|
Fair Play Men
The Fair Play Men were illegal settlers (squatters) who established their own system of self-rule from 1773 to 1785 in the West Branch Susquehanna River valley of Pennsylvania in what is now the United States. Because they settled in territory claimed by Native Americans, they had no recourse to the Pennsylvania colonial government. Accordingly they established what was known as the Fair Play System, with three elected commissioners who ruled on land claims and other issues for the group. In a remarkable coincidence, the Fair Play Men made their own declaration of independence from Britain on July 4, 1776 beneath the "Tiadaghton Elm" on the banks of Pine Creek. The 1768 Treaty of Fort Stanwix The British colonial government purchased land from the Iroquois in the Treaty of Fort Stanwix of 1768, opening new lands in Pennsylvania and New York for settlement, including what is now Lycoming County, Pennsylvania. Lycoming County is about 100 mi (160 km) northwest of Philadelp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avis, Pennsylvania
The Borough of Avis is a borough in Clinton County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 1,484 at the 2010 census. Geography Avis is located in southeastern Clinton County at (41.185234, -77.316455). It is on the north side of the valley of the West Branch Susquehanna River, which passes to the south. U.S. Route 220, a four-lane freeway, runs along the southern edge of the borough, with access from Exit 118 (Pennsylvania Route 150) to the south of town and from Exit 120 (Pennsylvania Route 44) to the east. The borough of Jersey Shore is to the east of Avis, and Williamsport is to the east via US 220, while Lock Haven, the Clinton county seat, is to the west. According to the United States Census Bureau, Avis has a total area of , all land. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 1,492 people, 633 households, and 417 families residing in the borough. The population density was . There were 652 housing units at an average density of . The racial make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East-northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A '' compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each separated by 90 degrees, and secondarily divided by four ordinal (intercardinal) directions—northeast, southeast, southwest, and northwest—each located halfway between two cardinal directions. Some disciplines such as meteorology and navigation further divide the compass with additional azimuths. Within European tradition, a fully defined compass has 32 "points" (and any finer subdivisions are described in fractions of points). Compass points or compass directions are valuable in that they allow a user to refer to a specific azimuth in a colloquial fashion, without having to compute or remember degrees. Designations The names of the compass point directions follow these rules: 8-wind compass rose * The four cardinal directi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Declaration Of Independence
The Declaration of Independence, formally The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen States of America in the original printing, is the founding document of the United States. On July 4, 1776, it was adopted unanimously by the Second Continental Congress, who convened at Pennsylvania State House, later renamed Independence Hall, in the Colonial history of the United States, colonial capital of Philadelphia. These delegates became known as the nation's Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Fathers. The Declaration explains why the Thirteen Colonies regarded themselves as independent sovereign states no longer subject to British colonization of the Americas, British colonial rule, and has become one of the most circulated, reprinted, and influential documents in history. On June 11, 1776, the Second Continental Congress appointed the Committee of Five, including John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Jefferson, Robert R. Livingston, and Roger Sherman, who were charged w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loyalist (American Revolution)
Loyalists were refugee colonists from Thirteen Colonies, thirteen of the 20 British American colonies who remained loyal to the British Crown, British crown during the American Revolution, often referred to as Tories, Royalists, or King's Men at the time. They were opposed by the Patriot (American Revolution), Patriots or Whigs, who supported the revolution and considered them "persons inimical to the liberties of America." Prominent Loyalists repeatedly assured the Government of the United Kingdom, British government that many thousands of them would spring to arms and fight for the Crown. The British government acted in expectation of that, especially during the Southern theater of the American Revolutionary War, Southern campaigns of 1780 and 1781. Britain was able to effectively protect the people only in areas where they had military control, thus the number of military Loyalists was significantly lower than what had been expected. Loyalists were often under suspicion of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress (1775–1781) was the meetings of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolution and American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War, which established American independence from the British Empire. The Congress constituted a new federation that it first named the United Colonies of North America, and in 1776, renamed the United States, United States of America. The Congress began convening in present-day Independence Hall in Philadelphia, on May 10, 1775, with representatives from 12 of the 13 colonies, following the Battles of Lexington and Concord, the first battles of the Revolutionary War, which were fought on April 19, 1775. The Second Continental Congress succeeded the First Continental Congress, which met from September 5 to October 26, 1774, also in Philadelphia. The Second Congress functioned as the ''de facto'' federation government at the outset of the Revolutionary War by raising militias, direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinton County, Pennsylvania
Clinton County is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. As of the 2020 census, the population was 37,450. Its county seat is Lock Haven. Clinton County comprises the Lock Haven, PA Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is also included in the Williamsport-Lock Haven, PA Combined Statistical Area. The county is part of the Central region of the commonwealth. History In the Treaty of Fort Stanwix of 1768, new lands in Pennsylvania were purchased from the Haudenosaunee for colonial settlement, including parts of what is now Clinton County. The land was formally associated with Northumberland County, but a group of organized settlers near modern Jersey Shore elected three commissioners each March who were responsible for seeing that everyone was dealt with fairly. This became known as the Fairplay System. Most of the rulings seem to have dealt with property issues, but they dealt with any legal or criminal cases in their area. They granted permission for new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies representing the Thirteen Colonies and later the United States during the American Revolutionary War. It was formed on June 14, 1775, by a resolution passed by the Second Continental Congress, meeting in Philadelphia after the war's outbreak at the Battles of Lexington and Concord on April 19, 1775. Therefore, June 14th is celebrated as the U.S. Army Birthday. The Continental Army was created to coordinate military efforts of the colonies in the war against the British Army during the American Revolutionary War, British, who sought to maintain control over the American colonies. General George Washington was appointed commander-in-chief of the Continental Army and maintained this position throughout the war. The Continental Army was supplemented by local Militia (United States), militias and volunteer troops that were either loyal to individual states or otherwise independent. Most of the Continental Army was disbanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which American Patriot (American Revolution), Patriot forces organized as the Continental Army and commanded by George Washington defeated the British Army during the American Revolutionary War, British Army. The conflict was fought in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. The war's outcome seemed uncertain for most of the war. However, Washington and the Continental Army's decisive victory in the Siege of Yorktown in 1781 led King George III and the Kingdom of Great Britain to negotiate an end to the war in the Treaty of Paris (1783), Treaty of Paris two years later, in 1783, in which the British monarchy acknowledged the independence of the Thirteen Colonies, leading to the establishment of the United States as an independent and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Work Projects Administration
The Works Progress Administration (WPA; from 1935 to 1939, then known as the Work Projects Administration from 1939 to 1943) was an American New Deal agency that employed millions of jobseekers (mostly men who were not formally educated) to carry out public works projects, including the construction of public buildings and roads. It was set up on May 6, 1935, by presidential order, as a key part of the Second New Deal. The WPA's first appropriation in 1935 was $4.9 billion (about $15 per person in the U.S., around 6.7 percent of the 1935 GDP). Headed by Harry Hopkins, the WPA supplied paid jobs to the unemployed during the Great Depression in the United States, while building up the public infrastructure of the US, such as parks, schools, and roads. Most of the jobs were in construction, building more than of streets and over 10,000 bridges, in addition to many airports and much housing. In 1942, the WPA played a key role in both building and staffing Internment of Japanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
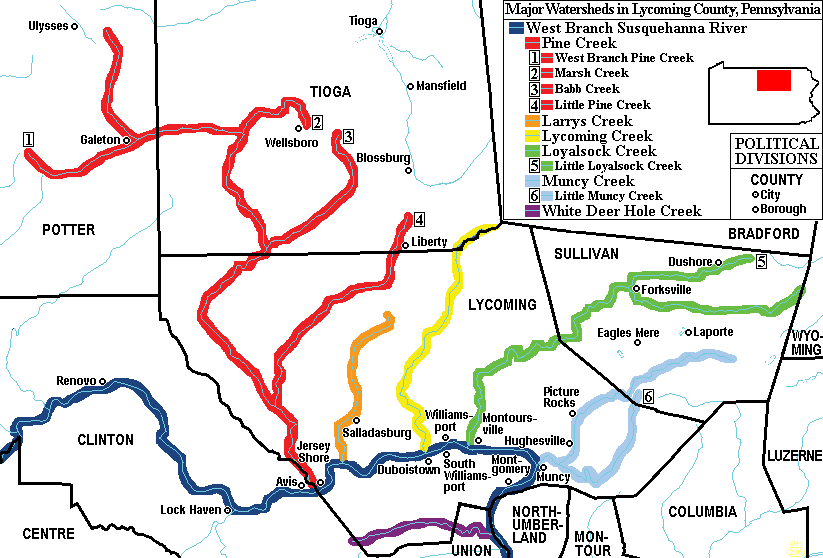
Larrys Creek
Larrys Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed August 8, 2011 tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River in Lycoming County in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. A part of the Chesapeake Bay drainage basin, its watershed drains in six townships and a borough. The creek flows south from the dissected Allegheny Plateau to the Ridge-and-valley Appalachians through sandstone, limestone, and shale from the Devonian, Mississippian, and Pennsylvanian periods. The valley's first recorded inhabitants were the Susquehannocks, followed by the Lenape and other tribes. ''Note:'' ISBN refers to the Heritage Books July 1996 reprint. URL is to a scan of the 1892 version with some OCR typos. The Great Shamokin Path crossed the creek near its mouth, where Larry Burt, the first Euro-American settler and the man who gave the creek its present name, also lived by 1769. In the 19th century, the creek and its water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycoming Creek
Lycoming Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 8, 2011 tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River located in Tioga County, Pennsylvania, Tioga and Lycoming County, Pennsylvania, Lycoming counties in Pennsylvania in the United States. Geography As the crow flies, Lycoming County is about northwest of Philadelphia and east-northeast of Pittsburgh. Lycoming stream, Creek has its river source in Tioga County and is in length from the Tioga County / Lycoming County line to its confluence with the West Branch Susquehanna River at Williamsport, Pennsylvania, Williamsport. Smaller streams feeding Lycoming Creek include Pleasant Stream, Grays Run, Roaring Branch, Hoagland Run, and Trout Run. Watershed Approximately 81.5% of the Lycoming Creek drainage basin, watershed is in Lycoming County, with 16.5% in Tioga County, and 1.5% in Sullivan County, Pennsylvania, Sullivan County. The watershed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purchase Line
The Purchase Line is the name commonly given to the line dividing Indian from British Colonial lands established in the Treaty of Fort Stanwix of 1768 in western Pennsylvania. In New York State documents, it is referred to as the Line of Property. That article contains the treaty text and other sections. History The relevant section of the treaty reads: * "from thence" ( Kittanning) "a direct Line to the nearest Fork of the west branch of Susquehanna" This line was not clearly defined until in a meeting between Indian and Pennsylvania representatives in 1773 at the well-known "Canoe Place" or upper limit of canoe navigation on the Susquehanna at its confluence with Cush Cushion Creek at present-day Cherry Tree, Pennsylvania. This was agreed to as the "nearest point" of the treaty. This became the tri-point between present-day Clearfield, Cambria, and Indiana counties, although the borough of Cherry Tree, Pennsylvania was later included entirely in Indiana Indiana ( ) is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |