|
Eumalacostraca
Eumalacostraca is a subclass of crustaceans, containing almost all living malacostracans, or about 40,000 described species. The remaining subclasses are the Phyllocarida and possibly the Hoplocarida. Eumalacostracans have 19 segments (5 cephalic, 8 thoracic and 6 abdominal). This arrangement is known as the "caridoid facies", a term coined by William Thomas Calman in 1909. The thoracic limbs are jointed and used for swimming or walking. The common ancestor is thought to have had a carapace, and most living species possess one, but it has been lost in some subgroups. Caridoid facies Calman identified the following features as distinguishing eumalacostracan crustaceans: "Carapace enveloping the thoracic region; movably stalked eyes; biramous first antenna; scale-like exopod on the second antenna; natatory exopods on the thoracic limbs; elongate, ventrally flexible abdomen; tail fan formed by the lamellar rami of the uropods on either side of the telson." Classification Martin and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malacostraca
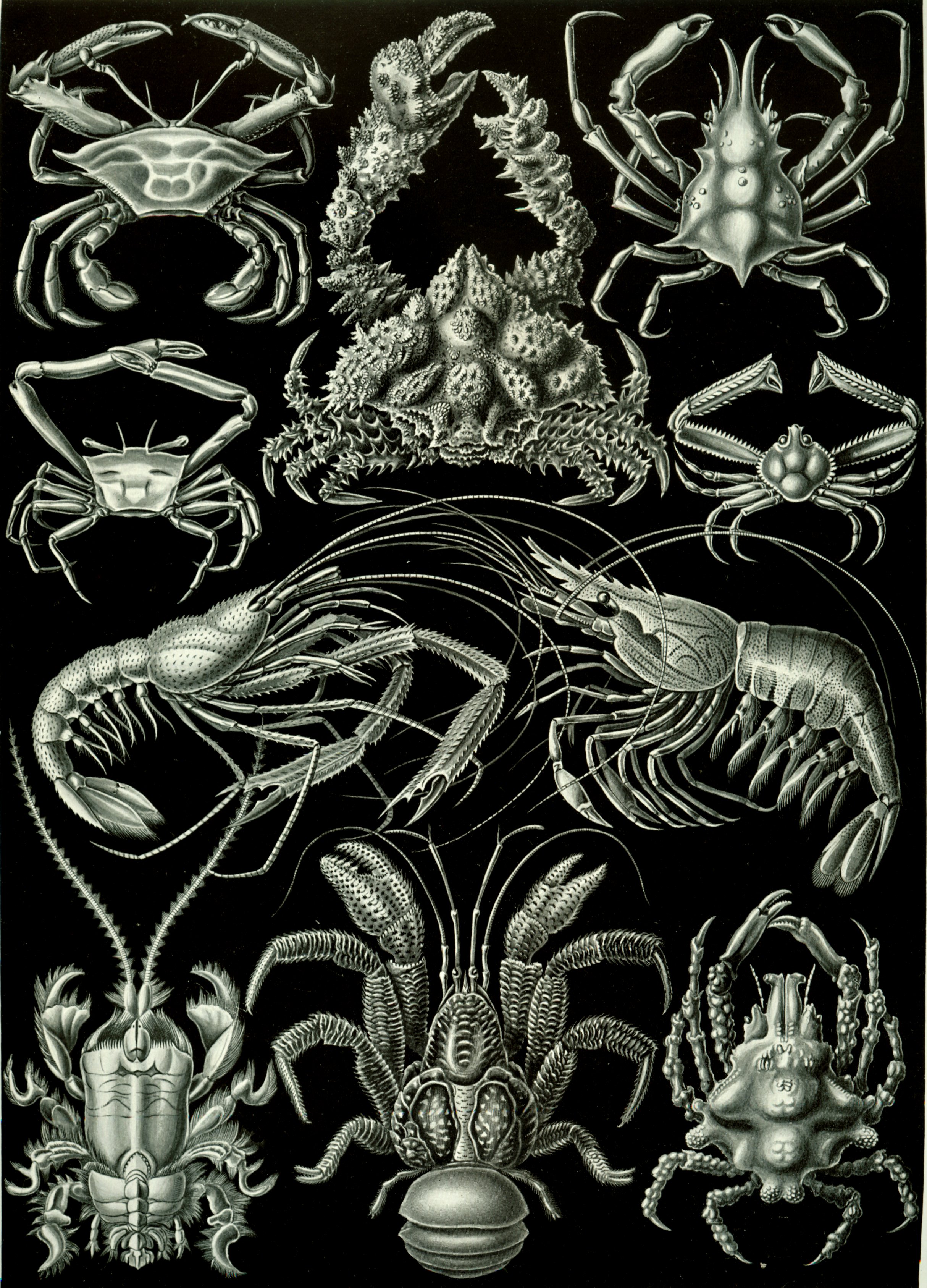
Malacostraca is the second largest of the six classes of pancrustaceans behind insects, containing about 40,000 living species, divided among 16 orders. Its members, the malacostracans, display a great diversity of body forms and include crabs, lobsters, spiny lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill, prawns, isopods, amphipods, mantis shrimp, and many other less familiar animals. They are abundant in all marine environments and have colonised freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are segmented animals, united by a common body plan comprising 20 body segments (rarely 21), and divided into a head, thorax, and abdomen. Etymology The name Malacostraca is . The word was used by Aristotle, who contrasted them with oysters, in comparison with which their shells are pliable. It was applied to this taxon by French zoologist Pierre André Latreille in 1802. He was curator of the arthropod collection at the National Museum of Natural History in Paris. This scientific name is misl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthropods including decapods (shrimps, prawns, crabs, lobsters and crayfish), seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, opossum shrimps, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods (insects and entognathans) emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed pan-group referred to as Pancrustacea. The three classes Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda and Remipedia are more closely related to the hexapods than they are to any of the other crustaceans ( oligostracans and multicrustaceans). The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Grobben
Karl Grobben (27 August 1854, in Brno – 13 April 1945, in Salzburg) was an Austrian zoologist. He graduated from, and later worked at, the University of Vienna, chiefly on molluscs and crustaceans. He was also the editor of a new edition of Carl Friedrich Wilhelm Claus' ''Lehrbuch der Zoologie'', and the coiner of the terms ''protostome'' and ''deuterostome''. Taxonomy Taxa named by Grobben include: *Eumalacostraca Grobben, 1892 * Sagittidae Claus & Grobben, 1905 * Sagittoidea Claus & Grobben, 1905 *Protostomia Grobben, 1908 *Deuterostomia Deuterostomes (from Ancient Greek, Greek: ) are bilaterian animals of the superphylum Deuterostomia (), typically characterized by their anus forming before the mouth during embryogenesis, embryonic development. Deuterostomia comprises three Phyl ... Grobben, 1908 Taxa named in Grobben's honour include: *'' Gerbillus grobbeni'' Klaptocz, 1909 *'' Sphaerophthalmus grobbeni'' Spandl, 1923 *'' Limnadia grobbeni'' Daday, 1925 *'' Actinia grob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucarida
Eucarida is a superorder of the Malacostraca, a class of the crustacean subphylum, comprising the decapods, krill, and Angustidontida. They are characterised by having the carapace fused to all thoracic segments, and by the possession of stalked eyes. Orders Eucarida is a diverse and abundant group, comprising the following three orders: Euphausiacea The members of the Euphausiacea are commonly called krill and are all marine shrimp-like species whose pleopods (abdominal appendages) function as swimmerets. They swarm and mostly feed on plankton. This group is composed of only 90 species, some of which are the most abundant species on the planet; in fact, it is estimated that the biomass of the Antarctic krill ''Euphausia superba is 500 million tons. Decapoda Decapoda is a group with 15,000 species which have 5 pairs of thoracopods and a well-developed carapace that covers the gills (which are exposed in krill). They include lobsters, crabs, shrimp and prawns. The decapods a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decapoda
The Decapoda or decapods, from Ancient Greek δεκάς (''dekás''), meaning "ten", and πούς (''poús''), meaning "foot", is a large order of crustaceans within the class Malacostraca, and includes crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, and prawns. Most decapods are scavengers. The order is estimated to contain nearly 15,000 extant species in around 2,700 genera, with around 3,300 fossil species. Nearly half of these species are crabs, with the shrimp (about 3,000 species) and Anomura including hermit crabs, king crabs, porcelain crabs, squat lobsters (about 2500 species) making up the bulk of the remainder. The earliest fossils of the group date to the Devonian. Anatomy Decapods can have as many as 38 appendages, arranged in one pair per body segment. As the name Decapoda (from the Greek , ', "ten", and , '' -pod'', "foot") implies, ten of these appendages are considered legs. They are the pereiopods, found on the last five thoracic segments. In many decapods, one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angustidontida
Angustidontidae is an extinct family of eucarid crustaceans and the sole representatives of the order Angustidontida. They were predators ranging in size from about in length and lived during the Late Devonian and Early Carboniferous periods. They were some of the earliest Eucarids to develop maxillipeds, modified from the first or second thoracopods. They were originally considered eurypterids, but later their possible relationship with decapods The Decapoda or decapods, from Ancient Greek δεκάς (''dekás''), meaning "ten", and πούς (''poús''), meaning "foot", is a large order (biology), order of crustaceans within the class Malacostraca, and includes crabs, lobsters, crayfis ... was established. References Prehistoric Malacostraca Prehistoric crustacean families Fossil taxa described in 1936 {{paleo-crustacean-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
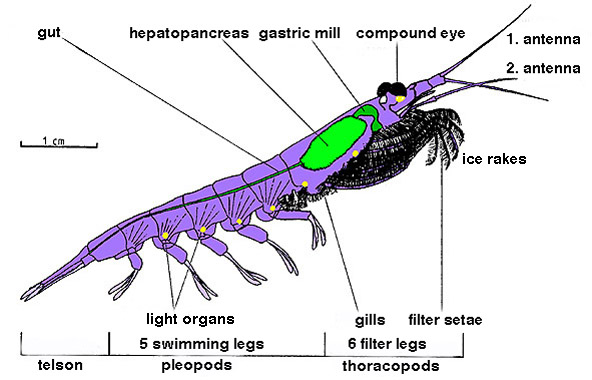
Euphausiacea
Krill ''(Euphausiids)'' (: krill) are small and exclusively marine crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, found in all of the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian word ', meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish. Krill are considered an important trophic level connection near the bottom of the food chain. They feed on phytoplankton and, to a lesser extent, zooplankton, and are also the main source of food for many larger animals. In the Southern Ocean, one species, the Antarctic krill, makes up an estimated biomass of around 379 million tonnes, making it among the species with the largest total biomass. Over half of this biomass is eaten by whales, seals, penguins, seabirds, squid, and fish each year. Most krill species display large daily vertical migrations, providing food for predators near the surface at night and in deeper waters during the day. Krill are fished commercially in the Southern Ocean and in the wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spelaeogriphacea
Spelaeogriphacea is an order of crustaceans that grow to no more than . Little is known about the ecology of the order. Only four species, all subterranean, have been described. Of the three genera, '' Potiicoara '' is known only from a cave in Brazil's Mato Grosso, '' Spelaeogriphus '' only from a cave on Table Mountain in South Africa, and the two '' Mangkurtu '' species only from individual Australian aquifers. Fossils of the group are known from the Early Carboniferous of Canada ('' Acadiocaris'') and the Early Cretaceous of Spain ('' Spinogriphus,'' Las Hoyas) and China ('' Liaoningogriphus,'' Yixian Formation The Yixian Formation (; formerly Romanization of Chinese, transcribed as Yihsien Formation or Yixiang Formation) is a geological formation in Jinzhou, Liaoning, People's Republic of China, that spans the Barremian stage of the Early Cretaceous. I ...), which are assigned to the family Acadiocarididae. References External links * Malacostraca Crustacean orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanaidacea
The crustacean order Tanaidacea (known as tanaids) make up a minor group within the class (biology), class Malacostraca. There are about 940 species in this order. Description Tanaids are small, shrimp-like creatures ranging from in adult size, with most species being from . Their carapace covers the first two segments of the thorax. There are three pairs of limbs on the thorax; a small pair of maxillipeds, a pair of large clawed gnathopods, and a pair of pereiopods adapted for burrowing into the mud. The remaining six thoracic segments each bear a pair of pereiopods, and each of the first five abdomen, abdominal segments normally carry pleopods. The final segment is fused with the telson and carries a pair of uropods. The gills lie on the inner surface of the carapace. The thoracic limbs wash water towards the mouth, filtering out small particles of food with the mouthparts or maxillipeds. Some species actively hunt prey, either as their only food source, or in combination with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopoda
Isopoda is an order of crustaceans. Members of this group are called isopods and include both aquatic species and terrestrial species such as woodlice. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the thorax, and five pairs of branching appendages on the abdomen that are used in respiration. Females brood their young in a pouch under their thorax called the marsupium. Isopods have various feeding methods: some eat dead or decaying plant and animal matter, others are grazers or filter feeders, a few are predators, and some are internal or external parasites, mostly of fish. Aquatic species mostly live on the seabed or the bottom of freshwater bodies of water, but some taxa can swim for short distance. Terrestrial forms move around by crawling and tend to be found in cool, moist places. Some species are able to roll themselves into a ball as a defense mechanism or to conserve moisture like species in the family Armadilli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphipoda
Amphipoda () is an order (biology), order of malacostracan crustaceans with no carapace and generally with laterally compressed bodies. Amphipods () range in size from and are mostly detritivores or scavengers. There are more than 10,700 amphipod species currently recognized. They are mostly marine animals, but are found in almost all aquatic environments. Some 2,250 species live in fresh water, and the order also includes the terrestrial Talitridae, sandhoppers such as ''Talitrus saltator'' and ''Arcitalitrus sylvaticus''. Etymology and names The name ''Amphipoda'' comes, via Neo-Latin ', from the Greek language, Greek root (linguistics), roots 'on both/all sides' and 'foot'. This contrasts with the related Isopoda, which have a single kind of thoracic leg. Particularly among Angling, anglers, amphipods are known as ''freshwater shrimp'', ''scuds'', or ''sideswimmers''. Description Anatomy The body of an amphipod is divided into 13 segments, which can be tagmosis, grouped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |