|
Epoxides
In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether, where the ether forms a three-atom Ring (chemistry), ring: two atoms of carbon and one atom of oxygen. This triangular structure has substantial ring strain, making epoxides highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often Volatility (chemistry), volatile. Nomenclature A compound containing the epoxide functional group can be called an epoxy, epoxide, oxirane, and ethoxyline. Simple epoxides are often referred to as oxides. Thus, the epoxide of ethylene (C2H4) is ethylene oxide (C2H4O). Many compounds have trivial names; for instance, ethylene oxide is called "oxirane". Some names emphasize the presence of the epoxide functional group, as in the compound ''1,2-epoxyheptane'', which can also be called ''1,2-heptene oxide''. A polymer formed from epoxide precursors is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propylene Oxide
Propylene oxide is an epoxide with the molecular formula C3H6O. This colourless volatile liquid with an odour similar to ether, is produced on a large scale industrially. Its major application is its use for the production of polyether polyols for use in making polyurethane plastics. It is a chiral epoxide, although it is commonly used as a racemic mixture. This compound is sometimes called 1,2-propylene oxide to distinguish it from its isomer 1,3-propylene oxide, better known as oxetane. Production Industrial production of propylene oxide starts from propylene. Two general approaches are employed, one involving chlorohydrin formation and the other involving oxidation. In 2005, about half of the world production was through chlorohydrin technology and one half via oxidation routes. The latter approach is growing in importance. Chlorohydrin route The traditional route proceeds via the conversion of propylene to propylene chlorohydrin according to the following simplified sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
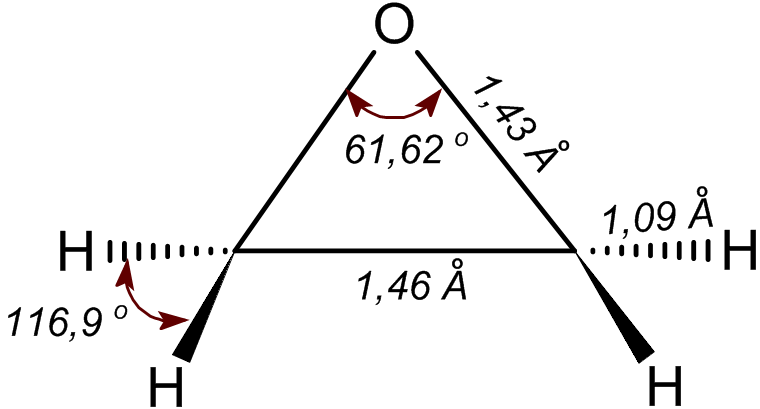
Ethylene Oxide
Ethylene oxide is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula . It is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide: a three-membered ring (chemistry), ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor. Because it is a strained ring, ethylene oxide easily participates in a number of addition reactions that result in ring-opening. Ethylene oxide is isomeric with acetaldehyde and with vinyl alcohol. Ethylene oxide is industrially produced by oxidation of ethylene in the presence of a silver catalyst. The reactivity that is responsible for many of ethylene oxide's hazards also makes it useful. Although too dangerous for direct household use and generally unfamiliar to consumers, ethylene oxide is used for making many consumer products as well as non-consumer chemicals and intermediates. These products include detergents, thickeners, solvents, plastics, and various organic chemicals such as ethylen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group, a single oxygen atom bonded to two separate carbon atoms, each part of an organyl group (e.g., alkyl or aryl). They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the organyl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the organyl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. Silver is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native metal, native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures. Other than in currency and as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as Alpha-olefin, α-olefins. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) Preferred IUPAC name, recommends using the name "alkene" only for Open-chain compound, acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for Cyclic compound, cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with ''n'' being a >1 natural number (which is two hydrogens less than the corresponding alkane). When ''n'' is four or more, isomers are possible, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-butyl Hydroperoxide
''tert''-Butyl hydroperoxide (tBuOOH) is the organic compound with the formula (CH3)3COOH. It is one of the most widely used hydroperoxides in a variety of oxidation processes, like the Halcon process. It is normally supplied as a 69–70% aqueous solution. Compared to hydrogen peroxide and organic peracids, ''tert''-butyl hydroperoxide is less reactive and more soluble in organic solvents. Overall, it is renowned for the convenient handling properties of its solutions. Its solutions in organic solvents are highly stable. Application Industrially, ''tert''-butyl hydroperoxide is used to prepare propylene oxide. In the Halcon process, molybdenum-based catalysts are used for this reaction: :(CH3)3COOH + CH2=CHCH3 → (CH3)3COH + CH2OCHCH3 The byproduct t-butanol can be dehydrated to isobutene and converted to MTBE. On a much smaller scale, ''tert''-butyl hydroperoxide is used to produce some fine chemicals by the Sharpless epoxidation. Synthesis and production Many sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylbenzene
Ethylbenzene is an organic compound with the formula . It is a highly flammable, colorless liquid with an odor similar to that of gasoline. This monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is important in the petrochemical industry as a reaction intermediate in the production of styrene, the precursor to polystyrene, a common plastic material. In 2012, more than 99% of ethylbenzene produced was consumed in the production of styrene. Occurrence and applications Ethylbenzene occurs naturally in coal tar and petroleum. The dominant application of ethylbenzene is its role as an intermediate in the production of polystyrene. Catalytic dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene gives hydrogen and styrene: : → C6H5CH=CH2 + As of May 2012, more than 99% of all the ethylbenzene produced is used for this purpose. Ethylbenzene hydroperoxide, a reagent and radical initiator, is produced by autoxidation of ethylbenzene: :C6H5CH2CH3 + O2 → C6H5CH(O2H)CH3 Niche uses Ethylbenzene is added to gasoline as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterogeneous Catalysis
Heterogeneous catalysis is catalysis where the Phase (matter), phase of catalysts differs from that of the reagents or product (chemistry), products. The process contrasts with homogeneous catalysis where the reagents, products and catalyst exist in the same phase. Phase distinguishes between not only solid, liquid, and gas components, but also immiscible mixtures (e.g., oil and water), or anywhere an interface is present. Heterogeneous catalysis typically involves solid phase catalysts and gas phase reactants. In this case, there is a cycle of molecular adsorption, reaction, and desorption occurring at the catalyst surface. Thermodynamics, mass transfer, and heat transfer influence the Reaction rate, rate (kinetics) of reaction. Heterogeneous catalysis is very important because it enables faster, large-scale production and the selective product formation. Approximately 35% of the world's GDP is influenced by catalysis. The production of 90% of chemicals (by volume) is assisted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propylene
Propylene, also known as propene, is an unsaturated organic compound with the chemical formula . It has one double bond, and is the second simplest member of the alkene class of hydrocarbons. It is a colorless gas with a faint petroleum-like odor. Propylene is a product of combustion from forest fires, cigarette smoke, and motor vehicle and aircraft exhaust. It was discovered in 1850 by A. W. von Hoffmann's student Captain (later Major General) John Williams Reynolds as the only gaseous product of thermal decomposition of amyl alcohol to react with chlorine and bromine. Production Steam cracking The dominant technology for producing propylene is steam cracking, using propane as the feedstock. Cracking propane yields a mixture of ethylene, propylene, methane, hydrogen gas, and other related compounds. The yield of propylene is about 15%. The other principal feedstock is naphtha, especially in the Middle East and Asia. Propylene can be separated by fractional distill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incomplete Combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion does not always result in fire, because a flame is only visible when substances undergoing combustion vaporize, but when it does, a flame is a characteristic indicator of the reaction. While activation energy must be supplied to initiate combustion (e.g., using a lit match to light a fire), the heat from a flame may provide enough energy to make the reaction self-sustaining. The study of combustion is known as combustion science. Combustion is often a complicated sequence of elementary reaction, elementary Radical (chemistry), radical reactions. Solid fuels, such as wood and coal, first undergo endothermic pyrolysis to produce gaseous fuels whose combustion then supplies the heat required to produce more of them. Combustion is often hot e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal, a group 11 element, and one of the noble metals. It is one of the least reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemical elements, being the second-lowest in the reactivity series. It is solid under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state (metallurgy), native state), as gold nugget, nuggets or grains, in rock (geology), rocks, vein (geology), veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as in electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |