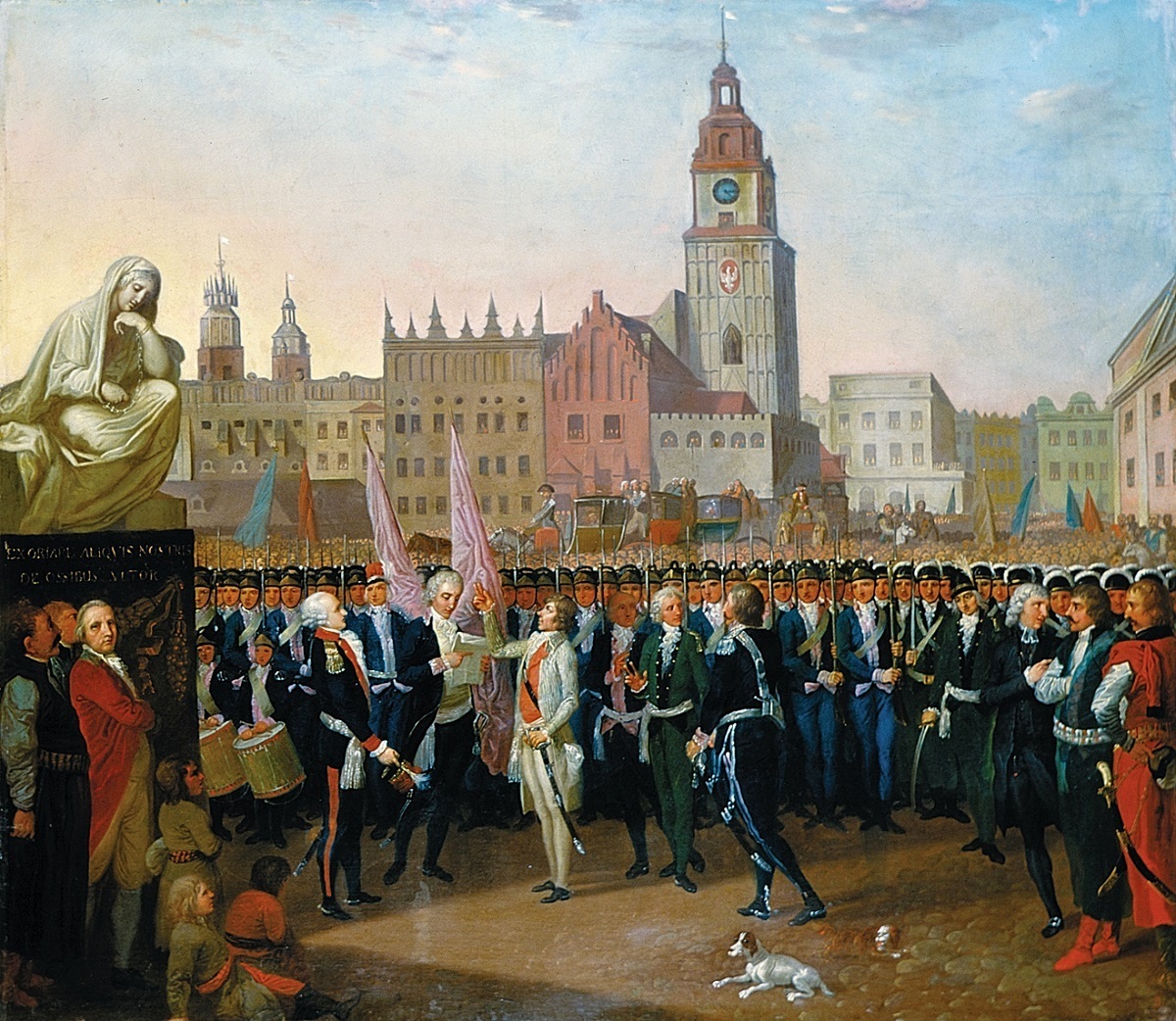|
Targowica Confederation
The Targowica Confederation (, , ) was a confederation established by Polish and Lithuanian magnates on 27 April 1792, in Saint Petersburg, with the backing of the Russian Empress Catherine II. The confederation opposed the Constitution of 3 May 1791 and fought in the Polish–Russian War of 1792, which led to the Second and Third Partitions of Poland. History The Targowica confederation opposed the Constitution of 3 May 1791, which had been adopted by the Great Sejm, especially the provisions limiting the privileges of the nobility. The text of the founding act of the confederation was drafted by the Russian general Vasili Stepanovich Popov, Chief of Staff of Prince Grigori Alexandrovich Potemkin. Its purpose was proclaimed in the small town of Targowica and the Potocki's estate (now in Holovanivsk Raion in Kirovohrad Oblast, Ukraine) on May 14, 1792. Four days later two Russian armies invaded the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth without a formal declaration of war. The forces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
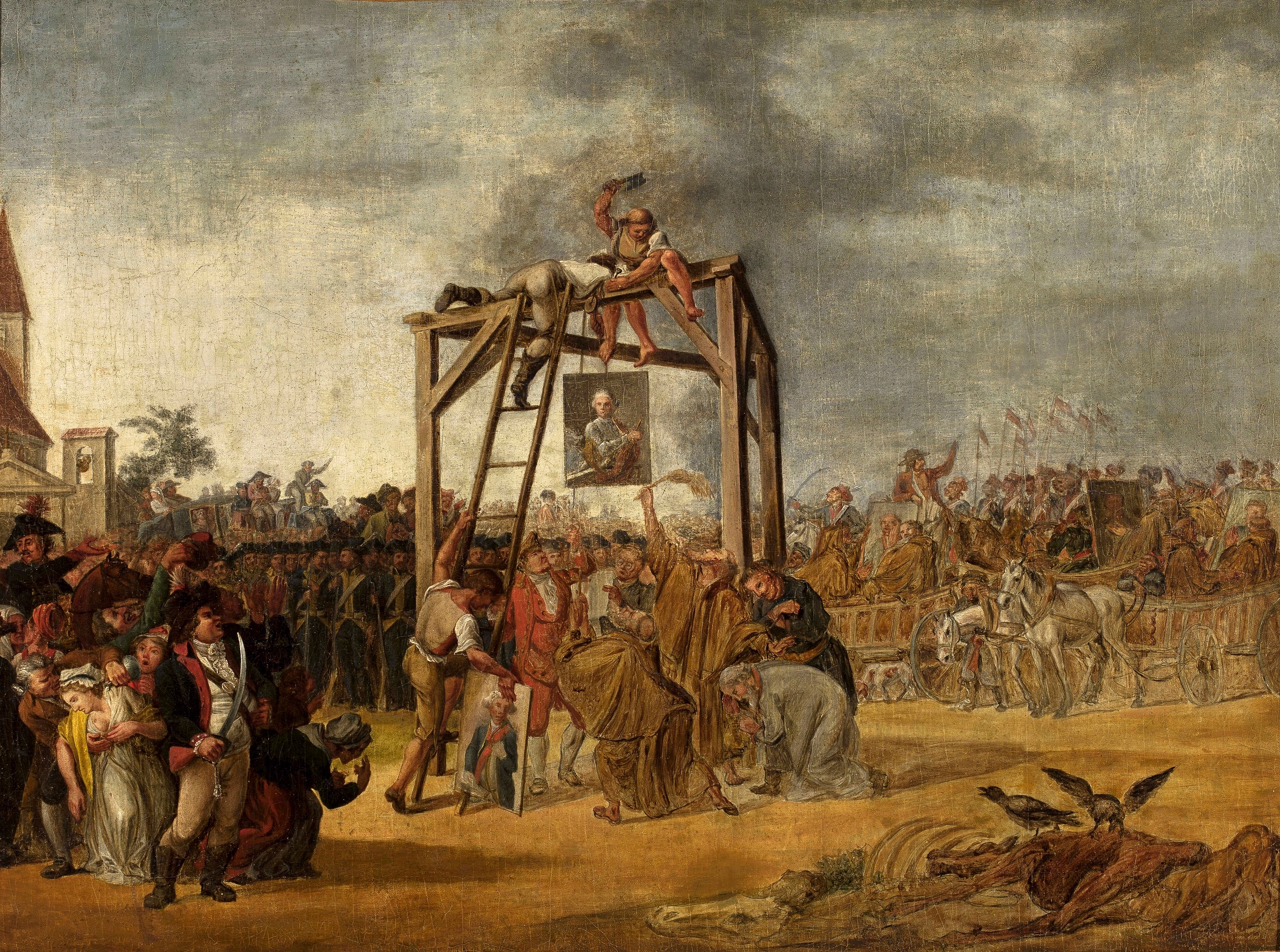
Norblin Hanging Of Traitors In Effigie (1781–1854), French musician, cello teacher at the Paris Conservatoire
{{surname ...
Norblin is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Jan Piotr Norblin (Jean Pierre) (1740–1830), French-Polish painter, draughtsman, engraver, and caricaturist *Louis Norblin Louis Pierre Martin Norblin (2 December 1781, in Warsaw – 14 July 1854, in Connantre) was a French musician. His father was Polish-French painter Jan Piotr Norblin (1740–1830). He taught cello at the Paris Conservatoire, where his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stanisław August Poniatowski
Stanisław II August (born Stanisław Antoni Poniatowski; 17 January 1732 – 12 February 1798), known also by his regnal Latin name Stanislaus II Augustus, and as Stanisław August Poniatowski (), was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1764 to 1795, and the last monarch of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Born into wealthy Polish aristocracy, Poniatowski arrived as a diplomat at the Russian imperial court in Saint Petersburg in 1755 at the age of 22 and became intimately involved with the future empress Catherine the Great. With her aid, he was elected King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania by the Sejm in September 1764 following the death of Augustus III. Contrary to expectations, Poniatowski attempted to reform and strengthen the large but ailing Commonwealth. His efforts were met with external opposition from neighbouring Prussia, Russia and Austria, all committed to keeping the Commonwealth weak. From within he was opposed by conservative interests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Józef Kazimierz Kossakowski
Józef is a Polish variant of the masculine given name Joseph. Art * Józef Chełmoński (1849-1914), Polish painter * Józef Gosławski (1908-1963), Polish sculptor Clergy * Józef Glemp (1929-2013), Polish cardinal * Józef Kowalski (1911-1942), Polish priest * Józef Milik (1922-2006), Polish priest and biblical scholar * Józef Tischner (1931-2000), Polish priest * Józef Andrzej Załuski (1702-1774), Polish priest and Bishop of Kyiv * Józef Życiński (1948-2011), Polish archbishop Literature * Józef Maksymilian Ossoliński (1748-1826), Polish novelist and poet * Józef Wybicki (1747-1822), Polish poet Military * Józef Bem (1794-1850), Polish general and engineer * Józef Grzesiak (1900-1975), Polish resistance member and scoutmaster * Józef Haller (1873-1960), Polish general * Józef Piotrowski (1840-1923), Polish participant in the January Uprising * Józef Poniatowski (1763-1813), Polish general * Józef Sowiński (1777-1831), Polish general * Józ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
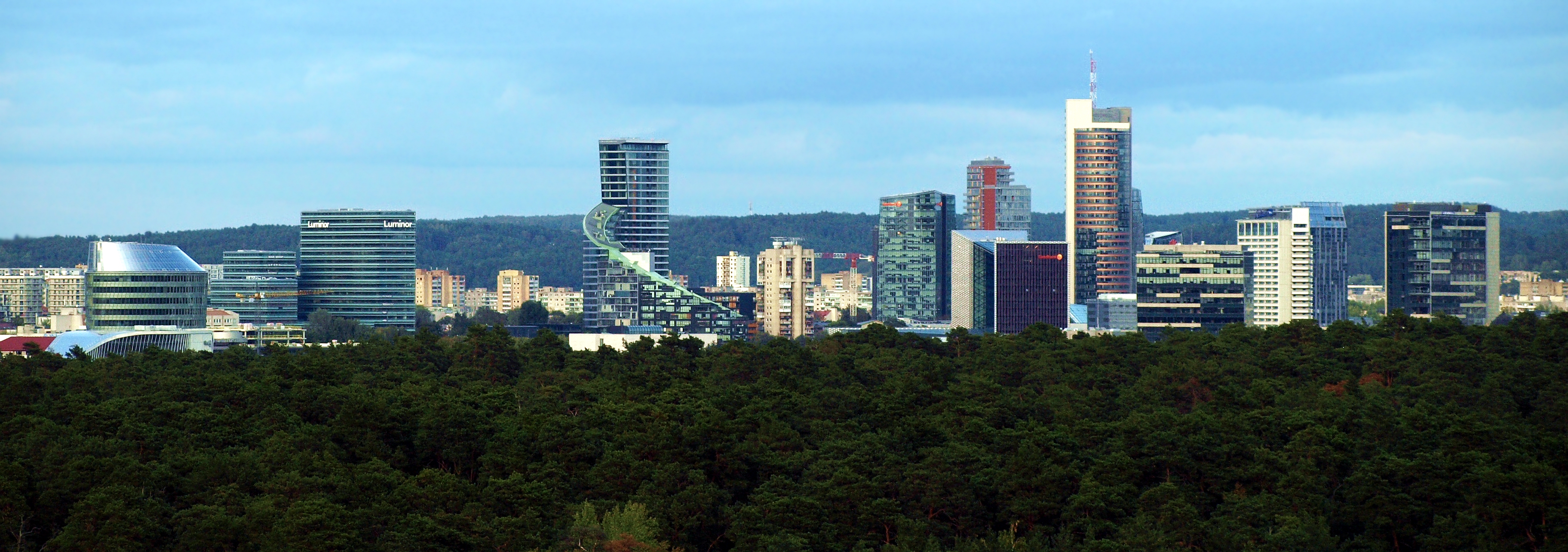
Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population was 607,667, and the Vilnius urban area (which extends beyond the city limits) has an estimated population of 747,864. Vilnius is notable for the architecture of its Vilnius Old Town, Old Town, considered one of Europe's largest and best-preserved old towns. The city was declared a World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1994. The architectural style known as Vilnian Baroque is named after the city, which is farthest to the east among Baroque architecture, Baroque cities and the largest such city north of the Alps. The city was noted for its #Demographics, multicultural population during the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, with contemporary sources comparing it to Babylon. Before World War II and The Holocaust in Lithuania, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Szymon Kossakowski
Szymon Marcin Kossakowski (; 1741 in Šilai, Jonava – 1794) was a Polish–Lithuanian nobleman (szlachcic), and one of the leaders of the Targowica Confederation. In 1793, he became the last Grand Hetman of Lithuania. Biography He participated in the Radom Confederation and the Bar Confederation. He was known as a supporter of the Russian Empire during the Kościuszko Uprising and earlier, he was deemed a traitor. In the aftermath of the Vilnius Uprising, he was captured and hanged in the town hall square of Vilnius with the inscription of ''He who swings will not drown'' and was buried in the cellars of the church in Jonava Jonava () is the ninth largest city in Lithuania with a population of . It is located in Kaunas County in central Lithuania, north east of Kaunas, the second-largest city in Lithuania. It is served by Kaunas International Airport. ''Achema'', t .... References 1741 births 1794 deaths People from Jonava District Municipality People from T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bila Tserkva
Bila Tserkva ( ; , ) is a city in central Ukraine. It is situated on the Ros (river), Ros River in the historical region of right-bank Ukraine. It is the largest city in Kyiv Oblast (which does not include the city of Kyiv) and serves as the administrative centre of Bila Tserkva Raion and Bila Tserkva urban Hromadas of Ukraine, hromada, and has a population of , 205,000 (2024 estimate). The oldest preserved document that mentions the city, at that time called ''Yuryiv'', is the ''Hypatian Codex'' (1115). Historically, the city has been at the centre of the ''Porossia'' (River Ros) region. Founded as a border fortification of Kievan Rus', Bila Tserkva later became property of Polish nobility and served as a prominent commercial centre. Since the 19th century, industry and tourism have been important elements of the city's economy. Under Ukrainian SSR, Soviet rule, Bila Tserkva became a centre of agricultural education. During the Cold War, a major Soviet Air Force base was loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kościuszko Uprising
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794, Second Polish War, Polish Campaign of 1794, and the Polish Revolution of 1794, was an uprising against the Russian and Prussian influence on the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in Poland-Lithuania and the Prussian partition in 1794. It was a failed attempt to liberate the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from external influence after the Second Partition of Poland (1793) and the creation of the Targowica Confederation. Background Decline of the Commonwealth By the early 18th century, the magnates of Poland and Lithuania controlled the state – or rather, they managed to ensure that no reforms would be carried out that might weaken their privileged status (the " Golden Freedoms"). Through the abuse of the '' liberum veto'' rule which enabled any deputy to paralyze the Sejm (Commonwealth's parliament) proceedings, deputies bribed by magnates or foreign powers or those sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Franciszek Ksawery Branicki
Franciszek Ksawery Branicki (1730–1819) was a Polish nobleman, magnate, French count, diplomat, politician, military commander, and one of the leaders of the Targowica Confederation. Many consider him to have been a traitor who participated with the Russians in the dismemberment of his nation. Early life Born into the mighty House of Branicki, he was the son Piotr Branicki, Chorąży of Halicz, Castellan of Bratslav (1708-1762) and his wife, Melania Teresa Szembek (b. 1712). He was the brother of Princess Elżbieta Sapieha. Career He was appointed Great Crown Podstoli in 1764, Ambassador to Berlin in 1765, Master of the Hunt of the Crown in 1766–1773, Artillery General of Lithuania in 1768–1773, Ambassador to Moscow in 1771, Crown Hetman in 1773 and was Great Crown Hetman of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth between 1774 and 1794. In 1774, Stanisław August Poniatowski ceded to him, as mark of his confidence and esteem, the immense estate of Bila Tserkva in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Karol Boscamp-Lasopolski
Karol Boscamp-Lasopolski (also Boskamp, de Boscamp, de Boskamp) (died 28 June 1794) was a Dutch diplomat in service of Poland and Russia. He was a Chamberlain in the court of Polish king Stanisław August Poniatowski. He was lynched by a mob during the Warsaw Uprising of 1794. Biography Little is known about his youth. He was born in the Netherlands; some other sources note his French origin. He served as a courier for the Prussian envoy in Istanbul during the Seven Years' War. In 1761 he served as an adviser to Crimean Khan, Qırım Giray. After he became estranged from the Khan, he left for Poland. From 1764 he served in the Polish diplomatic service, first under Familia, and soon under king Stanisław August Poniatowski. He used his expertise on the Ottoman politics to aid Polish relations, worked with the envoy Tomasz Aleksandrowicz and was one of the founders of the School of Oriental Languages in Istanbul, which served as an unofficial Polish embassy there.Władysław Kon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hanging
Hanging is killing a person by suspending them from the neck with a noose or ligature strangulation, ligature. Hanging has been a standard method of capital punishment since the Middle Ages, and has been the primary execution method in numerous countries and regions. The first known account of execution by hanging is in Homer's ''Odyssey''. Hanging is also a Suicide by hanging, method of suicide. Methods of judicial hanging There are numerous methods of hanging in execution that instigate death either by cervical fracture or by Strangling, strangulation. Short drop The short drop is a method of hanging in which the condemned prisoner stands on a raised support, such as a stool, ladder, cart, horse, or other vehicle, with the noose around the neck. The support is then moved away, leaving the person dangling from the rope. Suspended by the neck, the weight of the body tightens the noose around the neck, effecting strangulation and death. Loss of consciousness is typically rapid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Józef Ankwicz
Józef Ankwicz (; 1750 – 9 May 1794), of Awdaniec coat of arms, also known as ''Józef z Posławic'' and ''Józef Awdaniec'', was a politician and noble (''szlachcic'') in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. He held the office of castellan of Nowy Sącz from 1782. Deputy to the Great Sejm, and most infamously, the Grodno Sejm: for his actions during the latter he is remembered as one of the most prominent collaborators with the foreign partitioners of Poland. Biography Son of Stanisław Walenty Ankwicz and Salomea Schwarcemberg-Czerny. Married to Anna Biberstein-Starowieyska, father of Andrzej Alojzy Jan Stanisław Ankwicz (archbishop of Lviv) and daughters Kordula and Krystyna. He was also awarded with Order of Saint Stanislaus in 1781. In 1782 he received the office of castellan of Nowy Sącz. Elected deputy to the Sejms in the period 1782 - 1790, he was a member of the royal faction. In 1784 he received the Order of the White Eagle from king of Poland, Stanisław Augu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Général En Chef
is the French language, French word for general. There are two main categories of generals: the general officers (), which are the highest-ranking commanding officers in the armed forces, and the specialist officers with flag rank (), which are high-level officers in the other uniformed services. General officers Army History The French army of the monarchy had several ranks of general officer: * ("brigadier of the armies of the King"): a rank in a grey area of seniority, conferred on certain colonels who were in command of a brigade (''cf.'' the grey area of the naval "commodore" rank given to certain captains, the equivalent of army full colonels, who had been in command of a group of ships and over the captains of the group's other ships). These officers wore a colonel's uniform with a star on the shoulder straps. This rank was abolished in 1788. * ("field marshal"(major general)): the first substantive rank of general. The wore a special uniform, blue and red, with a sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |