|
FORECAST (model)
FORECAST is a management-oriented, stand-level, forest-growth and ecosystem-dynamics model. The model was designed to accommodate a wide variety of silvicultural and harvesting systems and natural disturbance events (e.g., fire, wind, insect epidemics) in order to compare and contrast their effect on forest productivity, stand dynamics, and a series of biophysical indicators of non-timber values. Model description Projection of stand growth and ecosystem dynamics is based upon a representation of the rates of key ecological processes regulating the availability of, and competition for, light and nutrient resources (a representation of moisture effects on soil processes, plant physiology and growth, and the consequences of moisture competition is being added). The rates of these processes are calculated from a combination of historical bioassay data (such as biomass accumulation in plant components and changes in stand density over time) and measures of certain ecosystem variables ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allometry
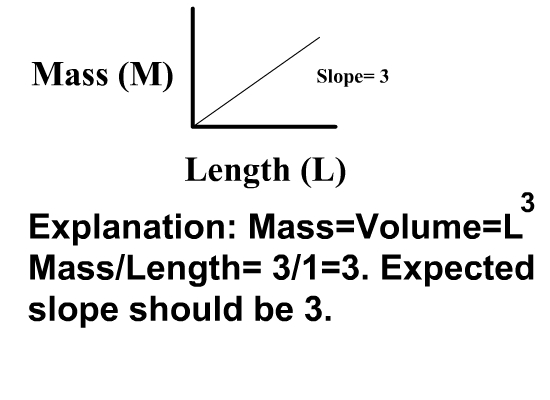
Allometry is the study of the relationship of body size to shape, anatomy, physiology and finally behaviour, first outlined by Otto Snell in 1892, by D'Arcy Thompson in 1917 in ''On Growth and Form'' and by Julian Huxley in 1932. Overview Allometry is a well-known study, particularly in statistical shape analysis for its theoretical developments, as well as in biology for practical applications to the differential growth rates of the parts of a living organism's body. One application is in the study of various insect species (e.g., Hercules beetles), where a small change in overall body size can lead to an enormous and disproportionate increase in the dimensions of appendages such as legs, antennae, or horns The relationship between the two measured quantities is often expressed as a power law equation (Allometric equation) which expresses a remarkable scale symmetry: : y = kx^a \,\! or in a logarithmic form: : \log y = a \log x + \log k\,\! or similarly \ln y = a \ln x ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem Management
Ecosystem management is an approach to natural resource management that aims to ensure the long-term sustainability and persistence of an ecosystems function and services while meeting socioeconomic, political, and cultural needs. Although indigenous communities have employed sustainable ecosystem management approaches for millennia, ecosystem management emerged formally as a concept in the 1990s from a growing appreciation of the complexity of ecosystems, as well as humans' reliance and influence on natural systems (e.g., disturbance, ecological resilience). Building upon traditional natural resource management, ecosystem management integrates ecological, socioeconomic, and institutional knowledge and priorities through diverse stakeholder participation. In contrast to command and control approaches to natural resource management, which often lead to declines in ecological resilience, ecosystem management is a holistic, adaptive method for evaluating and achieving resilience and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Due to climate change, deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Increased warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also causin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoculture
In agriculture, monoculture is the practice of growing one crop species in a field at a time. Monoculture is widely used in intensive farming and in organic farming: both a 1,000-hectare/acre cornfield and a 10-ha/acre field of organic kale are monocultures. Monoculture of crops has allowed farmers to increase efficiency in planting, managing, and harvesting, mainly by facilitating the use of machinery in these operations, but monocultures can also increase the risk of diseases or pest outbreaks. Diversity can be added both in time, as with a crop rotation or sequence, or in space, with a polyculture or intercropping (see table below). Continuous monoculture, or monocropping, where farmers raise the same species year after year, can lead to the quicker buildup and spread of pests and diseases in a susceptible crop. The term "oligoculture" has been used to describe a crop rotation of just a few crops, as practiced in several regions of the world. The concept of monocultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Cohort
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines a forest as, "Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a canopy cover of more than 10 percent, or trees able to reach these thresholds ''in situ''. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use." Using this definition, '' Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020'' (FRA 2020) found that forests covered , or approximately 31 percent of the world's land area in 2020. Forests are the predominant terrestrial ecosystem of Earth, and are found around the globe. More than half of the world's forests are found in only five countries (Brazil, Canada, China, Russia, and the United States). The largest share of forests (45 percent) are in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Community
A plant community is a collection or association of plant species within a designated geographical unit, which forms a relatively uniform patch, distinguishable from neighboring patches of different vegetation types. The components of each plant community are influenced by soil type, topography, climate and human disturbance. In many cases there are several soil types present within a given plant community. This is because the soil type within an area is influenced by two factors, the rate at which water infiltrates or exits (via evapotranspiration) the soil, as well as the rate at which organic matter (any carbon-based compound within the environment, such as decaying plant matter) enters or decays from the soil. Plant communities are studied substantially by ecologists, due to providing information on the effects of dispersal, tolerance to environmental conditions, and response to disturbance of a variety of plant species, information valuable to the comprehension of various pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desorption
Desorption is the physical process where a previously adsorbed substance is released from a surface. This happens when a molecule gains enough energy to overcome the activation barrier of the bounding energy that keeps it in the surface. There are a lot of different types of desorption, depending on the mechanism that separates the adsorbate from the substrate; therefore there is no one equation that describes the process. Note that desorption is the opposite of adsorption, which differs from absorption because it refers to substances being stuck to the surface, as opposed to being absorbed into the bulk. Desorption can occur after a reaction between a catalyst and an adsorbed compound; or during stripping or chromatography which are types of separation processes. Desorption mechanisms Depending on the nature of the adsorbent-to-surface bond, there are a multitude of mechanisms for desorption. The surface bond of a sorbant can be cleaved thermally, through chemical reacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cation-exchange Capacity
Cation-exchange capacity (CEC) is a measure of how many cations can be retained on soil particle surfaces. Negative charges on the surfaces of soil particles bind positively-charged atoms or molecules (cations), but allow these to exchange with other positively charged particles in the surrounding soil water. This is one of the ways that solid materials in soil alter the chemistry of the soil. CEC affects many aspects of soil chemistry, and is used as a measure of soil fertility, as it indicates the capacity of the soil to retain several nutrients (e.g. K+, NH4+, Ca2+) in plant-available form. It also indicates the capacity to retain pollutant cations (e.g. Pb2+). Definition and principles Cation-exchange capacity is defined as the amount of positive charge that can be exchanged per mass of soil, usually measured in cmolc/kg. Some texts use the older, equivalent units me/100g or meq/100g. CEC is measured in moles of electric charge, so a cation-exchange capacity of 10 cmolc/kg cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogeochemical Cycle
A biogeochemical cycle (or more generally a cycle of matter) is the pathway by which a chemical substance cycles (is turned over or moves through) the biotic and the abiotic compartments of Earth. The biotic compartment is the biosphere and the abiotic compartments are the atmosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere. There are biogeochemical cycles for chemical elements, such as for calcium, carbon, hydrogen, mercury, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, selenium, iron and sulfur, as well as molecular cycles, such as for water and silica. There are also macroscopic cycles, such as the rock cycle, and human-induced cycles for synthetic compounds such as polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). In some cycles there are reservoirs where a substance can remain or be sequestered for a long period of time. Overview Energy flows directionally through ecosystems, entering as sunlight (or inorganic molecules for chemoautotrophs) and leaving as heat during the many transfers between tro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |