|
Euharamiyida
Euharamiyida also known as Eleutherodontida, is clade of early mammals or mammal-like cynodonts from the Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of Eurasia and possibly North America. The group is sometimes considered a sister group to Multituberculata, or part of an earlier divergence within the synapsid line. It is disputed whether or not they are related to the haramiyids from the Late Triassic, such as '' Haramiyavia''. The morphology of their teeth indicates that they were herbivorous or omnivorous. Some members of the group are known to be arboreal, including gliding forms similar to modern flying squirrels or colugos. Evolution The position of euharamyidans is contested. They are either considered crown group mammals as members of Allotheria, related to multituberculates, or stem-group mammals within Mammaliaformes. The position is often dependent on the relationships of euharamiyids to the Late Triassic haramiyids such as '' Haramiyavia'' and ''Thomasia''. In some studi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haramiyida
Haramiyida is a possibly Paraphyly, paraphyletic order of Mammaliaformes, mammaliaform cynodonts or mammals of controversial taxonomic affinites. Their teeth, which are by far the most common remains, resemble those of the multituberculates. However, based on ''Haramiyavia'', the jaw is less derived; and at the level of evolution of earlier basal mammals like ''Morganucodon'' and ''Kuehneotherium'', with a groove for Ossicles, ear ossicles on the dentary. Some authors have placed them in a clade with Multituberculata dubbed Allotheria within Mammalia. Other studies have disputed this and suggested the Haramiyida were not crown group mammals, but were part of an earlier offshoot of Mammaliaformes instead, either closely related or unrelated to Multituberculates. It is also disputed whether the Late Triassic species are closely related to the Jurassic and Cretaceous members belonging to Euharamiyida, Euharamiyida/Eleutherodontida, as some phylogenetic studies recover the two groups a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
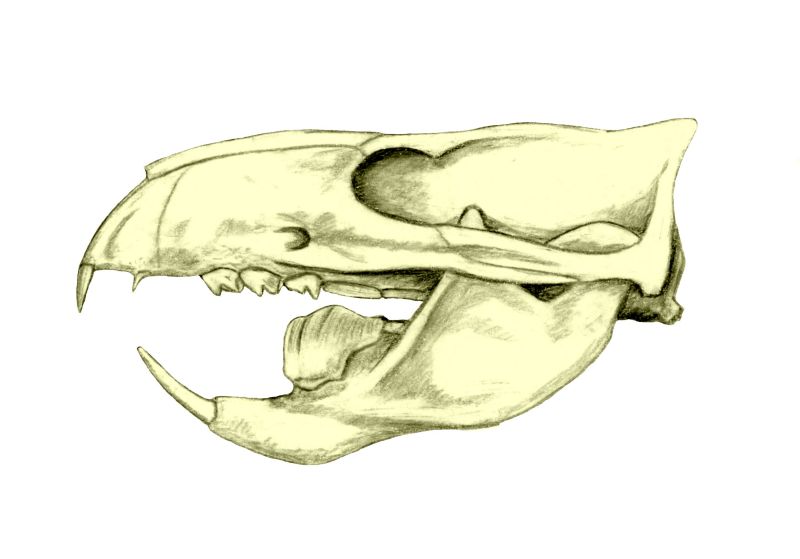
Multituberculata
Multituberculata (commonly known as multituberculates, named for the multiple tubercles of their teeth) is an extinct Order (biology), order of rodent-like mammals with a fossil record spanning over 130 million years. They first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, and reached a peak diversity during the Late Cretaceous and Paleocene. They eventually declined from the mid-Paleocene onwards, disappearing from the known fossil record in the late Eocene. They are the most diverse order of Mesozoic mammals with more than 200 species known, ranging from mouse-sized to beaver-sized. These species occupied a diversity of ecological niches, ranging from burrow-dwelling to squirrel-like arborealism to jerboa-like hoppers. Multituberculates are usually placed as Crown group, crown mammals outside either of the two main groups of living mammals, Theria — placentals and marsupials — and Monotremata,Agustí-Antón 2002, pp 3-4 but usually as closer to Theria than to monotremes. They are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multituberculates
Multituberculata (commonly known as multituberculates, named for the multiple tubercles of their teeth) is an extinct order of rodent-like mammals with a fossil record spanning over 130 million years. They first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, and reached a peak diversity during the Late Cretaceous and Paleocene. They eventually declined from the mid-Paleocene onwards, disappearing from the known fossil record in the late Eocene. They are the most diverse order of Mesozoic mammals with more than 200 species known, ranging from mouse-sized to beaver-sized. These species occupied a diversity of ecological niches, ranging from burrow-dwelling to squirrel-like arborealism to jerboa-like hoppers. Multituberculates are usually placed as crown mammals outside either of the two main groups of living mammals, Theria — placentals and marsupials — and Monotremata,Agustí-Antón 2002, pp 3-4 but usually as closer to Theria than to monotremes. They are considered to be closely rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sineleutherus
''Sineleutherus'' is an extinct genus of euharamiyids which existed in Asia during the Jurassic period. The type species is ''Sineleutherus uyguricus'', which was described by Thomas Martin, Alexander O. Averianov and Hans-Ulrich Pfretzschner in 2010; it lived in what is now China during the late Jurassic ( Oxfordian age) Qigu Formation. A second species, ''Sineleutherus issedonicus'', was described by A. O. Averianov, A. V. Lopatin and S. A. Krasnolutskii in 2011. It lived in what is now Sharypovsky District (Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia) during the middle Jurassic (Bathonian age); its fossils were collected from the upper part of the Itat Formation The Itat Formation (Russian: итатская свита) is a geologic formation in western Siberia. It was deposited in the Bajocian to Bathonian ages of the Middle Jurassic. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from .... However, this is now believed to represent several euharamiyid taxa not closely rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleutherodon
''Kermackodon'' is a genus of extinct allotherian mammaliform, known from the Middle Jurassic of England. It combines features of multituberculates with those of euharamyidans. The remains of type species, ''K. multicuspis'' were collected from Kirtlington Quarry in Oxford, England, by a team lead from UCL led by Professor Kenneth Kermack after whom the taxon is named, from sediments of the Forest Marble Formation, dating to the Bathonian In the geologic timescale the Bathonian is an age (geology), age and stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Middle Jurassic. It lasted from approximately 168.2 ±1.2 annum, Ma to around 165.3 ±1.1 Ma (million years ago). The Bathonian Age succeeds ... stage of the Middle Jurassic. The genus and species were named by Percy M. Butler and Jerry Hooker in 2005. The remains comprise a left upper molar (M2), a lower last premolar, initially considered a left but later considered more likely to be right (p4), and an incomplete non-last upper premol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwanatheria
Gondwanatheria is an extinct group of mammaliaforms that lived in parts of Gondwana, including Madagascar, India, South America, Africa, and Antarctica during the Upper Cretaceous through the Miocene (and possibly much earlier, if '' Allostaffia'' is a member of this group). Until recently, they were known only from fragmentary remains. They are generally considered to be closely related to the multituberculates and likely the euharamiyidians, well known from the Northern Hemisphere, with which they form the clade Allotheria. Classification For several decades the affinities of the group were not clear, being first interpreted as early xenarthrans, or "toothless" mammals similar to the modern anteater. A variety of studies have placed them as allotheres related to multituberculates, possibly even true multituberculates, closer to cimolodonts than "plagiaulacidans" are. However, a more recent study recovered them as nested among haramiyidans, rendering them as non-mammalian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cifelliodon
''Cifelliodon'' is an extinct genus of mammaliaforms from the Lower Cretaceous of North America. In the describing paper, it was considered one of the latest surviving haramiyids yet known, belonging to the family Hahnodontidae. Its discovery led to the proposal to remove hahnodontids from the larger well-known group, the multituberculates. However, later papers have considered it to be a basal allotherian outside of Haramiyida. The sole species in the genus, ''Cifelliodon wahkarmoosuch'', was found in the geological rock unit called the Yellow Cat Member, part of the Cedar Mountain Formation in Grand County, Utah. This rock unit dates to between 139-124 million years old. It was found alongside the remains of several dinosaurs - a large iguanodontian, a dromaeosaur, and an ornithopod - and parts of a crocodyliform. Etymology The genus name, ''Cifelliodon'', means Cifelli's tooth, and honours the well-known mammal palaeontologist, Richard Cifelli. The species name, ''C. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xianshou
''Xianshou'' is a genus of glidingQing-Jin Meng; David M. Grossnickle; Di Liu; Yu-Guang Zhang; April I. Neander; Qiang Ji; Zhe-Xi Luo (2017). "New gliding mammaliaforms from the Jurassic". ''Nature''. in press. . haramiyidan synapsid known from the Oxfordian stage of the Jurassic period, approximately 160 million years ago. Two species, ''X. linglong'' and ''X. songae,'' are known from fossils of the Tiaojishan Formation in the Liaoning province of China. Etymology The genus name is derived from Chinese ''xiān'' (仙), meaning "immortal" or "celestial being", and ''shòu'' (獸), meaning "creature" or "beast". The specific name ''linglong'' is derived from both the Chinese word for "exquisite" (玲瓏), and from the name of the town Linglongta, where the holotype was discovered. ''X. songae'' is named for the collector of the specimen, Rufeng Song. Description ''X. linglong ''is believed to have weighed in life. It can be distinguished from ''X. songae'' and '' Shenshou'' b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maiopatagium
''Maiopatagium'' is an extinct genus of gliding euharamiyida, euharamiyids which existed in Asia during the Jurassic period. It possessed a patagium between its limbs and presumably had similar lifestyle to living Flying squirrel, flying squirrels and Colugo, colugos. The type species is ''Maiopatagium furculiferum'', which was described from the Tiaojishan Formation by Zhe-Xi Luo in 2017 in paleontology, 2017; it lived in what is now the Liaoning region of China during the late Jurassic (Oxfordian (stage), Oxfordian age). ''Maiopatagium'' and ''Vilevolodon'', described concurrently, offer clues to the ways various synapsids have taken to the skies over evolutionary time scales. A second species, ''M. sibiricum'', was described from the Bathonian aged Itat Formation in western Siberia, Russia in 2019 References Euharamiyida Bathonian life Callovian life Oxfordian life Middle Jurassic synapsids of Asia Late Jurassic synapsids of Asia Jurassic China Fossils of China Paleo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
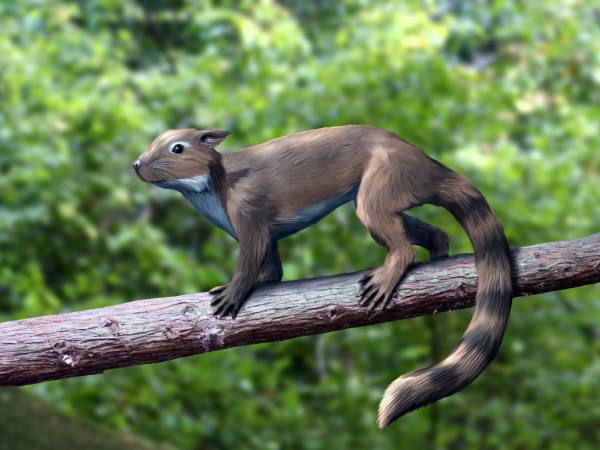
Shenshou
''Shenshou'' is a genus of haramiyidan dating from the Oxfordian stage of the Late Jurassic, approximately 160 million years ago. Fossils were recovered from the Tiaojishan Formation in the Liaoning province of China. Etymology The generic name is derived from Mandarin (神獸 shénshòu) ''shen'', meaning deity, and ''shou'', meaning animal, while the specific name is in reference to Lu Jianhua, the scientist who collected the holotype specimen. Description ''Shenshou'' is thought to be arboreal because it had a light frame, a prehensile and elongated tail, and hands and feet which had evolved for clutching and enabled the animal to climb. These features, including the large incisors of ''Shenshou'', made the animal resemble a squirrel. However, ''Shenshou'' are not the direct ancestors of squirrels, the resemblance being purely due to convergent evolution. Individuals are believed to have weighed . The presence of a three-boned middle ear suggests these animals were mammals; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allotheria
Allotheria (meaning "other beasts", from the Ancient Greek language, Greek , '–other and , '–wild animal) is an extinct clade of mammals known from the Mesozoic and early Cenozoic. Shared characteristics of the group are the presence of lower Molar (tooth), molariform Tooth (animal), teeth equipped with longitudinal rows of cusps and enlarged incisors. Typically, the canine teeth are also lost. Allotheria includes Multituberculata, Gondwanatheria (which may be part of Multituberculata, as the sister group to Cimolodonta), and probably Haramiyida, (sometimes only including Euharamiyida) although some studies have recovered haramiyidans to be basal mammaliaforms unrelated to multituberculates. Allotherians are often placed as crown group mammals, more closely related to living marsupials and placentals (Theria) than to monotremes or Eutriconodonta, eutriconodonts, though some studies place the entirety of Allotheria outside of crown Mammalia. References Further reading Z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shenshou NT Small
''Shenshou'' is a genus of haramiyidan dating from the Oxfordian stage of the Late Jurassic, approximately 160 million years ago. Fossils were recovered from the Tiaojishan Formation in the Liaoning province of China. Etymology The generic name is derived from Mandarin (神獸 shénshòu) ''shen'', meaning deity, and ''shou'', meaning animal, while the specific name is in reference to Lu Jianhua, the scientist who collected the holotype specimen. Description ''Shenshou'' is thought to be arboreal because it had a light frame, a prehensile and elongated tail, and hands and feet which had evolved for clutching and enabled the animal to climb. These features, including the large incisors of ''Shenshou'', made the animal resemble a squirrel. However, ''Shenshou'' are not the direct ancestors of squirrels, the resemblance being purely due to convergent evolution. Individuals are believed to have weighed . The presence of a three-boned middle ear suggests these animals were mammals; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |