Equivalent Circuit Model For Li-ion Cells on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The equivalent circuit model (ECM) is a common 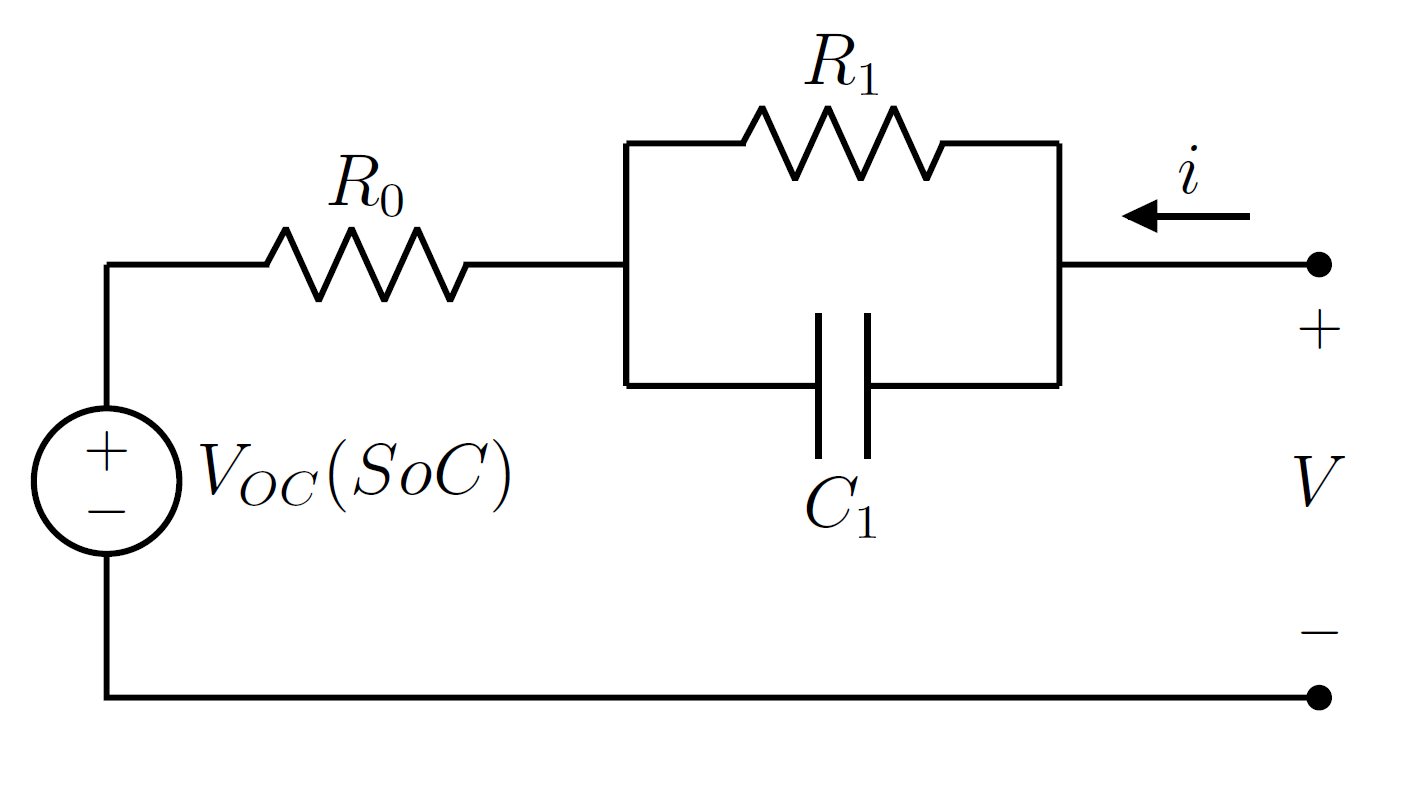
 The open-circuit voltage of a Li-ion cell (or battery) is its terminal voltage in equilibrium conditions, ''i.e.'' measured when no load current is applied and after a long rest period. The open-circuit voltage is a decreasing
The open-circuit voltage of a Li-ion cell (or battery) is its terminal voltage in equilibrium conditions, ''i.e.'' measured when no load current is applied and after a long rest period. The open-circuit voltage is a decreasing
 The state of charge is usually computed integrating the current drained/supplied by/to the battery through the formula known as ''Coulomb Counting'':
where is the cell nominal capacity (expressed in ampere-hours). The voltage across each RC parallel is simulated as:
where and are, respectively, the polarization resistance and capacity. Finally, knowing the open-circuit voltage-state of charge relationship and the internal resistance , the cell terminal voltage can be computed as:
The state of charge is usually computed integrating the current drained/supplied by/to the battery through the formula known as ''Coulomb Counting'':
where is the cell nominal capacity (expressed in ampere-hours). The voltage across each RC parallel is simulated as:
where and are, respectively, the polarization resistance and capacity. Finally, knowing the open-circuit voltage-state of charge relationship and the internal resistance , the cell terminal voltage can be computed as:

Li-ion battery modeling through equivalent circuit models
Equivalent circuit models for Li-ion cells
Introduction to EIS methodology
Mathematical modeling Lithium-ion batteries
lumped-element model
The lumped-element model (also called lumped-parameter model, or lumped-component model) is a simplified representation of a physical system or circuit that assumes all components are concentrated at a single point and their behavior can be de ...
for Lithium-ion battery
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energ ...
cells. The ECM simulates the terminal voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
dynamics of a Li-ion cell through an equivalent
Equivalence or Equivalent may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
*Album-equivalent unit, a measurement unit in the music industry
*Equivalence class (music)
*'' Equivalent VIII'', or ''The Bricks'', a minimalist sculpture by Carl Andre
*'' Equiva ...
electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e.g., voltage sou ...
composed passive elements, such as resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electronic component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active e ...
s and capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
s, and a voltage generator. The ECM is widely employed in several application fields, including computerized simulation, because of its simplicity, its low computational demand, its ease of characterization, and its structural flexibility. These features make the ECM suitable for real-time Battery Management System
A battery management system (BMS) is any electronic system that manages a rechargeable battery (cell or battery pack) by facilitating the safe usage and a long life of the battery in practical scenarios while monitoring and estimating its various s ...
(BMS) tasks like state of charge
State of charge (SOC) quantifies the remaining capacity available in a battery at a given time and in relation to a given state of ageing. It is usually expressed as percentage (0% = empty; 100% = full). An alternative form of the same measure i ...
(SoC) estimation, State of Health (SoH) monitoring and battery thermal management. 
Model structure
The equivalent-circuit model is used to simulate the voltage at the cell terminals when anelectric current
An electric current is a flow of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is defined as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface. The moving particles are called charge c ...
is applied to discharge or recharge it. The most common circuital representation consists of three elements in series: a variable voltage source, representing the open-circuit voltage
Open-circuit voltage (abbreviated as OCV or VOC) is the voltage, difference of electrical potential between two Terminal (electronics), terminals of an electronic device when disconnected from any Electric Circuit, circuit. There is no External ...
(OCV) of the cell, a resistor representing ohmic internal resistance
In electrical engineering, a practical electric power source which is a linear circuit may, according to Thévenin's theorem, be represented as an ideal voltage source in series with an impedance. This impedance is termed the internal resis ...
of the cell and a set of resistor-capacitor (RC) parallels accounting for the dynamic voltage drop
In electronics, voltage drop is the decrease of electric potential along the path of a current flowing in a circuit. Voltage drops in the internal resistance of the source, across conductors, across contacts, and across connectors are unde ...
s.
Open-circuit voltage
 The open-circuit voltage of a Li-ion cell (or battery) is its terminal voltage in equilibrium conditions, ''i.e.'' measured when no load current is applied and after a long rest period. The open-circuit voltage is a decreasing
The open-circuit voltage of a Li-ion cell (or battery) is its terminal voltage in equilibrium conditions, ''i.e.'' measured when no load current is applied and after a long rest period. The open-circuit voltage is a decreasing nonlinear
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system (or a non-linear system) is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathe ...
function of the state of charge, and its shape depends on the chemical composition of the anode
An anode usually is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, which is usually an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the devic ...
(usually made of graphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable ...
) and cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device such as a lead-acid battery. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. Conventional curren ...
( LFP, NMC, NCA, LCO...) of the cell. The open-circuit voltage, represented in the circuit by a state of charge-driven voltage generator, is the major voltage contribution and is the most informative indicator of cell's state of charge.
Internal resistance
The internal resistance, represented in the circuit by a simple resistor, is used to simulate the instantaneous voltage drops due to ohmic effects such aselectrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a varie ...
s resistivity, electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
conductivity and contact resistance
Electrical contact resistance (ECR, or simply contact resistance) is resistance to the flow of electric current caused by incomplete contact of the surfaces through which the current is flowing, and by films or oxide layers on the contacting sur ...
(''e.g.'' solid-electrolyte interface (SEI) and collectors contact resistance).
Internal resistance is strongly influenced by several factors, such as:
* Temperature''.'' The internal resistance increases significantly at low temperatures. This effect makes lithium-ion batteries particularly inefficient at low temperatures.
* State of charge''.'' The internal resistance shows a remarkable dependence on the state of charge of the cell. In particular, at low state of charge (near-discharged cell) and high state of charge (fully charged cell), an increase in internal resistance is experienced.
* Cell aging''.'' The internal resistance increases as the Li-ion cell ages. The main cause of the resistance increase is the thickening of the solid-electrolyte interface (SEI), a solid barrier with protective functions that grows naturally on the anode surface, composed of electrolyte decomposition-derived compounds.
RC parallels
One or more RC parallels are often added to the model to improve its accuracy in simulating dynamic voltage transients. The number of RC parallels is an arbitrary modeling choice: in general, a large number of RC parallels improves the accuracy of the model but complicates the identification process and increases the computational load, while a small number will result in a computationally light and easy-to-characterize model but less accurate in predicting cell voltage during transients. Commonly, one or two RC parallels are considered the optimal choices.Model equations
The ECM can be described by astate-space representation
In control engineering and system identification, a state-space representation is a mathematical model of a physical system that uses state variables to track how inputs shape system behavior over time through first-order differential equations o ...
that has current () as input and voltage at the cell terminals () as output. Consider a generic ECM model with a number of RC parallels . The states of the model, (''i.e.'', the variables that evolve over time via differential equations), are the state of charge () and the voltage drops across the RC parallels (). The state of charge is usually computed integrating the current drained/supplied by/to the battery through the formula known as ''Coulomb Counting'':
where is the cell nominal capacity (expressed in ampere-hours). The voltage across each RC parallel is simulated as:
where and are, respectively, the polarization resistance and capacity. Finally, knowing the open-circuit voltage-state of charge relationship and the internal resistance , the cell terminal voltage can be computed as:
The state of charge is usually computed integrating the current drained/supplied by/to the battery through the formula known as ''Coulomb Counting'':
where is the cell nominal capacity (expressed in ampere-hours). The voltage across each RC parallel is simulated as:
where and are, respectively, the polarization resistance and capacity. Finally, knowing the open-circuit voltage-state of charge relationship and the internal resistance , the cell terminal voltage can be computed as:
Introduction to experimental identification
Experimental identification of the ECM involves the estimation of unknown parameters, especially the capacitance , the open-circuit voltage curve , and the passive components and ,. Commonly, identification is addressed in sequential steps.Capacity assessment
Cell capacity is usually measured by fully discharging the cell at constant current. The capacity test is commonly carried out by discharging the cell completely (from upper voltage limit to lower voltage limit ) at the rated current of 0.5 C/1C (that is, the current required, according to the manufacturer, to fully discharge it in two/one hours) and after a full charge (usually conducted via CC-CV charging strategy). Capacity can be computed as: .Open-circuit voltage characterization
There are two main experimental techniques for characterizing the open-circuit voltage: # Pulse test: the cell is fully discharged/charged with a train of current pulses. Each pulse discharges a predetermined portion of the cell capacity, and thus allows a new point to be explored. After each current pulse, the cell is left to rest for several hours and then the open-circuit voltage is measured. Finally, the curve is obtained by fitting the collected SoC, ">math display="inline">SoC, points by an arbitrarily chosen function (typically polynomial). This method is believed to be quick and effective, but the quality result depends on the experiment design and the time invested in it. # Slow galvanostatic discharge'''': another method to evaluate the open-circuit voltage of the cell is to slowly discharge/charge it under galvanostatic conditions (i.e., at low constant currents). In fact, for small currents, the approximation applies. Also in this case, since the accuracy of the estimate depends on how small the discharge current is, the quality of the result is closely related to the time invested in the test.Dynamic response characterization
The parameters that characterize the dynamic response, namely the ohmic resistance and the parameters of RC parallels ,, are usually identified experimentally in two different ways: #Time domain
In mathematics and signal processing, the time domain is a representation of how a signal, function, or data set varies with time. It is used for the analysis of mathematical functions, physical signals or time series of economic or environmental ...
identification: the parameters are optimized by analyzing the behavior over time of the cell voltage in response to a determined current profile. For example, a pulse test can be used for this purpose: can be identified (at different state of charge levels) by measuring the instantaneous voltage drops upon application/removal of each pulse, while and can be identified, by means of a dedicated optimization procedure, to best simulate the dynamic response during cell relaxation.
# Frequency domain
In mathematics, physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency (and possibly phase), rather than time, as in time ser ...
identification: dynamic parameters can be optimized by analyzing the frequency response
In signal processing and electronics, the frequency response of a system is the quantitative measure of the magnitude and Phase (waves), phase of the output as a function of input frequency. The frequency response is widely used in the design and ...
of the cell. For this purpose, an AC current (or voltage) signal of varying frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
is injected into the cell, and the resulting voltage (or current) response is evaluated in terms of amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of am ...
and phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
*Phase space, a mathematica ...
. This analysis, called Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) requires dedicated laboratory instrumentation and produces highly reliable results. EIS results, typically evaluated using the Nyquist diagram, allows the different impedance terms of the cell (, and ) to be quantified separately.
Applications
Some of the possible uses of ECM include: * Online state estimation in Battery Management Systems: ECM is widely used within model-based observers designed to predict non-measurable internal states of the battery, such as state of charge and State of Health. For example, ECMs of different order are frequently used within Extended Kalman Filters developed for online state of charge estimation. * Simulation and system design: ECM is often used in the design phase of abattery pack
A battery pack is a set of any number of (preferably) identical Battery (electricity), batteries or individual battery cells. They may be configured in a series, parallel or a mixture of both to deliver the desired voltage and current. The term ' ...
. Simulating electrical load
An electrical load is an electrical component or portion of a Electric Circuit, circuit that consumes (active) electric power, such as electrical appliances and Electric light, lights inside the home. The term may also refer to the power Power con ...
profiles at the cell level allows the sizing of the system in terms of capacity and voltage. In addition, ECM can be used to simulate the battery heat generation, and thus design and size the battery cooling system.
See also
*Battery management system
A battery management system (BMS) is any electronic system that manages a rechargeable battery (cell or battery pack) by facilitating the safe usage and a long life of the battery in practical scenarios while monitoring and estimating its various s ...
* Equivalent circuit
In electrical engineering, an equivalent circuit refers to a theoretical circuit that retains all of the electrical characteristics of a given circuit. Often, an equivalent circuit is sought that simplifies calculation, and more broadly, that is ...
* Internal resistance
In electrical engineering, a practical electric power source which is a linear circuit may, according to Thévenin's theorem, be represented as an ideal voltage source in series with an impedance. This impedance is termed the internal resis ...
* Lithium-ion battery
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energ ...
* State of charge
State of charge (SOC) quantifies the remaining capacity available in a battery at a given time and in relation to a given state of ageing. It is usually expressed as percentage (0% = empty; 100% = full). An alternative form of the same measure i ...
, State of health
References
{{Reflist, 2External links
Li-ion battery modeling through equivalent circuit models
Equivalent circuit models for Li-ion cells
Introduction to EIS methodology
Mathematical modeling Lithium-ion batteries