|
Ethanol Precipitation
Ethanol precipitation is a method used to purify and/or concentrate RNA, DNA, and polysaccharides such as pectin and xyloglucan from aqueous solutions by adding salt and ethanol as an antisolvent. In DNA extraction, after separating DNA from other cell constituents in water, DNA is precipitated out of solution by neutralizing it with positively charged ions. The addition of ethanol to the solution is necessary to reduce the polarity of the solvent and allow the positively charged ions to interact with the negatively charged phosphate groups of DNA. DNA precipitation Theory DNA is typically separated from other cell constituents in a two-phase solution of phenol and water. Due to its highly charged phosphate backbone DNA is polar and will concentrate in the water phase while lipids and proteins will concentrate in the phenol phase. To precipitate the DNA out of the water, the negatively charged phosphate groups of the DNA backbone are neutralized by the addition of positively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with water (hydrolysis) using amylase enzymes as catalyst, which produces constituent sugars (monosaccharides or oligosaccharides). They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Examples include storage polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen and galactogen and structural polysaccharides such as hemicellulose and chitin. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure, these macromolecules can have distinct properties from their monosaccharide building blocks. They may be amorphous or even insoluble in water. When all the monosaccharides in a polysaccharide are the same type, the polysaccharide is called a homopolysaccharide or homoglycan, but when more t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Gravity
The standard acceleration of gravity or standard acceleration of free fall, often called simply standard gravity and denoted by or , is the nominal gravitational acceleration of an object in a vacuum near the surface of the Earth. It is a constant defined by standard as . This value was established by the third General Conference on Weights and Measures (1901, CR 70) and used to define the standard weight of an object as the product of its mass and this nominal acceleration. The acceleration of a body near the surface of the Earth is due to the combined effects of gravity and centrifugal acceleration from the rotation of the Earth (but the latter is small enough to be negligible for most purposes); the total (the apparent gravity) is about 0.5% greater at the poles than at the Equator. Although the symbol is sometimes used for standard gravity, (without a suffix) can also mean the local acceleration due to local gravity and centrifugal acceleration, which varies depending on on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin Column-based Nucleic Acid Purification
Spin column-based nucleic acid purification is a solid phase extraction method to quickly purify nucleic acids. This method relies on the fact that nucleic acid will bind to the solid phase of silica under certain conditions. Procedure The different stages of the method are lyse, bind, wash, and elute. More specifically, this entails the lysis of target cells to release nucleic acids, selective binding of nucleic acid to a silica membrane, washing away particulates and inhibitors that are not bound to the silica membrane, and elution of the nucleic acid, with the end result being purified nucleic acid in an aqueous solution. For lysis, the cells (blood, tissue, etc.) of the sample must undergo a treatment to break the cell membrane and free the nucleic acid. Depending on the target material, this can include the use of detergent or other buffers, proteinases or other enzymes, heating to various times/temperatures, or mechanical disruption such as cutting with a knife or homogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
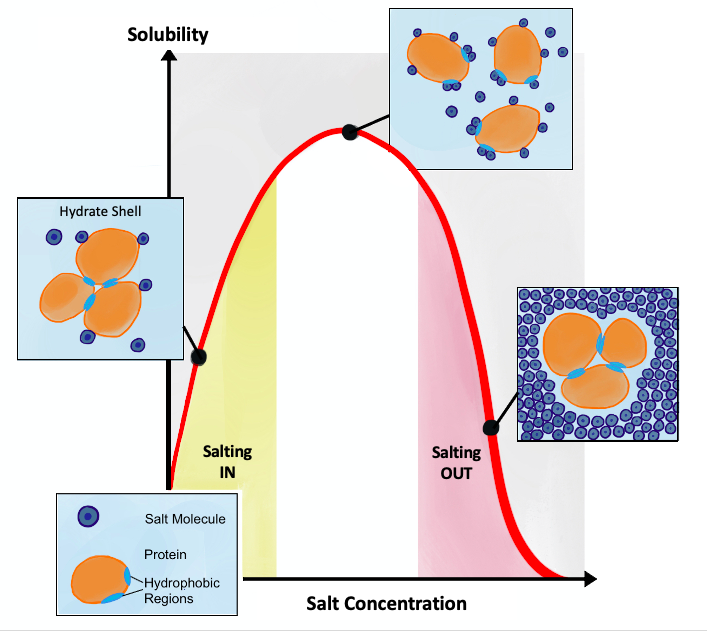
Salting Out
Salting out (also known as salt-induced precipitation, salt fractionation, anti-solvent crystallization, precipitation crystallization, or drowning out) is a purification technique that utilizes the reduced solubility of certain molecules in a solution of very high ionic strength. Salting out is typically used to precipitate large biomolecules, such as proteins or DNA. Because the salt concentration needed for a given protein to precipitate out of the solution differs from protein to protein, a specific salt concentration can be used to precipitate a target protein. This process is also used to concentrate dilute solutions of proteins. Dialysis can be used to remove the salt if needed. Principle Salt compounds dissociate in aqueous solutions. This property is exploited in the process of salting out. When the salt concentration is increased, some of the water molecules are attracted by the salt ions, which decreases the number of water molecules available to interact with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salting In
Salting in refers to the effect where increasing the ionic strength of a solution increases the solubility of a solute, such as a protein Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab .... This effect tends to be observed at lower ionic strengths. Protein solubility is a complex function of physicochemical nature of the protein, pH, temperature, and the concentration of the salt used. It also depends on whether the salt is kosmotropic, whereby the salt will stabilize water. The solubility of proteins usually increases slightly in the presence of salt, referred to as "salting in". However, at high concentrations of salt, the solubility of the proteins drop sharply and proteins can precipitate out, referred to as "salting out". Anionic interactions Initial salting in at low con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol–chloroform Extraction
Phenol–chloroform extraction is a liquid-liquid extraction technique in molecular biology used to separate nucleic acids from proteins and lipids. Process Aqueous samples, lysed cells, or homogenised tissue are mixed with equal volumes of a phenol:chloroform mixture. This mixture is then centrifuged. Because the phenol:chloroform mixture is immiscible with water, the centrifuge will cause two distinct phases to form: an upper aqueous phase, and a lower organic phase. The aqueous phase rises to the top because it is less dense than the organic phase containing the phenol:chloroform. This difference in density is why phenol, which only has a slightly higher density than water, must be mixed with chloroform to form a mixture with a much higher density than water. The hydrophobic lipids will partition into the lower organic phase, and the proteins will remain at the interphase between the two phases, while the nucleic acids (as well as other contaminants such as salts, sugars, etc.) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Extraction
The first isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was done in 1869 by Friedrich Miescher. DNA extraction is the process of isolating DNA from the cells of an organism isolated from a sample, typically a biological sample such as blood, saliva, or tissue. It involves breaking open the cells, removing proteins and other contaminants, and purifying the DNA so that it is free of other cellular components. The purified DNA can then be used for downstream applications such as PCR, sequencing, or cloning. Currently, it is a routine procedure in molecular biology or forensic analyses. This process can be done in several ways, depending on the type of the sample and the downstream application, the most common methods are: mechanical, chemical and enzymatic lysis, precipitation, purification, and concentration. The specific method used to extract the DNA, such as phenol-chloroform extraction, alcohol precipitation, or silica-based purification. For the chemical method, many different k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopropanol
Isopropyl alcohol (IUPAC name propan-2-ol and also called isopropanol or 2-propanol) is a colorless, flammable, organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor. Isopropyl alcohol, an organic polar molecule, is miscible in water, ethanol, and chloroform, demonstrating its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances including ethyl cellulose, polyvinyl butyral, oils, alkaloids, and natural resins. Notably, it is not miscible with salt solutions and can be separated by adding sodium chloride in a process known as salting out. It forms an azeotrope with water, resulting in a boiling point of 80.37 °C and is characterized by its slightly bitter taste. Isopropyl alcohol becomes viscous at lower temperatures, freezing at −89.5 °C, and has significant ultraviolet-visible absorbance at 205 nm. Chemically, it can be oxidized to acetone or undergo various reactions to form compounds like isopropoxides or aluminium isopropoxide. As an isopropyl group linked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denaturation (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose folded structure present in their native state due to various factors, including application of some external stress or compound, such as a strong acid or base, a concentrated inorganic salt, an organic solvent (e.g., alcohol or chloroform), agitation, radiation, or heat. If proteins in a living cell are denatured, this results in disruption of cell activity and possibly cell death. Protein denaturation is also a consequence of cell death. Denatured proteins can exhibit a wide range of characteristics, from conformational change and loss of solubility or dissociation of cofactors to aggregation due to the exposure of hydrophobic groups. The loss of solubility as a result of denaturation is called ''coagulation''. Denatured proteins, e.g., metalloenzymes, lose their 3D structure or metal cofactor, and therefore, cannot function. Proper protein folding is key to whether a globular or memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffer Solution
A buffer solution is a solution where the pH does not change significantly on dilution or if an acid or base is added at constant temperature. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications. In nature, there are many living systems that use buffering for pH regulation. For example, the bicarbonate buffering system is used to regulate the pH of blood, and bicarbonate also acts as a buffer in the ocean. Principles of buffering Buffer solutions resist pH change because of a chemical equilibrium between the weak acid HA and its conjugate base A−: When some strong acid is added to an equilibrium mixture of the weak acid and its conjugate base, hydrogen ions (H+) are added, and the equilibrium is shifted to the left, in accordance with Le Chatelier's principle. Because of this, the hydrogen ion concentration increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyacrylamide
Polyacrylamide (abbreviated as PAM or pAAM) is a polymer with the formula (-CH2CHCONH2-). It has a linear-chain structure. PAM is highly water-absorbent, forming a soft gel when hydrated. In 2008, an estimated 750,000,000 kg were produced, mainly for water treatment and the paper and mineral industries. Physicochemical properties Polyacrylamide is a polyolefin. It can be viewed as polyethylene with amide substituents on alternating carbons. Unlike various nylons, polyacrylamide is not a polyamide because the amide groups are not in the polymer backbone. Owing to the presence of the amide (CONH2) groups, alternating carbon atoms in the backbone are stereogenic (colloquially: chiral). For this reason, polyacrylamide exists in atactic, syndiotactic, and isotactic forms, although this aspect is rarely discussed. The polymerization is initiated with radicals and is assumed to be stereorandom. Copolymers and modified polymers Linear polyacrylamide is a water-soluble polymer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |