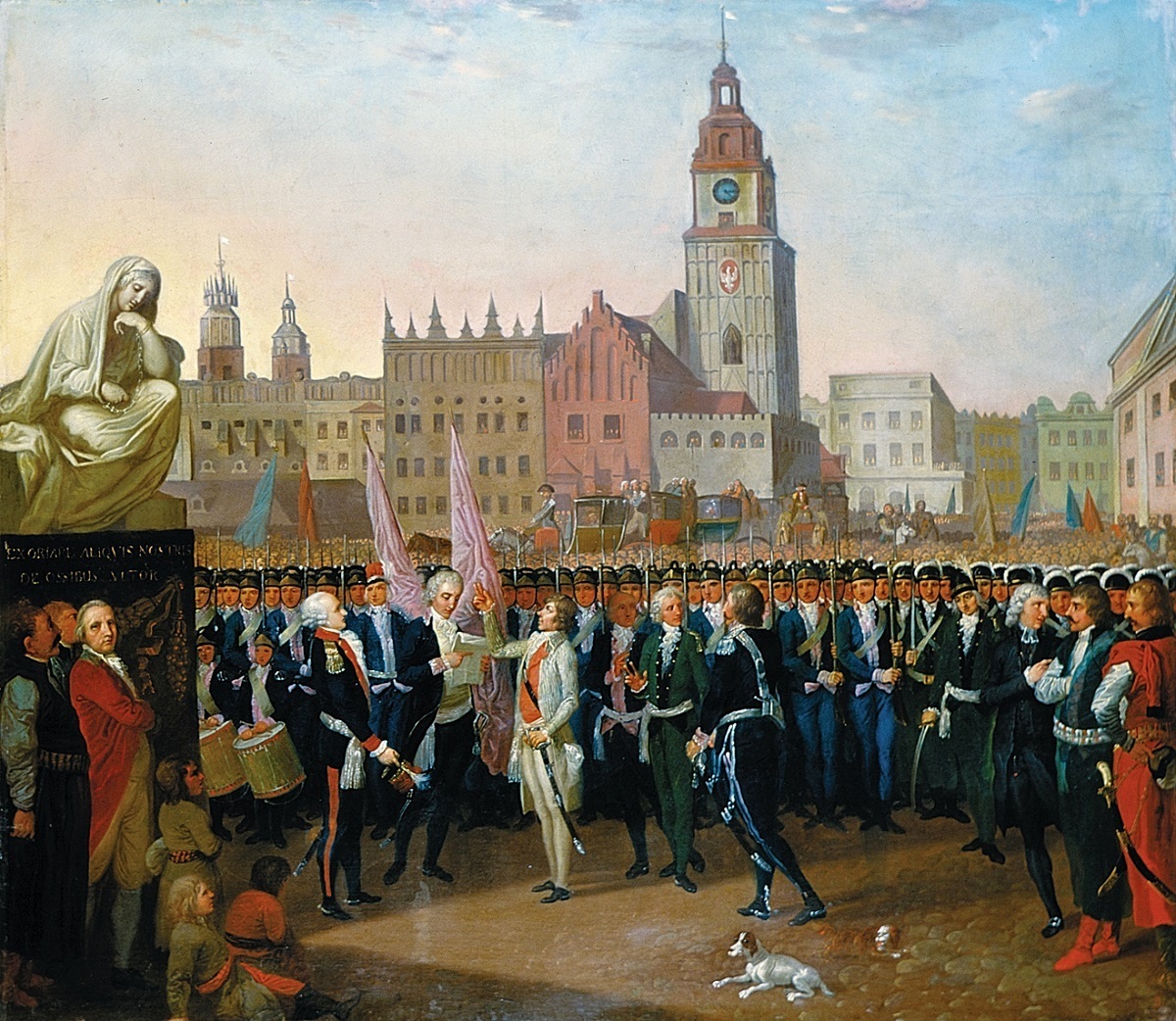|
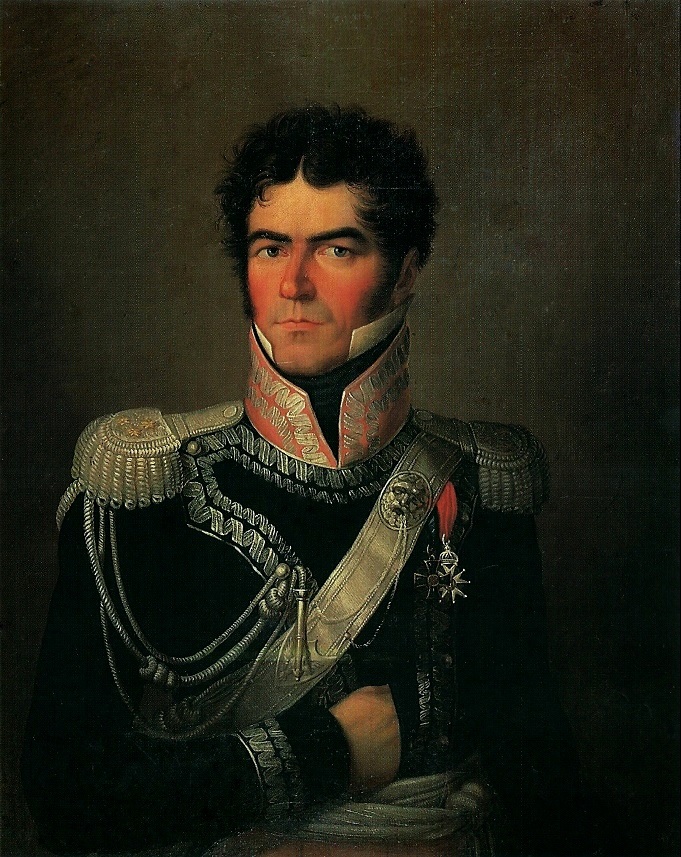
Eustachy Erazm Sanguszko
Prince Eustachy Erazm Sanguszko (1768–1844) was a Polish Szlachta, nobleman, general, military commander, diplomat and politician. Early life Eustachy Erazm Sanguszko was born in 1768 to Hieronim Janusz Sanguszko and Cecylia Usrzula Potocka. French Royal army In the years 1780–1786, Sanguszko graduated from the military school of Strasbourg and served in the Régiment Royal-Allemand (together with Stanisław Mokronowski) of the French Royal Army (1652–1830), French Royal army. Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth Four-Year Sejm On 3 February 1789, Sanguszko began service in the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Crown Army as a captain in the . On 5 October 1789, he was promoted to Major (rank), major, and on 28 April 1792, to vice-brigadier. He was a representative of the Lublin Voivodeship (1474–1795), Lublin Voivodeship in the Great Sejm of 1788–1792. Sanguszko partook in the Polish–Russian War of 1792, War of the Second Partition where he fought at the Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eustachy Sanguszko 1814
Eustachy is a given name. Notable people with the name include: *Eustachy Erazm Sanguszko (1768–1844), Polish general and politician *Eustachy Sapieha (1881–1963), Polish nobleman, prince, politician, Minister of Foreign Affairs and deputy to the Polish parliament *Eustachy Stanisław Sanguszko (1842–1903), Polish noble (szlachcic), conservative politician *Eustachy Tyszkiewicz (1814–1874), Polish–Lithuanian noble, archaeologist and historian from the former Grand Duchy of Lithuania *Larry Eustachy (born 1955), former NCAA Men's Basketball coach {{given name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Of The Kingdom Of Poland
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland (; ) was a political and legal concept formed in the 14th century in the Kingdom of Poland, assuming unity, indivisibility and continuity of the state. Under this idea, the state was no longer seen as the Patrimonialism, patrimonial property of the monarch or dynasty, but became a common good of the political community of the kingdom. This notion allowed the state to maintain stability even during periods of interregnum and paved the way for a unique political system in Poland, characterized by a noble-based parliament and the Free election (Poland), free election of the monarch. Additionally, the concept of the Crown extended beyond existing borders, asserting that previously lost territories still rightfully belonged to it. The term ''Crown of the Kingdom of Poland'' also referred to all the lands under the rule of the Polish king. This meaning became especially significant after the Union of Lublin, union with the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a Warsaw metropolitan area, greater metropolitan area of 3.27 million residents, which makes Warsaw the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 6th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures and comprises List of districts and neighbourhoods of Warsaw, 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers . Warsaw is classified as an Globalization and World Cities Research Network#Alpha 2, alpha global city, a major political, economic and cultural hub, and the country's seat of government. It is also the capital of the Masovian Voivodeship. Warsaw traces its origins to a small fishing town in Masovia. The city rose to prominence in the late 16th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Szczekociny
The Battle of Szczekociny was fought on the 6 June 1794 near the town of Szczekociny, Lesser Poland, between Poland and the combined forces of the Russian Empire and Kingdom of Prussia. Polish forces were led by Tadeusz Kościuszko, and the Russians and Prussians by Alexander Tormasov, future eminent general of the Napoleonic Wars. Tormasov was aided by Prussian General Francis Favrat, who emphasized the use of artillery, which put Russian-Prussian forces in the advantage. Background Following the Russian defeat at the Battle of Raclawice, the Prussians entered Poland to help confront the Polish revolt. Prussia and Russia were threatened by the sanctuary Poland offered serfs and Prussia was additionally threatened by their burghers lured to Poland's promise of democracy and free-market economy. On the morning of the 6 June, General Wodzicki noted, "It is impossible that Denisov could have amassed such an army. My eyes must be wrong, but I can see Prussians." Kosciuszko had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kościuszko Uprising
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794, Second Polish War, Polish Campaign of 1794, and the Polish Revolution of 1794, was an uprising against the Russian and Prussian influence on the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in Poland-Lithuania and the Prussian partition in 1794. It was a failed attempt to liberate the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from external influence after the Second Partition of Poland (1793) and the creation of the Targowica Confederation. Background Decline of the Commonwealth By the early 18th century, the magnates of Poland and Lithuania controlled the state – or rather, they managed to ensure that no reforms would be carried out that might weaken their privileged status (the " Golden Freedoms"). Through the abuse of the '' liberum veto'' rule which enabled any deputy to paralyze the Sejm (Commonwealth's parliament) proceedings, deputies bribed by magnates or foreign powers or those sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Russian Army
The Imperial Russian Army () was the army of the Russian Empire, active from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was organized into a standing army and a state militia. The standing army consisted of Regular army, regular troops and two forces that served on separate regulations: the Cossacks, Cossack troops and the Islam in Russia, Muslim troops. A regular Russian army existed after the end of the Great Northern War in 1721.День Сухопутных войск России. Досье [''Day of the Ground Forces of Russia. Dossier''] (in Russian). TASS. 31 August 2015. During his reign, Peter the Great accelerated the modernization of Russia's armed forces, including with a decree in 1699 that created the basis for recruiting soldiers, military regulations for the organization of the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Targowica Confederation
The Targowica Confederation (, , ) was a confederation established by Polish and Lithuanian magnates on 27 April 1792, in Saint Petersburg, with the backing of the Russian Empress Catherine II. The confederation opposed the Constitution of 3 May 1791 and fought in the Polish–Russian War of 1792, which led to the Second and Third Partitions of Poland. History The Targowica confederation opposed the Constitution of 3 May 1791, which had been adopted by the Great Sejm, especially the provisions limiting the privileges of the nobility. The text of the founding act of the confederation was drafted by the Russian general Vasili Stepanovich Popov, Chief of Staff of Prince Grigori Alexandrovich Potemkin. Its purpose was proclaimed in the small town of Targowica and the Potocki's estate (now in Holovanivsk Raion in Kirovohrad Oblast, Ukraine) on May 14, 1792. Four days later two Russian armies invaded the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth without a formal declaration of war. The forces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigadier
Brigadier ( ) is a military rank, the seniority of which depends on the country. In some countries, it is a senior rank above colonel, equivalent to a brigadier general or commodore (rank), commodore, typically commanding a brigade of several thousand soldiers. In other countries, it is a Non-commissioned officer, non-commissioned rank. Origins and history The word and rank of "Brigadier" originates from France. In the French Army, the Brigadier des Armées du Roi (Brigadier of the King's Armies) was a general officer rank, created in 1657. It was an intermediate between the rank of Mestre de camp and that of Maréchal de camp. The rank was first created in the cavalry at the instigation of Marshal Turenne on June 8, 1657, then in the infantry on March 17, 1668, and in the dragoons on April 15, 1672. In peacetime, the brigadier commanded his regiment and, in maneuvers or in wartime, he commanded two or three - or even four - regiments combined to form a brigade (including his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtuti Militari
The War Order of Virtuti Militari (Latin: ''"For Military Virtue"'', ) is Poland's highest military decoration for heroism and courage in the face of the enemy at war. It was established in 1792 by the last King of Poland Stanislaus II of Poland, Stanislaus II Augustus and is the oldest Military awards and decorations, military decoration in the world still in use. It is awarded in five classes either for personal heroism or, to commanders, for leadership. Some of the heroic actions recognized by an award of the Virtuti Militari are equivalent to those meriting the Commonwealth of Nations, British Victoria Cross and the United States, American Medal of Honor. Soon after its introduction, however, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was destroyed in the partitions of Poland (1795), and the partitioning powers abolished the decoration and prohibited its wearing. Since then, the award has been reintroduced, renamed and banned several times, with its fate closely reflecting the Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Zieleńce
The Battle of Zieleńce was a battle in the Polish–Russian War of 1792, in defence of the Polish Constitution of 3 May 1791. The battle took place on 18 June 1792, between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Army of Józef Poniatowski and an Imperial Russian Army group under the command of General Irakly Morkov, which was a part of General Mikhail Krechetnikov's Russian forces invading the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from the south. The battle ended in Polish victory, as the Russian assault was repulsed, although the Poles soon withdrew from the battlefield. Prelude Polish forces had been retreating for several weeks, avoiding a decisive engagement with the numerically superior Russian forces. On 15 June, the combined Polish forces reached Połonne. After a meeting, the Polish commanders decided to withdraw because they did not have the possibility of defending a town that did not have fortifications. On 17 June, Polish commander Prince Józef Poniatowski received ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Russian War Of 1792
The Polish–Russian War of 1792 (also, War of the Second Partition, and in Polish sources, War in Defence of the Constitution) was fought between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth on one side, and the Targowica Confederation (conservative nobility of the Commonwealth opposed to the new Constitution of 3 May 1791) and the Russian Empire under Catherine the Great on the other. The war took place in two theaters: a northern in Lithuania and a southern in what is now Ukraine. In both, the Polish forces retreated before the numerically superior Russian forces, though they offered significantly more resistance in the south, thanks to the effective leadership of Polish commanders Prince Józef Poniatowski and Tadeusz Kościuszko. During the three-month-long struggle several battles were fought, but no side scored a decisive victory. The largest success of the Polish forces was the defeat of one of the Russian formations at the Battle of Zieleńce on 18 June; in the aftermath of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Sejm
The Great Sejm, also known as the Four-Year Sejm (Polish language, Polish: ''Sejm Wielki'' or ''Sejm Czteroletni''; Lithuanian language, Lithuanian: ''Didysis seimas'' or ''Ketverių metų seimas'') was a Sejm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Sejm (parliament) of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that was held in Warsaw between 1788 and 1792. Its principal aim became to restore sovereignty to, and reform, the Commonwealth politically and economically. The Sejm's great achievement was the adoption of the Constitution of 3 May 1791, often described as Europe's first modern written national constitution, and the world's second, after the United States Constitution. The Polish Constitution was designed to redress long-standing political defects of the federation, federative Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and its system of Golden Liberty, Golden Liberties. The Constitution introduced political equality between townspeople and szlachta, nobility and placed the peasants under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |