|
Escherichia Virus CC31
''Escherichia virus CC31'', formerly known as ''Enterobacter virus CC31'', is a dsDNA bacteriophage of the subfamily ''Tevenvirinae'' responsible for infecting the bacteria Family (biology), family of Enterobacteriaceae. It is one of two discovered viruses of the genus ''Karamvirus'', diverging away from the previously discovered ''T4virus'', as a clonal complex (CC).Bielak, E.M., Hasman, H. and Aarestrup, F.M., 2012. ''Diversity and epidemiology of plasmids from Enterobacteriaceae from human and non-human reservoirs'' (Doctoral dissertation, Technical University of DenmarkDanmarks Tekniske Universitet, National Food InstituteFødevareinstituttet, Division of Epidemiology and Microbial GenomicsAfdeling for Epidemiologi og Genomisk Mikrobiologi). ''CC31'' was first isolated from ''Escherichia coli'' B strain S/6/4 and is primarily associated with ''Escherichia,'' even though is named after ''Enterobacter.'' Viral classification and structure ''Enterobacter virus CC31'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriophage
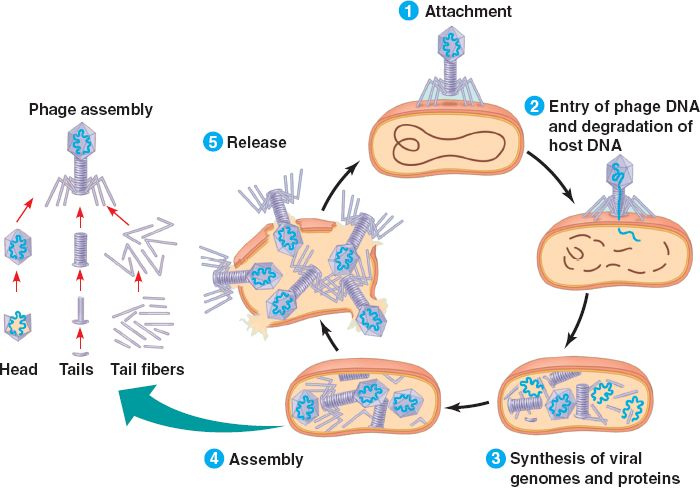
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a phage (), is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria. The term is derived . Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that Capsid, encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. Bacteriophage MS2, MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm. Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of biomass after prokaryotes, where up to 9x108 virus, virions per millilitre have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |