|
Ensoniq ES-5506 OTTO
The Ensoniq ES-5506 "OTTO" is a chip used in implementations of sample-based synthesis. Musical instruments and IBM PC compatible sound cards were the most popular applications. OTTO is capable of altering the pitch and timbre of a digital recording and is capable of operating with up to 32 channels at once. Each channel can have several parameters altered, such as pitch, volume, waveform, and filtering. The chip is a VLSI device designed to be manufactured on a 1.5 micrometre double-metal CMOS process. It consists of approximately 80,000 transistors. It was part of the fourth generation of Ensoniq audio technology. Major features * Real-time digital filters * Frequency interpolation * 32 independent voices * Loop start and stop positions for each voice (bidirectional and reverse looping) * Motorola 68000 compatibility for asynchronous bus communication * Separate host and sound memory interface * At least 18-bit accuracy * 6-channel stereo serial communication port * Programmabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ensoniq ES-5506 OTTO Sound Chip With 32 Voice Wavetable Oscillator
Ensoniq Corp. was an American electronics manufacturer, best known throughout the mid-1980s and 1990s for its musical instruments, principally Sampler (musical instrument), samplers and synthesizers. Company history In spring 1983, former MOS Technology engineers Robert Yannes, Robert "Bob" Yannes, Bruce Crockett, Charles Winterble, David Ziembicki, and Al Charpentier formed Peripheral Visions. The team had designed the Commodore 64, and hoped to build another computer. To raise funds, Peripheral Visions agreed to build a computer keyboard for the Atari 2600, but the video game crash of 1983 canceled the project and Commodore sued the new company, claiming that it owned the keyboard project. Renaming itself as Ensoniq, the new company instead designed a music synthesizer. Ensoniq grew rapidly over the next few years with the success of the Mirage and the ESQ-1. The plant in Great Valley, Pennsylvania employed nearly 200 people and housed the manufacturing facility. A number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorola 68000
The Motorola 68000 (sometimes shortened to Motorola 68k or m68k and usually pronounced "sixty-eight-thousand") is a 16/32-bit complex instruction set computer (CISC) microprocessor, introduced in 1979 by Motorola Semiconductor Products Sector. The design implements a 32-bit instruction set, with 32-bit registers and a 16-bit internal data bus. The address bus is 24 bits and does not use memory segmentation, which made it easier to program for. Internally, it uses a 16-bit data arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and two more 16-bit ALUs used mostly for addresses, and has a 16-bit external data bus. For this reason, Motorola termed it a 16/32-bit processor. As one of the first widely available processors with a 32-bit instruction set, and running at relatively high speeds for the era, the 68k was a popular design through the 1980s. It was widely used in a new generation of personal computers with graphical user interfaces, including the Macintosh 128K, Amiga, Atari ST, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ensoniq SoundscapeDB
The SoundscapeDB is an Ensoniq-designed and produced MIDI daughtercard designed to interface with the "Waveblaster" pin header available on many older sound cards. It was released in 1994. During the early 1990s, Creative Labs created the Waveblaster connector for their Sound Blaster 16 sound cards. This connector would be for their sample-based synthesis upgrade daughtercard, which they also called the Waveblaster. Other sound card manufacturers took advantage of this and put the connector on their cards as well, and many manufacturers also began developing their own upgrade daughtercards. Ensoniq's daughterboard (DB), the SoundscapeDB, is basically a Soundscape S-2000 with the digital sound reproduction section removed. It was simply the MIDI synthesizer (sample-based synthesizer) of the full Soundscape. The DB contained an Ensoniq OTTOR2 synthesizer chip, a Motorola 68EC000 controller, and a 2 MB patch set ROM. Ensoniq switched to a "revised and improved" 1 MB ROM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ensoniq Soundscape Elite
The Soundscape Elite was Ensoniq's high-end ISA PC sound card offering. It offers the highest MIDI quality of any PC sound card Ensoniq produced. The board is an evolution of the company's previous Soundscape S-2000. The Soundscape ELITE was launched in March 1995. Google Groups, April 2, 1995. Overview 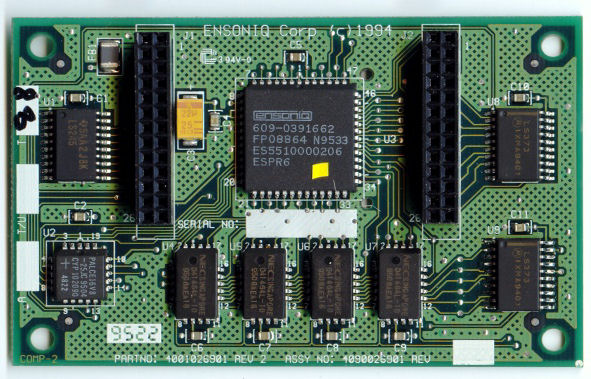 The card's layout is quite similar to the Soundscape S-2000, and uses the same synthesizer chips and codecs. Changes include a revision of the 2
The card's layout is quite similar to the Soundscape S-2000, and uses the same synthesizer chips and codecs. Changes include a revision of the 2
|
Ensoniq Soundscape S-2000
Soundscape S-2000 was Ensoniq's first direct foray into the PC sound card market. The card arrived on the market in 1994. It is a full-length ISA digital audio and sample-based synthesis device, equipped with a 2 MiB Ensoniq-built ROM-based patch set. Some OEM versions of the card feature a smaller 1 MiB patch set. It was praised for its then-high quality music synthesis and sound output, high compatibility and good software support. Hardware overview Ensoniq advertisements for the Soundscape stated "Finally, A Sound Card from a company that knows sound!", claiming that "the same wavetable technology that drives our $3,000 keyboards is available for your PC". The card uses an 'OTTO' synthesizer chip with a companion 'Sequoia' chip for MIDI duties, along with a Motorola 68EC000 8 MHz controller (a low-cost variant of the ubiquitous 68000 with selectable bus width) and a small amount of RAM. Although it has RAM, the card does not support uploading of sound samples for the synthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ensoniq TS10/TS12 Synthesizers
Ensoniq Corp. was an American electronics manufacturer, best known throughout the mid-1980s and 1990s for its musical instruments, principally samplers and synthesizers. Company history In spring 1983, former MOS Technology engineers Robert "Bob" Yannes, Bruce Crockett, Charles Winterble, David Ziembicki, and Al Charpentier formed Peripheral Visions. The team had designed the Commodore 64, and hoped to build another computer. To raise funds, Peripheral Visions agreed to build a computer keyboard for the Atari 2600, but the video game crash of 1983 canceled the project and Commodore sued the new company, claiming that it owned the keyboard project. Renaming itself as Ensoniq, the new company instead designed a music synthesizer. Ensoniq grew rapidly over the next few years with the success of the Mirage and the ESQ-1. The plant in Great Valley, Pennsylvania employed nearly 200 people and housed the manufacturing facility. A number of successful products followed which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seta SSV System
In biology, setae (singular seta ; from the Latin word for " bristle") are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms. Animal setae Protostomes Annelid setae are stiff bristles present on the body. They help, for example, earthworms to attach to the surface and prevent backsliding during peristaltic motion. These hairs make it difficult to pull a worm straight from the ground. Setae in oligochaetes (a group including earthworms) are largely composed of chitin. They are classified according to the limb to which they are attached; for instance, notosetae are attached to notopodia; neurosetae to neuropodia. Crustaceans have mechano- and chemosensory setae. Setae are especially present on the mouthparts of crustaceans and can also be found on grooming limbs. In some cases, setae are modified into scale like structures. Setae on the legs of krill and other small crustaceans help them to gather phytoplankton. It captures them and al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taito F3 System
The Taito F3 Package System (Taito Cybercore in North America) is a 32-bit arcade system board released by Taito in 1992. Specifications * CPU: Motorola MC68EC020; * Sound CPU: Motorola MC68000; * Sound chip: Ensoniq ES5505 and ES5510 (DSP); * Video resolution: 320×224; * Board composition: Board and F3 cartridge; * Hardware features: four scrolling layers, two sprite banks, Alpha blending Games * '' Arabian Magic'' * ''Arkanoid Returns'' * '' Bubble Memories'' * ''Bubble Symphony'' / ''Bubble Bobble 2'' * '' Cleopatra Fortune'' * '' Command War - Super Special Battle & War Game'' * '' Darius Gaiden - Silver Hawk'' * '' Dungeon Magic'' * '' Elevator Action Returns'' * '' Gekirindan'' * '' Grid Seeker'' * '' International Cup '94'' * '' Kaiser Knuckle'' / ''Global Champion'' / ''Dan-Ku-Ga'' * '' Kirameki Star Road'' * '' LandMaker'' * '' Puzzle Bobble 2'' / ''Bust-A-Move Again'' * ''Puzzle Bobble 2x'' * '' Puzzle Bobble 3'' * '' Puzzle Bobble 4'' * '' Pop 'N Pop'' * '' Puchi Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink). A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electrical power, power. The transistor is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits. Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld proposed the concept of a field-effect transistor in 1926, but it was not possible to actually co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sample-based Synthesis
Sample-based synthesis is a form of audio synthesis that can be contrasted to either subtractive synthesis or additive synthesis. The principal difference with sample-based synthesis is that the seed waveforms are sampled sounds or instruments instead of fundamental waveforms such as sine and saw waves used in other types of synthesis. History Before digital recording became practical, instruments such as the Welte (1930s), phonogene (1950s) and the Mellotron The Mellotron is an electro-mechanical musical instrument developed in Birmingham, England, in 1963. It is played by pressing its keys, each of which pushes a length of magnetic tape against a capstan, which pulls it across a playback head. A ... (1960s) used analog optical disks or analog tape decks to play back sampled sounds. When sample-based synthesis was first developed, most affordable consumer synthesizers could not record arbitrary samples, but instead formed timbres by combining pre-recorded samples fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips (including CMOS BIOS), and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors ( CMOS sensors), data converters, RF circuits ( RF CMOS), and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. The CMOS process was originally conceived by Frank Wanlass at Fairchild Semiconductor and presented by Wanlass and Chih-Tang Sah at the International Solid-State Circuits Conference in 1963. Wanlass later filed US patent 3,356,858 for CMOS circuitry and it was granted in 1967. commercialized the technology with the trademar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)