|
Eucarida
Eucarida is a superorder of the Malacostraca, a class of the crustacean subphylum, comprising the decapods, krill, and Angustidontida. They are characterised by having the carapace fused to all thoracic segments, and by the possession of stalked eyes. Orders Eucarida is a diverse and abundant group, comprising the following three orders: Euphausiacea The members of the Euphausiacea are commonly called krill and are all marine shrimp-like species whose pleopods (abdominal appendages) function as swimmerets. They swarm and mostly feed on plankton. This group is composed of only 90 species, some of which are the most abundant species on the planet; in fact, it is estimated that the biomass of the Antarctic krill ''Euphausia superba is 500 million tons. Decapoda Decapoda is a group with 15,000 species which have 5 pairs of thoracopods and a well-developed carapace that covers the gills (which are exposed in krill). They include lobsters, crabs, shrimp and prawns. The decapods a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malacostraca
Malacostraca is the second largest of the six classes of pancrustaceans behind insects, containing about 40,000 living species, divided among 16 orders. Its members, the malacostracans, display a great diversity of body forms and include crabs, lobsters, spiny lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill, prawns, isopods, amphipods, mantis shrimp, and many other less familiar animals. They are abundant in all marine environments and have colonised freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are segmented animals, united by a common body plan comprising 20 body segments (rarely 21), and divided into a head, thorax, and abdomen. Etymology The name Malacostraca is . The word was used by Aristotle, who contrasted them with oysters, in comparison with which their shells are pliable. It was applied to this taxon by French zoologist Pierre André Latreille in 1802. He was curator of the arthropod collection at the National Museum of Natural History in Paris. This scientific name is misl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
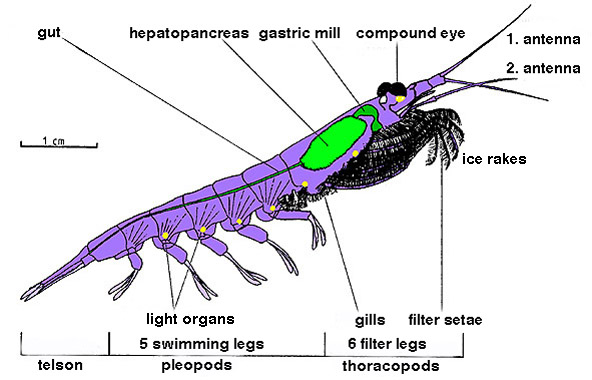
Euphausiacea
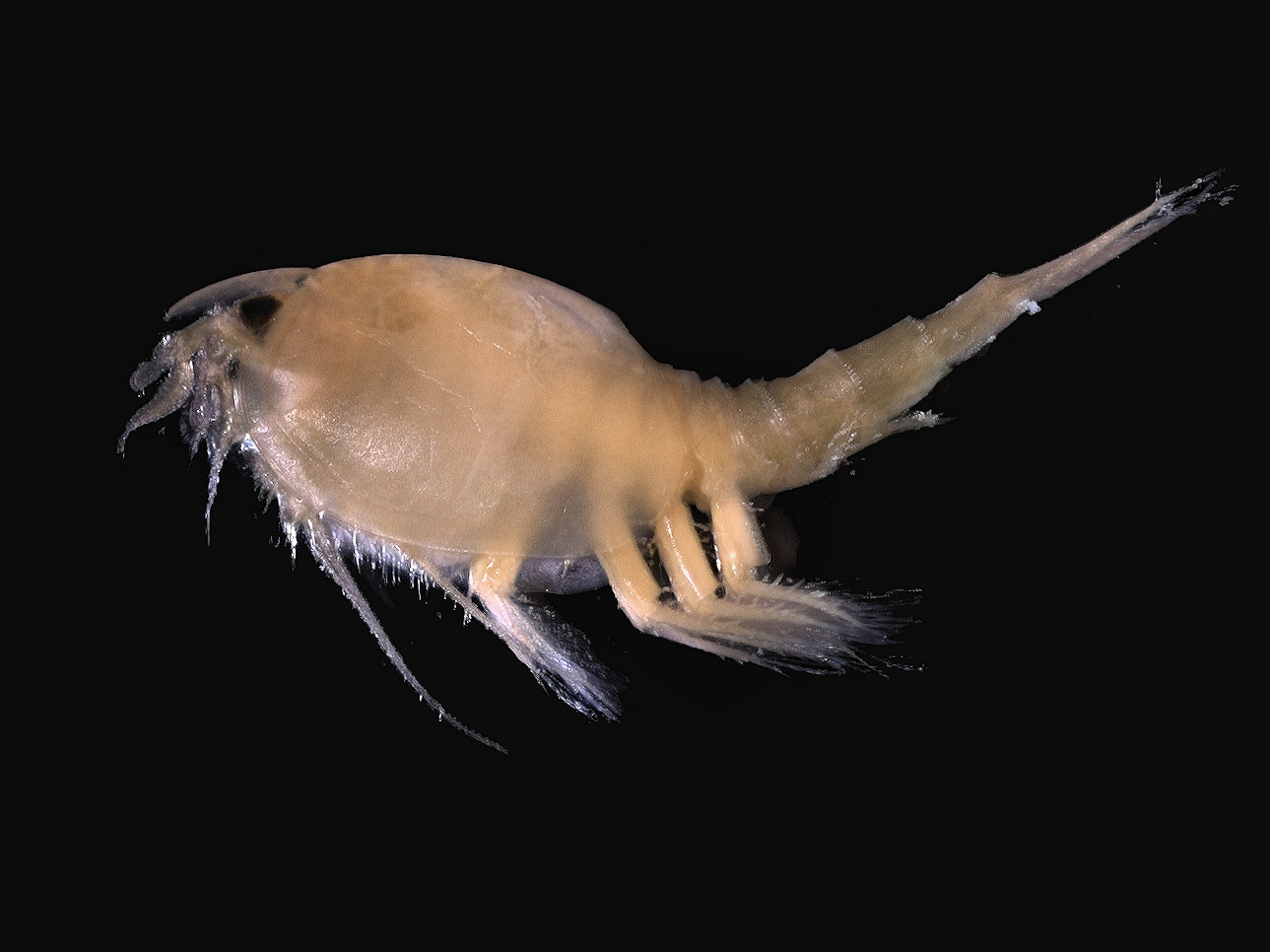
Krill ''(Euphausiids)'' (: krill) are small and exclusively marine crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, found in all of the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian word ', meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish. Krill are considered an important trophic level connection near the bottom of the food chain. They feed on phytoplankton and, to a lesser extent, zooplankton, and are also the main source of food for many larger animals. In the Southern Ocean, one species, the Antarctic krill, makes up an estimated biomass of around 379 million tonnes, making it among the species with the largest total biomass. Over half of this biomass is eaten by whales, seals, penguins, seabirds, squid, and fish each year. Most krill species display large daily vertical migrations, providing food for predators near the surface at night and in deeper waters during the day. Krill are fished commercially in the Southern Ocean and in the wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krill
Krill ''(Euphausiids)'' (: krill) are small and exclusively marine crustaceans of the order (biology), order Euphausiacea, found in all of the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian language, Norwegian word ', meaning "small Fry (biology), fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish. Krill are considered an important trophic level connection near the bottom of the food chain. They feed on phytoplankton and, to a lesser extent, zooplankton, and are also the main source of food for many larger animals. In the Southern Ocean, one species, the Antarctic krill, makes up an estimated biomass (ecology), biomass of around 379 million tonnes, making it among the species with the largest total biomass. Over half of this biomass is eaten by whales, Pinniped, seals, penguins, seabirds, squid, and fish each year. Most krill species display large diel vertical migration, daily vertical migrations, providing food for predators near the surface at night an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendrobranchiata
Dendrobranchiata is a suborder of Decapoda, decapods, commonly known as prawns. There are 540 extant species in seven families, and a fossil record extending back to the Devonian. They differ from related animals, such as Caridea and Stenopodidea, by the branching form of the gills and by the fact that they do not brood their eggs, but release them directly into the water. They may reach a length of over and a mass of , and are widely shrimp fishery, fished and shrimp farm, farmed for human consumption. Shrimp and prawns While Dendrobranchiata and Caridea belong to different Order (biology), suborders of Decapoda, they are very similar in appearance, and in many contexts such as commercial farming and Fishery, fisheries, they are both often referred to as "shrimp" and "prawn" interchangeably. In the United Kingdom, Australia and some other Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth, the word "prawn" is used almost exclusively, while the opposite is the case in North America. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Thomas Calman
William Thomas Calman (29 December 1871 – 29 September 1952) was a Scottish zoologist, specialising in the Crustacea. From 1927 to 1936 he was Keeper of Zoology at the British Museum (Natural History) (now the Natural History Museum). Life He was born in Dundee, the son of Thomas Calman, a music teacher, and Agnes Beatts Maclean. He studied at the High School of Dundee. In the scientific societies in Dundee, he met D'Arcy Thompson. He later became Thompson's lab boy, which allowed him to attend lectures at University College, Dundee for free. A. D. Peacock, one of Thompson's successors to the chair of Natural history at Dundee, believed this appointment came about following a letter sent by Calman in 1891 asking Thompson's advice as to applying for a post in Edinburgh. After his graduation with distinction in 1895, he took on a lecturership at the university, where he remained for eight years. When Thompson died, Calman, along with Douglas Young, wrote his obituary noti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angustidontidae
Angustidontidae is an extinct family of eucarid crustaceans and the sole representatives of the order Angustidontida. They were predators ranging in size from about in length and lived during the Late Devonian and Early Carboniferous periods. They were some of the earliest Eucarids to develop maxillipeds, modified from the first or second thoracopods. They were originally considered eurypterids, but later their possible relationship with decapods The Decapoda or decapods, from Ancient Greek δεκάς (''dekás''), meaning "ten", and πούς (''poús''), meaning "foot", is a large order (biology), order of crustaceans within the class Malacostraca, and includes crabs, lobsters, crayfis ... was established. References Prehistoric Malacostraca Prehistoric crustacean families Fossil taxa described in 1936 {{paleo-crustacean-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphionidacea
''Amphionides reynaudii'' is a species of caridean shrimp, whose identity and position in the crustacean system remained enigmatic for a long time. It is a small (less than one inch long) planktonic crustacean found throughout the world's tropical oceans, which until 2015 was considered the sole representative of the order Amphionidacea, due to unusual morphological features. Molecular data however confirm it as a member of the caridean family Pandalidae, and the confusion of morphology is because only larval phases have so far been studied. Description ''Amphionides'' specimens observed have been up to long. In view of adult shrimp morphology, ''Amphionides'' appears unusual, with many body parts being reduced or absent. For example, it has only one pair of mouthparts – the maxillae – the mandibles and maxillules being vestigial. Males and females differ in the form of the antennae, and also by the presence in males of the eighth thoracic appendage, albeit in a reduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angustidontida
Angustidontidae is an extinct family of eucarid crustaceans and the sole representatives of the order Angustidontida. They were predators ranging in size from about in length and lived during the Late Devonian and Early Carboniferous periods. They were some of the earliest Eucarids to develop maxillipeds, modified from the first or second thoracopods. They were originally considered eurypterids, but later their possible relationship with decapods The Decapoda or decapods, from Ancient Greek δεκάς (''dekás''), meaning "ten", and πούς (''poús''), meaning "foot", is a large order (biology), order of crustaceans within the class Malacostraca, and includes crabs, lobsters, crayfis ... was established. References Prehistoric Malacostraca Prehistoric crustacean families Fossil taxa described in 1936 {{paleo-crustacean-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacea
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthropods including decapods (shrimps, prawns, crabs, lobsters and crayfish), seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, opossum shrimps, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods (insects and entognathans) emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed pan-group referred to as Pancrustacea. The three classes Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda and Remipedia are more closely related to the hexapods than they are to any of the other crustaceans ( oligostracans and multicrustaceans). The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleocyemata
Pleocyemata is a suborder of decapod crustaceans, erected by Martin Burkenroad in 1963. Burkenroad's classification replaced the earlier sub-orders of Natantia and Reptantia with the monophyletic groups Dendrobranchiata (prawns) and Pleocyemata. Pleocyemata contains all the members of the Reptantia (including crabs, lobsters, crayfish, and others), as well as the Stenopodidea (which contains the so-called "boxer shrimp" or "barber-pole shrimp"), and Caridea, which contains the true shrimp. Anatomy All members of the Pleocyemata are united by a number of features, the most important of which is that the fertilised eggs are incubated by the female, and remain stuck to the pleopods (swimming legs) until the zoea larvae are ready to hatch. It is this characteristic that gives the group its name. Pleocyemata also possess a lamellar gill structure as opposed to the branches found in the Dendrobranchiata. Systematics The cladogram below shows Pleocyemata as the sister clade to D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobster
Lobsters are Malacostraca, malacostracans Decapoda, decapod crustaceans of the family (biology), family Nephropidae or its Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on the sea floor. Three of their five pairs of legs have claws, including the first pair, which are usually much larger than the others. Highly prized as seafood, lobsters are economically important and are often one of the most profitable commodities in the coastal areas they populate. Commercially important species include two species of ''Homarus'' from the northern Atlantic Ocean and Scampi (other), scampi (which look more like a shrimp, or a "mini lobster")—the Northern Hemisphere genus ''Nephrops'' and the Southern Hemisphere genus ''Metanephrops''. Distinction Although several other groups of crustaceans have the word "lobster" in their names, the unqualified term "lobster" generally refers to the clawed lobsters of the fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura (meaning "short tailed" in Greek language, Greek), which typically have a very short projecting tail-like abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomen, usually hidden entirely under the Thorax (arthropod anatomy), thorax. Their exoskeleton is often Sclerotization, thickened and hard. They generally have Arthropod leg, five pairs of legs, and they have "Pincers (tool), pincers" or "claws" on the ends of the frontmost pair, scientifically termed the ''chelae''. They are present in all the world's oceans, Freshwater crab, in freshwater, and Terrestrial crab, on land, often hiding themselves in small crevices or burrowing into sediment. Crabs are omnivores, feeding on a variety of food, including a significant proportion of Algae eater, algae, as well as Detritivore, detritus and other invertebrates. Crab meat, Crabs are widely consumed by humans as food, with over 1.5 million tonnes Crab fisheries, caught annually. True crabs first appeared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |