|
Execution Of Louis XVI
Louis XVI, former Bourbon King of France since the Proclamation of the abolition of the monarchy, abolition of the monarchy, was publicly executed on 21 January 1793 during the French Revolution at the ''Place de la RĂ©volution'' in Paris. At Trial of Louis XVI, his trial four days prior, the National Convention had convicted the former king of high treason in a near-unanimous vote; while no one voted "not guilty", several deputies abstained. Ultimately, they condemned him to death by a Plurality voting, simple majority. The execution by guillotine was performed by Charles-Henri Sanson, then High Executioner of the French First Republic and previously royal executioner under Louis. Often viewed as a turning point in both French and European history, the execution inspired various reactions around the world. To some, Louis' death at the hands of his former subjects symbolized the end of an unbroken thousand-year period of monarchy in France and the true beginning of democracy with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JĂ©rĂ´me PĂ©tion De Villeneuve
Jérôme Pétion de Villeneuve (; 3 January 1756 – 18 June 1794) was a French writer and politician who served as the second mayor of Paris, from 1791 to 1792, and the first regular president of the National Convention in 1792. During the French Revolution, he was associated with the moderate Girondins, and voted against the immediate execution of Louis XVI at the king's trial in January 1793, though he supported a suspended sentence. This led to Pétion's proscription by the Convention alongside other Girondin deputies following the radical insurrection of 31 May – 2 June 1793, and ultimately his suicide together with fellow-Girondin François Buzot while evading arrest during the Terror. Early life and work Jérôme Pétion de Villeneuve was the son of a prosecutor at Chartres. Though it is known that he was trained as a lawyer, very few specifics are known about Petion's early life, as he was virtually unknown prior to the French Revolution. He became a lawyer in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girondins
The Girondins (, ), also called Girondists, were a political group during the French Revolution. From 1791 to 1793, the Girondins were active in the Legislative Assembly and the National Convention. Together with the Montagnards, they initially were part of the Jacobin movement. They campaigned for the end of the monarchy, but then resisted the spiraling momentum of the Revolution, which caused a conflict with the more radical Montagnards. They dominated the movement until their fall in the insurrection of 31 May – 2 June 1793, which resulted in the domination of the Montagnards and the purge and eventual mass execution of the Girondins. This event is considered to mark the beginning of the Reign of Terror. The Girondins were a group of loosely affiliated individuals rather than an organized political party and the name was at first informally applied because the most prominent exponents of their point of view were deputies to the Legislative Assembly from the département ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Mailhe
Jean-Baptiste Mailhe (; 2 June 1750 – 1 June 1834) was a politician during the French Revolution. He gave his name to the Mailhe amendment, which sought to delay the execution of Louis XVI. Biography Mailhe was born in 1750 in Guizerix, Gascony, the son of a landowner. He became a lawyer in Toulouse. Elected to the Legislature in 1791, he was part of the Diplomatic Committee and sat alongside the Girondins, who supported the policy of war against Austria. Re-elected in September 1792 as Member of Parliament for the Haute-Garonne in the National Convention, he sat with La Plaine, remaining close to the Girondists. The Trial of Louis XVI Mailhe led the committee to decide whether King Louis XVI could be tried despite the constitution stating that the king was inviolable. Mailhe's report concluded that constitutional inviolability was a gift of the people, and so could be revoked by them. Thus King Louis XVI could indeed be tried by the National Convention. At the trial of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Les Éditions Sociales
LES or Les may refer to: People * Les (given name) * Les (surname) * L.E.S. (producer), hip hop producer Space flight * Launch Entry Suit, worn by Space Shuttle crews * Launch escape system, for spacecraft emergencies * Lincoln Experimental Satellite series, 1960s and 1970s Biology and medicine * Lazy eye syndrome, or amblyopia, a disorder in the human optic nerve * The Liverpool epidemic strain of ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' * Lower esophageal sphincter * Lupus erythematosus systemicus Places * The Lower East Side neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City * Les, Catalonia, a municipality in Spain * LeÅŸ, a village in Nojorid Commune, Bihor County, Romania * ''Les'', the Hungarian name for LeÈ™u Commune, BistriÅ£a-Năsăud County, Romania * Les, a village in Tejakula district, Buleleng regency, Bali, Indonesia * Lesotho, IOC and UNDP country code * Lès, a word featuring in many French placenames Transport * Leigh-on-Sea railway station, National Rail station code * L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Poperen
Jean Poperen (9 January 1925, Angers – 23 August 1997) was a French politician. Poperen joined the Communist Party (PCF) at 18, and was also a member of the Union of Communist Students. He left the PCF after the Hungarian Revolution of 1956 and became a founding member of the Unified Socialist Party (PSU) in 1960. Disagreeing with the PSU's party line, he founded the Union of Socialist Groups and Clubs (UGCS). The UGCS participated in the Federation of the Democratic and Socialist Left and joined the new Socialist Party at the party's second national congress. Poperen, a member of the party's left-wing, was the party's second-in-command from 1981 to 1987. Poperen also served in the Michel Rocard government, and was PS deputy for the RhĂ´ne The RhĂ´ne ( , ; Occitan language, Occitan: ''RĂ²se''; Franco-Provençal, Arpitan: ''RĂ´no'') is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and Southeastern France befo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armoire De Fer
L'armoire de fer (French: 'iron chest') in general refers to an iron chest used to house important papers. A notable and frequent use of the term refers to a hiding place at the apartments of Louis XVI of France at the Tuileries Palace where some secret documents were kept. The existence of this iron cabinet, hidden behind wooden panelling, was publicly revealed in November 1792 to Jean-Marie Roland, vicomte de la Platière, Girondin Minister of the Interior. History A locksmith by the name of François Gamain helped reveal these documents to the authorities, who rewarded him with a government pension. The cabinet hid correspondence between Louis XVI and, among others, Mirabeau, whose venality and duplicity were exposed. Also, the cabinet included the correspondence of the King with the financier Maximilien Radix de Sainte-Foix, an important secret advisor of the sovereign; with the bankers Joseph Duruey, and Tourteau de Septeuil; with Arnaud Laporte, a Royalist government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Constitution Of 1791
The French Constitution of 1791 () was the first written constitution in France, created after the collapse of the absolute monarchy of the . One of the basic precepts of the French Revolution was adopting constitutionality and establishing popular sovereignty. Drafting process Early efforts Following the Tennis Court Oath, the National Assembly began the process of drafting a constitution as its primary objective. The Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, adopted on 26 August 1789 eventually became the preamble of the constitution adopted on 3 September 1791. The Declaration offered sweeping generalizations about rights, liberty, and sovereignty. A twelve-member Constitutional Committee was convened on 14 July 1789 (coincidentally the day of the Storming of the Bastille). Its task was to do much of the drafting of the articles of the constitution. It included originally two members from the First Estate (Champion de Cicé, Archbishop of Bordeaux and Tal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximilien Robespierre
Maximilien François Marie Isidore de Robespierre (; ; 6 May 1758 – 28 July 1794) was a French lawyer and statesman, widely recognised as one of the most influential and controversial figures of the French Revolution. Robespierre fervently campaigned for the voting rights of universal manhood suffrage, all men and their unimpeded admission to the National Guard (France), National Guard. Additionally, he advocated the right to petition, the right to bear arms in self-defence, and the abolition of the Atlantic slave trade. A radical Jacobin leader, Robespierre was elected as a deputy to the National Convention in September 1792, and in July 1793, he was appointed a member of the Committee of Public Safety. Robespierre faced growing disillusionment due in part to the politically motivated violence associated with him. Increasingly, members of the Convention turned against him, and accusations came to a head on 9 Thermidor. Robespierre was arrested and with around 90 othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
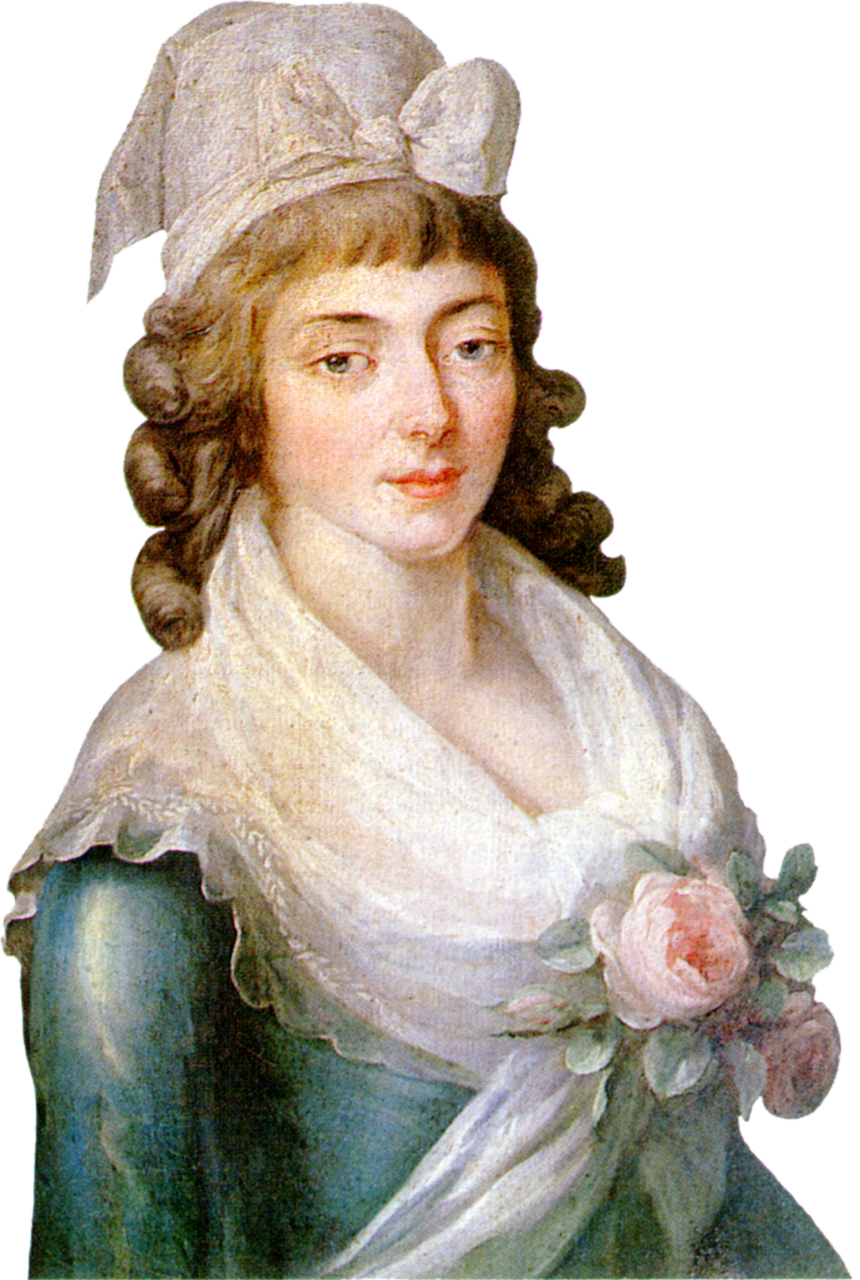
Élisabeth Of France
Élisabeth of France (Élisabeth Philippine Marie HĂ©lène; 3 May 1764 – 10 May 1794), also known as Madame Élisabeth, was a French princess. She was the youngest child of Louis, Dauphin of France, and Duchess Maria Josepha of Saxony, and she was a sister of King Louis XVI. Élisabeth's father, the Dauphin, was the son and heir of King Louis XV and his popular wife, Queen Marie LeszczyÅ„ska. Élisabeth remained beside her brother and his family during the French Revolution, and she was executed during the Reign of Terror at the Place de la RĂ©volution. The cause for her beatification and canonization has been introduced by the Catholic Church, and she has been declared a Servant of God by Pope Pius XII. Early life Élisabeth Philippe Marie HĂ©lène was born on 3 May 1764 in the Palace of Versailles. She was the youngest child of Louis, Dauphin of France, and Marie-Josèphe of Saxony. Her paternal grandparents were King Louis XV and Queen Marie LeszczyÅ„ska. As the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |