|
F.V.D. Doris
The F.V.D. Doris or Dresden Doris, later known as the Akaflieg Dresden D-B2 Doris, was a monoplane glider built in Germany in 1922. It was unusual in having wings which could independently adjust their angles of attack, a feature intended to increase the energy acquired from gusts of wind. Design and development After the collaboration between the Technical High School Dresden (TH Dresden) and the local flying club, the Flugtechnischer Verein Dresden (F.V.D.), that led to the quite successful 1921 F.V.D. Stehaufchen wing warping biplane glider, the group designed and built a monoplane, the Doris. Originally known as the Dresden Doris or, in the UK at least, as the F.V.D. monoplane, it was later incorporated retrospectively into the Akaflieg Dresden's design list as the D-B2 Doris. Most notably, it had wings which could adjust their relative angles of attack independently both of each other and of the pilot. The idea of such wings came from the poor understanding of slope so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
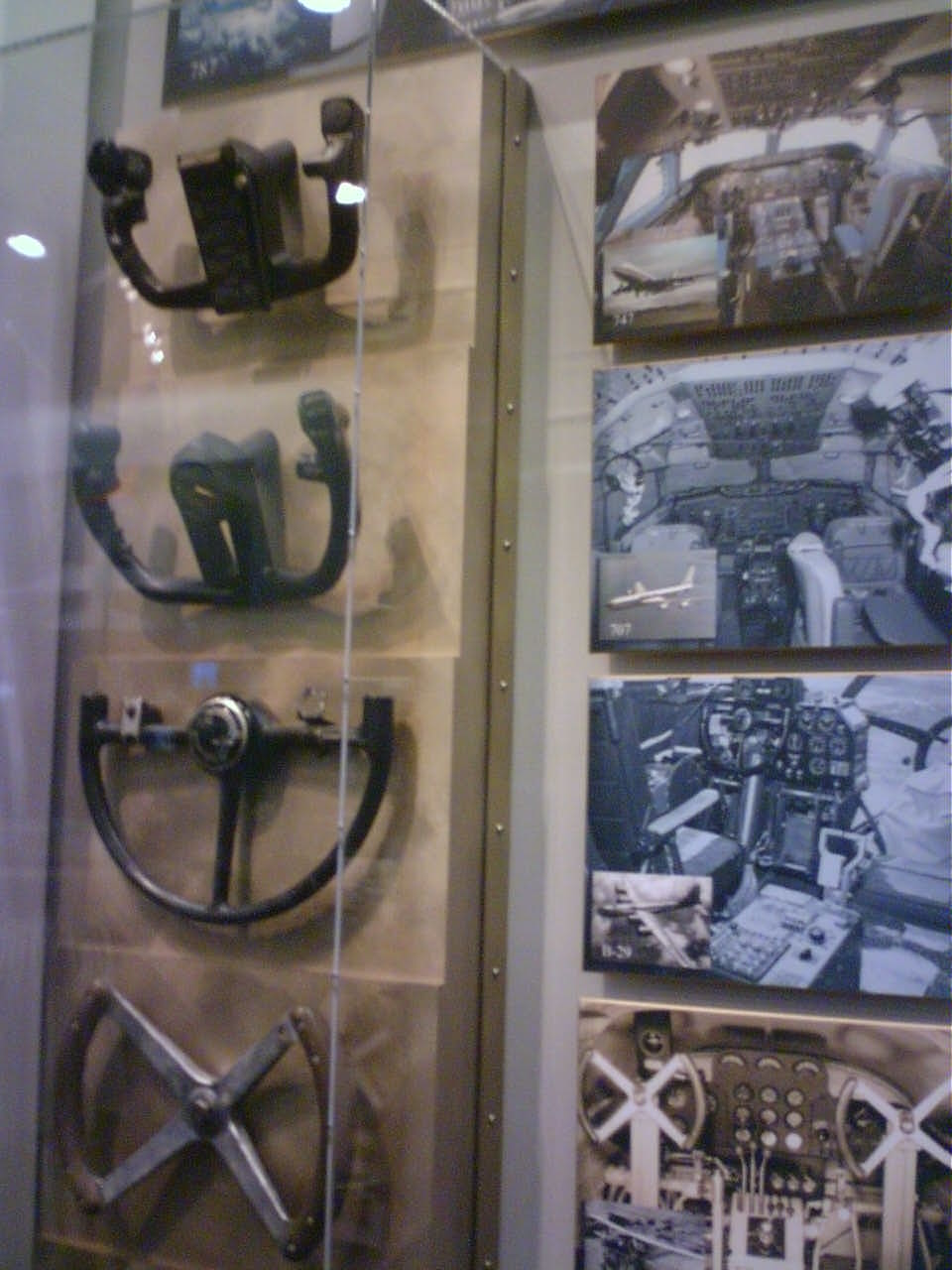
Control Column
A yoke, alternatively known as a control wheel or a control column, is a device used for Pilot (aeronautics), piloting some fixed-wing aircraft.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 563. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. . The aviator, pilot uses the yoke to control the Aircraft attitude, attitude of the plane, usually in both pitch and Flight dynamics, roll. Rotating the control wheel controls the ailerons and the roll axis. Fore and aft movement of the control column controls the Elevator (aircraft), elevator and the pitch axis. When the yoke is pulled back, the nose of the aircraft rises. When the yoke is pushed forward, the nose is lowered. When the yoke is turned left, the plane rolls to the left, and when it is turned to the right, the plane rolls to the right. Small to medium-size aircraft, usually limited to propeller-driven, feature a mechanical system whereby the yoke is connected directly to the control surfaces with cables a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pushrods
A valvetrain is a mechanical system that controls the operation of the intake and exhaust valves in an internal combustion engine. The intake valves control the flow of air/fuel mixture (or air alone for direct-injected engines) into the combustion chamber, while the exhaust valves control the flow of spent exhaust gases out of the combustion chamber once combustion is completed. Layout The valvetrain layout is largely dependent on the location of the camshaft. The common valvetrain configurations for piston engines, in order from oldest to newest, are: * Flathead engine: A single camshaft and the valves are located in the engine block below the cylinder or cylinder bank. * Overhead valve engine: A single camshaft remains in the block below the cylinder(s), however the valves are located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. * Overhead camshaft engine: Both the valves and one or more camshafts are located in the cylinder head above the cylinders or cylinder banks. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trailing Edge
The trailing edge of an aerodynamic surface such as a wing is its rear edge, where the airflow separated by the leading edge meets.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 521. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. Essential flight control surfaces are attached here to control the direction of the departing air flow, and exert a controlling force on the aircraft. Such control surfaces include ailerons on the wings for roll control, elevator (aircraft), elevators on the tailplane controlling Aircraft principal axes, pitch, and the rudder on the fin controlling Aircraft principal axes, yaw. Elevators and ailerons may be combined as elevons on tailless aircraft. The shape of the trailing edge is of prime importance in the aerodynamic function of any aerodynamic surface. A sharp trailing edge is always employed in an airfoil. George Batchelor has written about: :“ ... the remarkable controlling influence exerted by the sharp trailing edge of an aerof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leading Edge
The leading edge is the part of the wing that first contacts the air;Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 305. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. alternatively it is the foremost edge of an airfoil section. The first is an aerodynamic definition, the second a structural one. As an example of the distinction, during a tailslide, from an aerodynamic point of view, the trailing edge becomes the leading edge and vice versa but from a structural point of view the leading edge remains unchanged. Overview The structural leading edge may be equipped with one or more of the following: * Leading edge boots * Leading edge cuffs * Leading edge extensions * Leading edge slats * Leading edge slots * Krueger flaps * Stall strips * Vortex generators. Associated terms are leading edge radius and leading edge stagnation point. Seen in plan the leading edge may be straight or curved. A straight leading edge may be swept or unswept, the latter meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plywood
Plywood is a composite material manufactured from thin layers, or "plies", of wood veneer that have been stacked and glued together. It is an engineered wood from the family of manufactured boards, which include plywood, medium-density fibreboard (MDF), oriented strand board (OSB), and particle board (or chipboard). All plywoods bind resin and wood fibre sheets (cellulose cells are long, strong and thin) to form a composite material. The sheets of wood are stacked such that each layer has its grain set typically (see below) perpendicular to its adjacent layers. This alternation of the grain is called ''cross-graining'' and has several important benefits: it reduces the tendency of wood to split when nailed at the edges; it reduces thickness swelling and shrinkage, providing improved dimensional stability; and it makes the strength of the panel consistent across all directions. There is usually an odd number of plies, so that the sheet is balanced, that is, the surface layers ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Fabric Covering
Aircraft fabric covering is a term used for both the material used and the process of covering aircraft open structures. It is also used for reinforcing closed plywood structures. The de Havilland Mosquito is an example of this technique, as are the pioneering all-wood monocoque fuselages of certain World War I German aircraft like the LFG Roland C.II in its wrapped ''Wickelrumpf'' plywood strip and fabric covering. Early aircraft used organic materials such as cotton and cellulose nitrate Aircraft dope, dope; modern fabric-covered designs usually use Synthetic fibers, synthetic materials such as Dacron and butyrate dope for adhesive. Modern methods are often used in the restoration of older types that were originally covered using traditional methods. Purpose/requirements The purposes of the fabric covering of an aircraft are: * To provide a light airproof skin for lifting and control surfaces. * To provide structural strength to otherwise weak structures. * To cover other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Fairing
An aircraft fairing is a structure whose primary function is to produce a smooth outline and reduce drag.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, Third Edition'', page 206. Aviation Supplies & Academics Inc, Newcastle Washington, 1997. These structures are covers for gaps and spaces between parts of an aircraft to reduce form drag and interference drag, and to improve appearance.Bingelis, Tony: ''The Sportplane Builder'', pages 261-265. Experimental Aircraft Association Aviation Foundation, 1979. Types On aircraft, fairings are commonly found on: ; Belly fairing : Also called a "ventral fairing", it is located on the underside of the fuselage between the main wings. It can also cover additional cargo storage or fuel tanks. ; Cockpit fairing : Also called a "cockpit pod", it protects the crew on ultralight trikes. Commonly made from fiberglass, it may also incorporate a windshield.Cliche, Andre: ''Ultralight Aircraft Shopper's Guide'' 8th Edition, page C-17. Cybai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord (aircraft)
In aeronautics, the chord is an imaginary straight line segment joining the leading edge and trailing edge of an aerofoil cross section parallel to the direction of the airflow. The chord length is the distance between the trailing edge and the leading edge. L. J. Clancy (1975), ''Aerodynamics'', Section 5.2, Pitman Publishing Limited, London. The point on the leading edge used to define the main chord may be the surface point of minimum radius. p.18 For a turbine aerofoil, the chord may be defined by the line between points where the front and rear of a 2-dimensional blade section would touch a flat surface when laid convex-side up. The wing, horizontal stabilizer, vertical stabilizer and propeller/rotor blades of an aircraft are all based on aerofoil sections, and the term ''chord'' or ''chord length'' is also used to describe their width. The chord of a wing, stabilizer and propeller is determined by measuring the distance between leading and trailing edges in the direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spar (aviation)
In a fixed-wing aircraft, the spar is often the main structural member of the wing, running wingspan, spanwise at right angles (or thereabouts depending on Swept wing, wing sweep) to the fuselage. The spar carries flight Structural load, loads and the weight of the wings while on the ground. Other structural and forming members such as Rib (aircraft), ribs may be attached to the spar or spars, with stressed skin construction also sharing the loads where it is used. There may be more than one spar in a wing or none at all. Where a single spar carries most of the force, it is known as the main spar. Spars are also used in other aircraft airfoil, aerofoil surfaces such as the tailplane and Vertical stabilizer, fin and serve a similar function, although the loads transmitted may be different from those of a wing spar. Spar loads The wing spar provides the majority of the weight support and dynamic load integrity of cantilever monoplanes, often coupled with the strength of the wing D- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strut
A strut is a structural component commonly found in engineering, aeronautics, architecture and anatomy. Struts generally work by resisting longitudinal compression, but they may also serve in tension. A stay is sometimes used as a synonym for strut, but some sources distinguish that struts are braces for holding compressive forces apart, while stays are braces for keeping stretching forces together. Human anatomy Part of the functionality of the clavicle is to serve as a strut between the scapula and sternum, resisting forces that would otherwise bring the upper limb close to the thorax. Keeping the upper limb away from the thorax is vital for its range of motion. Complete lack of clavicles may be seen in cleidocranial dysostosis, and the abnormal proximity of the shoulders to the median plane in cases of this genetic condition exemplifies the clavicle's importance as a strut. Architecture and construction Strut is a common name in timber framing for a support or brace of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuselage
The fuselage (; from the French language, French ''fuselé'' "spindle-shaped") is an aircraft's main body section. It holds Aircrew, crew, passengers, or cargo. In single-engine aircraft, it will usually contain an Aircraft engine, engine as well, although in some amphibious aircraft the single engine is mounted on a hardpoint, pylon attached to the fuselage, which in turn is used as a floating Hull (watercraft), hull. The fuselage also serves to position the Flight control surfaces, control and Stabilizer (aeronautics), stabilization surfaces in specific relationships to Wing, lifting surfaces, which is required for aircraft stability and maneuverability. Types of structures Truss structure This type of structure is still in use in many lightweight aircraft using welding, welded steel tube trusses. A box truss fuselage structure can also be built out of wood—often covered with plywood. Simple box structures may be rounded by the addition of supported lightweight strin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |