|
Equivalent Circuit
In electrical engineering, an equivalent circuit refers to a theoretical circuit that retains all of the electrical characteristics of a given circuit. Often, an equivalent circuit is sought that simplifies calculation, and more broadly, that is a simplest form of a more complex circuit in order to aid analysis. In its most common form, an equivalent circuit is made up of linear, passive elements. However, more complex equivalent circuits are used that approximate the nonlinear behavior of the original circuit as well. These more complex circuits often are called ''macromodels'' of the original circuit. An example of a macromodel is the Boyle circuit for the 741 operational amplifier. Examples Thévenin and Norton equivalents One of linear circuit theory's most surprising properties relates to the ability to treat any two-terminal circuit no matter how complex as behaving as only a source and an impedance, which have either of two simple equivalent circuit forms: * Thévenin e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after the commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use. Electrical engineering is divided into a wide range of different fields, including computer engineering, systems engineering, power engineering, telecommunications, radio-frequency engineering, signal processing, instrumentation, photovoltaic cells, electronics, and optics and photonics. Many of these disciplines overlap with other engineering branches, spanning a huge number of specializations including hardware engineering, power electronics, Electromagnetism, electromagnetics and waves, microwave engineering, nanotechnology, electrochemistry, renewable energies, mechatronics/control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Bipolar Junction Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor (FET), uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current between the remaining two terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Diffused trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Electrical Resistance
The electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. Its reciprocal quantity is , measuring the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with mechanical friction. The SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm (), while electrical conductance is measured in siemens (S) (formerly called the 'mho' and then represented by ). The resistance of an object depends in large part on the material it is made of. Objects made of electrical insulators like rubber tend to have very high resistance and low conductance, while objects made of electrical conductors like metals tend to have very low resistance and high conductance. This relationship is quantified by resistivity or conductivity. The nature of a material is not the only factor in resistance and conductance, however; it also depends on the size and shape of an object because these properties are extensive rather tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Lipid Bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes form a continuous barrier around all cell (biology), cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the nuclear envelope, nuclear membrane surrounding the cell nucleus, and biological membrane, membranes of the membrane-bound organelles in the cell. The lipid bilayer is the barrier that keeps ions, proteins and other molecules where they are needed and prevents them from diffusing into areas where they should not be. Lipid bilayers are ideally suited to this role, even though they are only a few nanometers in width, because they are impermeable to most water-soluble (hydrophilic) molecules. Bilayers are particularly impermeable to ions, which allows cells to regulate salt concentrations and pH by transporting ions across their membranes using proteins called Ion transporter, ion pumps. Biological bilaye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Capacitance
Capacitance is the ability of an object to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related notions of capacitance: ''self capacitance'' and ''mutual capacitance''. An object that can be electrically charged exhibits self capacitance, for which the electric potential is measured between the object and ground. Mutual capacitance is measured between two components, and is particularly important in the operation of the capacitor, an elementary linear electronic component designed to add capacitance to an electric circuit. The capacitance between two conductors depends only on the geometry; the opposing surface area of the conductors and the distance between them; and the permittivity of any dielectric material between them. For many dielectric materials, the permittivity, and thus the capacitance, is independent of the potential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell, being selectively permeable to ions and organic mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
RC Circuit
A resistor–capacitor circuit (RC circuit), or RC filter or RC network, is an electric circuit composed of resistors and capacitors. It may be driven by a voltage source, voltage or current source and these will produce different responses. A first order RC circuit is composed of one resistor and one capacitor and is the simplest type of RC circuit. RC circuits can be used to filter a signal by blocking certain frequencies and passing others. The two most common RC filters are the high-pass filters and low-pass filters; band-pass filters and band-stop filters usually require RLC filters, though crude ones can be made with RC filters. Natural response The simplest RC circuit consists of a resistor with Electric resistance, resistance and a charged capacitor with capacitance connected to one another in a single loop, without an external voltage source. The capacitor will discharge its stored energy through the resistor. If is taken to be the voltage of the capacitor's top pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Internal Resistance
In electrical engineering, a practical electric power source which is a linear circuit may, according to Thévenin's theorem, be represented as an ideal voltage source in series with an impedance. This impedance is termed the internal resistance of the source. When the power source delivers current, the measured voltage output is lower than the no- load voltage; the difference is the voltage drop (the product of current and resistance) caused by the internal resistance. The concept of internal resistance applies to all kinds of electrical sources and is useful for analyzing many types of circuits. Battery A battery may be modeled as a voltage source in series with a resistance. These types of models are known as equivalent circuit models. Another common model being physiochemical models that are physical in nature involving concentrations and reaction rates. In practice, the internal resistance of a battery is dependent on its size, state of charge, chemical properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Open-circuit Voltage
Open-circuit voltage (abbreviated as OCV or VOC) is the voltage, difference of electrical potential between two Terminal (electronics), terminals of an electronic device when disconnected from any Electric Circuit, circuit. There is no External electric load, external load connected. No external electric current flows between the terminals. Alternatively, the open-circuit voltage may be thought of as the voltage that must be applied to a solar cell or a Electric battery, battery to stop the current. It is sometimes given the symbol Voc. In network analysis (electrical circuits), network analysis this voltage is also known as the Thévenin's theorem, Thévenin voltage. The open-circuit voltages of batteries and solar cells are often quoted under particular conditions (state-of-charge, illumination, temperature, etc.). The potential difference mentioned for batteries and cells is usually the open-circuit voltage. The value of the open-circuit voltage of a transducer equals its e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
State Of Charge
State of charge (SOC) quantifies the remaining capacity available in a battery at a given time and in relation to a given state of ageing. It is usually expressed as percentage (0% = empty; 100% = full). An alternative form of the same measure is the depth of discharge (DOD), calculated as 1 − SOC (100% = empty; 0% = full). It refers to the amount of charge that may be used up if the cell is fully discharged. State of charge is normally used when discussing the present state of a battery in use, while depth of discharge is most often used to discuss a constant variation of state of charge during repeated cycles. In electric vehicles In a battery electric vehicle (BEV), the state of charge indicates the remaining energy in the battery pack. It is the equivalent of a fuel gauge. The state of charge can help to reduce electrical car owners' anxiety when they are waiting in the line or stay at home since it will reflect the progress of charging and let owners know when it wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Mathematical Model
A mathematical model is an abstract and concrete, abstract description of a concrete system using mathematics, mathematical concepts and language of mathematics, language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed ''mathematical modeling''. Mathematical models are used in applied mathematics and in the natural sciences (such as physics, biology, earth science, chemistry) and engineering disciplines (such as computer science, electrical engineering), as well as in non-physical systems such as the social sciences (such as economics, psychology, sociology, political science). It can also be taught as a subject in its own right. The use of mathematical models to solve problems in business or military operations is a large part of the field of operations research. Mathematical models are also used in music, linguistics, and philosophy (for example, intensively in analytic philosophy). A model may help to explain a system and to study the effects of different components, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
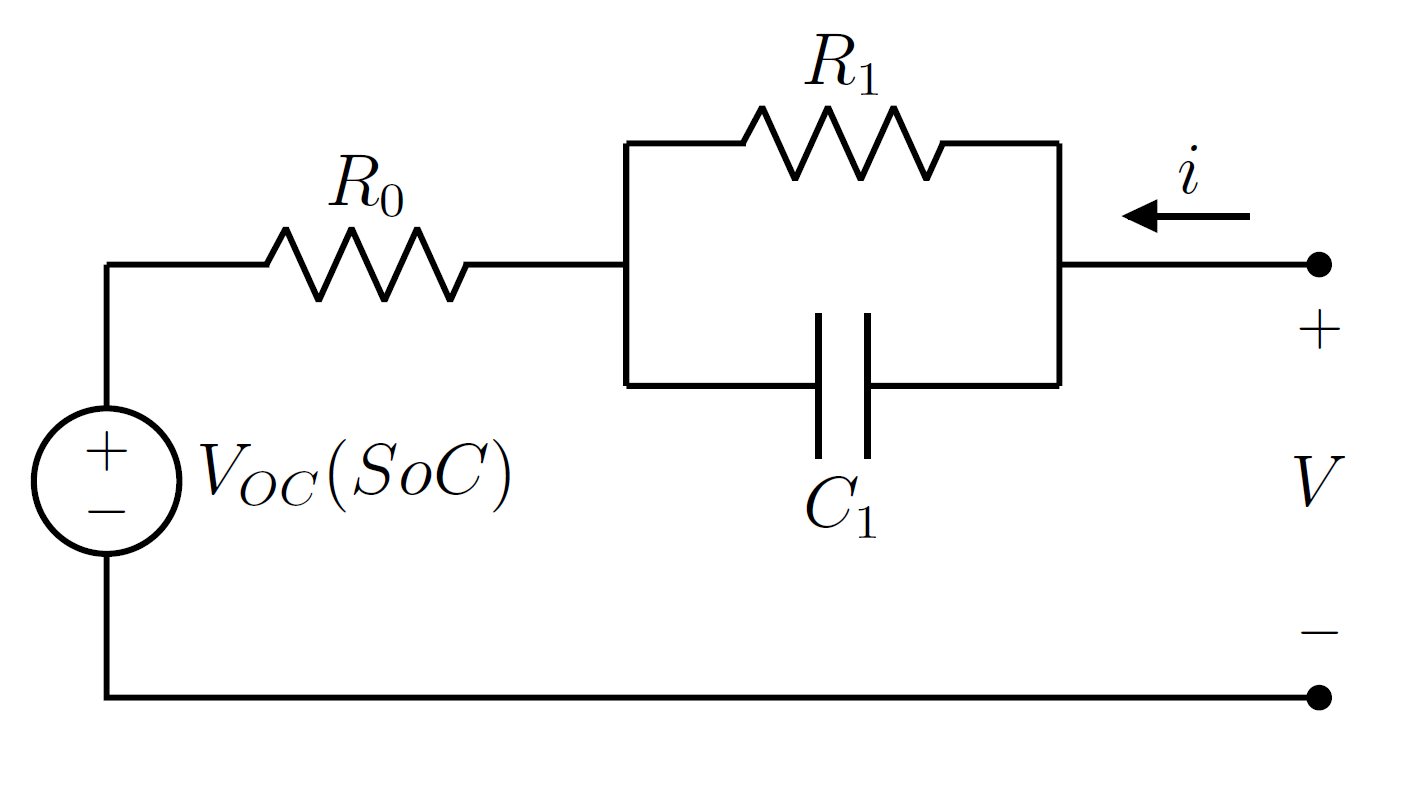 |
Equivalent Circuit Model For Li-ion Cells
The equivalent circuit model (ECM) is a common lumped-element model for Lithium-ion battery cells. The ECM Simulation, simulates the terminal voltage dynamics of a Li-ion cell through an Equivalent circuit, equivalent electrical network composed passive elements, such as resistors and capacitors, and a Voltage source, voltage generator. The ECM is widely employed in several application fields, including Computer simulation, computerized simulation, because of its simplicity, its low computational demand, its ease of characterization, and its structural flexibility. These features make the ECM suitable for real-time Battery management system, Battery Management System (BMS) tasks like state of charge (SoC) estimation, State of Health (SoH) monitoring and battery thermal management. Model structure The equivalent-circuit model is used to simulate the voltage at the cell terminals when an electric current is applied to discharge or recharge it. The most common circuital representat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |