrection
Resurrection or anastasis is the concept of coming back to life after death. Reincarnation is a similar process hypothesized by other religions involving the same person or deity returning to another body. The disappearance of a body is another similar but distinct belief in some religions. With the advent of written records, the earliest known recurrent theme of resurrection was in Egyptian and Canaanite religions, which had cults of dying-and-rising gods such as Osiris and Baal. Ancient Greek religion generally emphasised immortality, but in the mythos, a number of individuals were made physically immortal as they were resurrected from the dead. The universal resurrection of the dead at the end of the world is a standard eschatological belief in the Abrahamic religions. As a religious concept, resurrection is used in two distinct respects: # a belief in the ''individual resurrections'' of individual souls that is current and ongoing (e.g., Christian idealism, realized e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cunning Folk In Britain
The cunning folk were professional or semi-professional practitioners of magic (supernatural), magic in Europe from the Middle Ages, medieval period through the early 20th century. In Britain they were known by a variety of names in different regions of the country, including wise men and wise women, pellars, wizards, dyn hysbys, and sometimes white witches. These people practised folk and low magic – although often combined with elements of "high" or ceremonial magic – which they learned through the study of grimoires. Primarily using incantation, spells and charms as a part of their profession, they were most commonly employed to use their magic to combat malevolent witchcraft, to locate criminals, missing persons or stolen property, for fortune telling, for healing, for treasure hunting and to influence people to fall in love. Belonging "to the world of popular belief and custom", the cunning folk's magic has been defined as being "concerned not with the mysteries of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
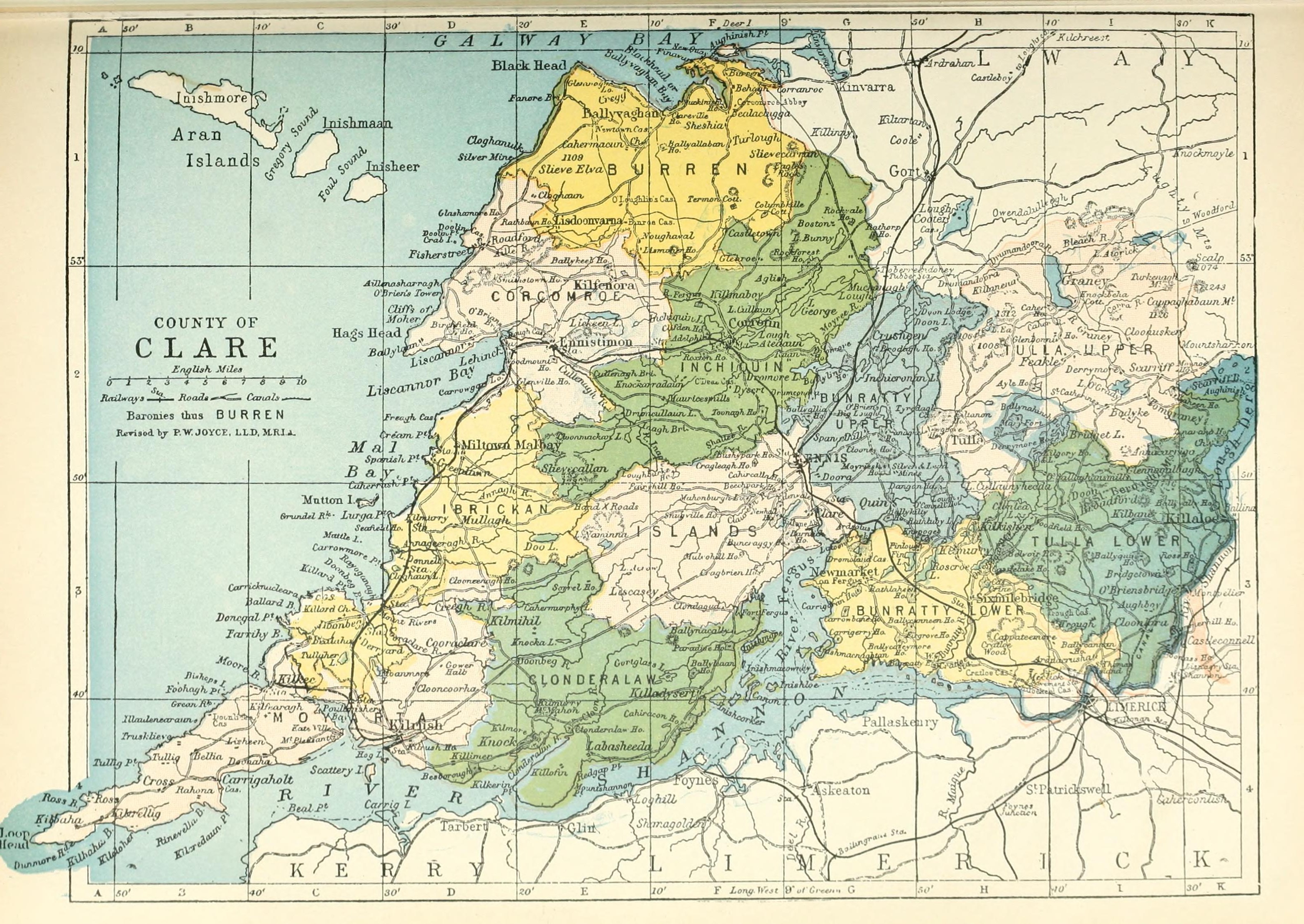
County Clare
County Clare () is a Counties of Ireland, county in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster in the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern part of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, bordered on the west by the Atlantic Ocean. Clare County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority. The county had a population of 127,938 at the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census. The county seat and largest settlement is Ennis. Etymology There are two main hypotheses for the origins of the county name "Clare". One is that the name is derived from Thomas de Clare, Lord of Thomond, Thomas de Clare an Anglo-Norman peer and soldier from the de Clare family, who was deeply embroiled in local politics and fighting in the 1270s and 1280 and had had acquired land in Kilkenny and Thomond that included the Castle of Clare. In 1590 County Clare was named after the castle, which is in a strategic location. An alternative hypothesis is that the county name ''Clare'' comes from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
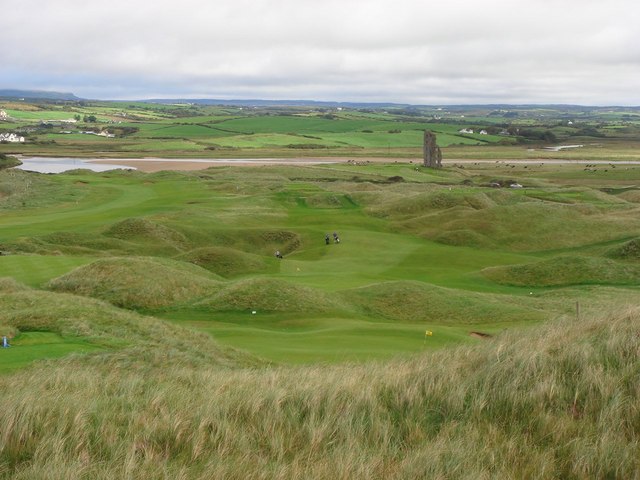
Lahinch
Lahinch or Lehinch ( ''or'' ) is a small town on Liscannor Bay, on the northwest coast of County Clare, Ireland. It lies on the N67 national secondary road, between Milltown Malbay and Ennistymon, roughly by road southwest of Galway and northwest of Limerick. The town is a seaside resort and is home to the Lahinch Golf Club. It has become a popular surfing location. Etymology Lahinch is the anglicised form of Leath Inse, meaning half island or peninsula. This is not related to ''Leacht Uí Chonchubhair'', which means "O'Connor's Grave", referring to the memorial cairn (Leacht) marking the burial place of one of the O’Connor chieftains, who were the ruling clan of the district of Corco Modhruadh Iartharach. The town was recorded by the Annals of the Four Masters as ''Leith Innse'', which is a variant of the Irish word for a peninsula ''leithinis'' ("half island"), which describes the village's location between the Inagh River and the sea. The town today is mostly spell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |