|
Engram (neuropsychology)
An engram is a unit of cognitive information imprinted in a physical substance, theorized to be the means by which memories are stored as biophysical or biochemical changes in the brain or other biological tissue, in response to external stimuli. Demonstrating the existence of, and the exact mechanism and location of, neurologically defined engrams has been a focus of persistent research for many decades. History The term "engram" was coined by memory researcher Richard Semon in reference to the physical substrate of memory in the organism. Semon warned, however: "In animals, during the evolutionary process, one organic system—the nervous system—has become specialised for the reception and transmission of stimuli. No monopoly of this function by the nervous system, however, can be deduced from this specialisation, not even in its highest state of evolution, as in Man." One of the first ventures on identifying the location of a memory in the brain was undertaken by Karl S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognition
Cognition is the "mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, imagination, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem-solving and decision-making, comprehension and production of language. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge to discover new knowledge. Cognitive processes are analyzed from very different perspectives within different contexts, notably in the fields of linguistics, musicology, anesthesia, neuroscience, psychiatry, psychology, education, philosophy, anthropology, biology, systemics, logic, and computer science. These and other approaches to the analysis of cognition (such as embodied cognition) are synthesized in the developing field of cognitive science, a progressively autonomou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amygdala
The amygdala (; : amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek language, Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is a paired nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclear complex present in the Cerebral hemisphere, cerebral hemispheres of vertebrates. It is considered part of the limbic system. In Primate, primates, it is located lateral and medial, medially within the temporal lobes. It consists of many nuclei, each made up of further subnuclei. The subdivision most commonly made is into the Basolateral amygdala, basolateral, Central nucleus of the amygdala, central, cortical, and medial nuclei together with the intercalated cells of the amygdala, intercalated cell clusters. The amygdala has a primary role in the processing of memory, decision making, decision-making, and emotions, emotional responses (including fear, anxiety, and aggression). The amygdala was first identified and named by Karl Friedrich Burdach in 1822. Structure Thirteen Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei have been identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Review Of Psychology
The ''Annual Review of Psychology'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes review articles about psychology. First published in 1950, its longest-serving editors have been Mark Rosenzweig (1969–1994) and Susan Fiske (2000–present). As of 2023, ''Annual Review of Psychology'' is being published as open access, under the Subscribe to Open model. As of 2024, '' Journal Citation Reports'' gives the journal a 2023 impact factor of 23.6, ranking it first of 92 journal titles in the category "Psychology (Science)" and first of 218 titles in the category "Psychology, Multidisciplinary (Social Science)". History In 1947, the board of directors of the publishing company Annual Reviews asked a number of psychologists if it would be useful to have a journal that published an annual volume of review articles that summarized recent developments in the field. Responses were very positive, so in September 1947 they announced that the first volume of the ''Annual Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optogenetics
Optogenetics is a biological technique to control the activity of neurons or other cell types with light. This is achieved by Gene expression, expression of Channelrhodopsin, light-sensitive ion channels, Halorhodopsin, pumps or Photoactivated adenylyl cyclase, enzymes specifically in the target cells. On the level of individual Cell (biology), cells, Photoactivated adenylyl cyclase, light-activated enzymes and transcription factors allow precise control of biochemical signaling pathways. In Neuroscience, systems neuroscience, the ability to control the activity of a genetically defined set of neurons has been used to understand their contribution to decision making, learning, fear memory, mating, addiction, feeding, and locomotion. In a first medical application of optogenetic technology, vision was partially restored in a blind patient with Retinitis pigmentosa. Optogenetic techniques have also been introduced to map the Brain connectivity estimators, functional connectivity of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
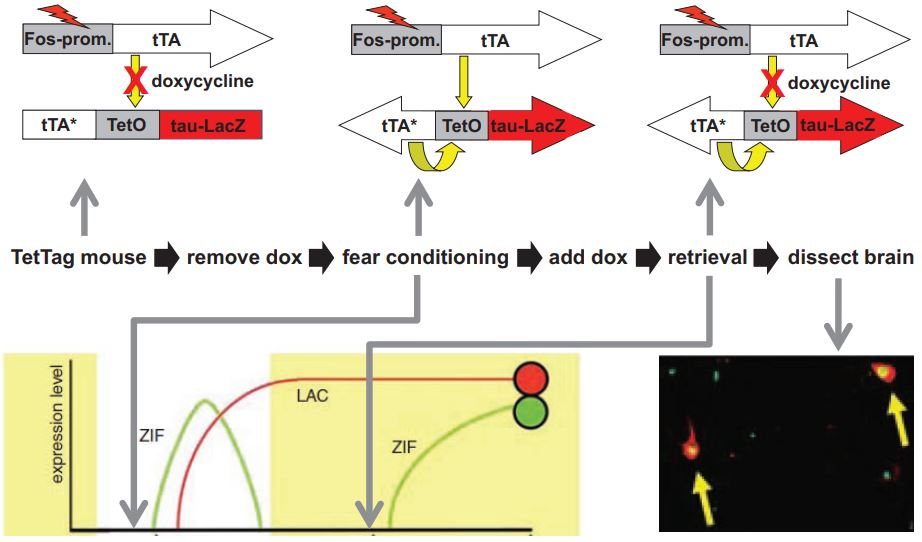
TetTag
The TetTag mouse is a bi-transgenic mutant used in neuroscience research that expresses a persistent marker (e.g. beta-galactosidase) under control of the immediate early gene ''fos''. This mouse strain allows the stable labeling of activated neurons in mice in a defined time window of several hours. Description Two independently generated transgenic strains were crossed to produce the TetTag strain. In the first transgenic construct, the tetracycline-controlled transactivator (tTA) protein and a two hour half-life Green Fluorescent Protein (shEGFP) are expressed under the direction of the '' fos'' minimal promoter. The second transgenic construct expresses a nuclear-localizing beta-galactosidase gene and the tetracycline regulated transactivator (tTA) under the control of the TetO tetracycline-responsive regulatory element. Memory research The TetTag mouse allows researchers to label activated neurons during a learning experiment (e.g. fear conditioning, water maze trainin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samskara (Indian Philosophy)
In Hindu Philosophy and some Indian religions, ''samskaras'' or ''sanskaras'' (Sanskrit: संस्कार) are mental impressions, recollections, or psychological imprints that colour one's thoughts and actions, and form the basis for the development of karma theory. In Buddhism, the Sanskrit term ''samskara'' is used to describe "mental formations," "will," and many other concepts; in Pāli it is referred to as '' saṅkhāra''. According to various schools of Indian philosophy, every action, intent or preparation by an individual leaves a ''samskara'' (impression, impact, imprint) in the deeper structure of the person's mind. These impressions then await volitional fruition in that individual's future, in the form of hidden expectations, circumstances or a subconscious sense of self-worth. These ''Samskaras'' manifest as tendencies, karmic impulses, subliminal impressions, habitual potencies or innate dispositions.Jeaneane Fowler (2002), Perspectives of Reality: An Introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Trace Theory
In psychology, multiple trace theory is a memory consolidation model advanced as an alternative model to Recognition memory, strength theory. It posits that each time some information is presented to a person, it is Neural coding, neurally encoded in a unique Neuronal memory allocation, memory trace composed of a combination of its attributes. Further support for this theory came in the 1960s from empirical findings that people could remember specific attributes about an object without remembering the object itself. The mode in which the information is presented and subsequently encoded can be flexibly incorporated into the model. This memory trace is unique from all others resembling it due to differences in some aspects of the item's attributes, and all memory traces incorporated since birth are combined into a multiple-trace representation in the brain. In memory research, a mathematical formulation of this theory can successfully explain empirical phenomena observed in Recognit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the average life expectancy following diagnosis is three to twelve years. The causes of Alzheimer's disease remain poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an allele of apolipoprotein E. Other risk factors include a history of head injury, clinical depression, and high blood pressure. The progression of the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatostatin
Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by #Nomenclature, several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the release of numerous secondary hormones. Somatostatin inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion. Somatostatin has two active forms produced by the alternative cleavage of a single preproprotein: one consisting of 14 amino acids (shown in infobox to right), the other consisting of 28 amino acids. Among the vertebrates, there exist six different somatostatin genes that have been named: ''SS1'', ''SS2'', ''SS3'', ''SS4'', ''SS5'' and ''SS6''. Zebrafish have all six. The six different genes, along with the five different somatostatin receptors, allow somatostatin to possess a large range of functions. Humans have only one somatostatin gene, ''SST''. Nomenclature Synonyms of "somatost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemogenetics
Chemogenetics is the process by which macromolecules can be engineered to interact with previously unrecognized small molecules. Chemogenetics as a term was originally coined to describe the observed effects of mutations on chalcone isomerase activity on substrate specificities in the flowers of ''Dianthus caryophyllus''. This method is very similar to optogenetics; however, it uses chemically engineered molecules and ligands instead of light and light-sensitive channels known as opsins. In recent research projects, chemogenetics has been widely used to understand the relationship between brain activity and behavior. Prior to chemogenetics, researchers used methods such as transcranial magnetic stimulation and deep brain stimulation to study the relationship between neuronal activity and behavior. Comparison to optogenetics Optogenetics and chemogenetics are the more recent and popular methods used to study this relationship. Both of these methods target specific brain circuits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optogenetics
Optogenetics is a biological technique to control the activity of neurons or other cell types with light. This is achieved by Gene expression, expression of Channelrhodopsin, light-sensitive ion channels, Halorhodopsin, pumps or Photoactivated adenylyl cyclase, enzymes specifically in the target cells. On the level of individual Cell (biology), cells, Photoactivated adenylyl cyclase, light-activated enzymes and transcription factors allow precise control of biochemical signaling pathways. In Neuroscience, systems neuroscience, the ability to control the activity of a genetically defined set of neurons has been used to understand their contribution to decision making, learning, fear memory, mating, addiction, feeding, and locomotion. In a first medical application of optogenetic technology, vision was partially restored in a blind patient with Retinitis pigmentosa. Optogenetic techniques have also been introduced to map the Brain connectivity estimators, functional connectivity of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a Private university, private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of modern technology and science. In response to the increasing Technological and industrial history of the United States, industrialization of the United States, William Barton Rogers organized a school in Boston to create "useful knowledge." Initially funded by a land-grant universities, federal land grant, the institute adopted a Polytechnic, polytechnic model that stressed laboratory instruction in applied science and engineering. MIT moved from Boston to Cambridge in 1916 and grew rapidly through collaboration with private industry, military branches, and new federal basic research agencies, the formation of which was influenced by MIT faculty like Vannevar Bush. In the late twentieth century, MIT became a leading center for research in compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |