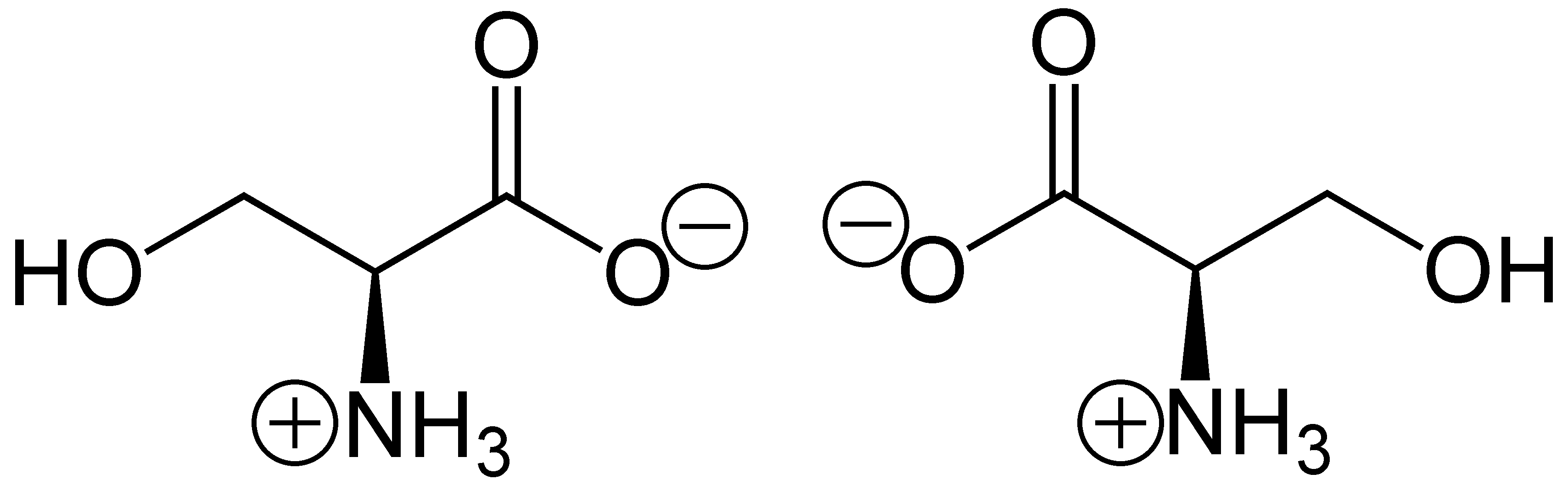|
Elementary Modes
Elementary modes may be considered minimal realizable flow patterns through a biochemical network that can sustain a steady state. This means that elementary modes cannot be decomposed further into simpler pathways. All possible flows through a network can be constructed from linear combinations of the elementary modes. The set of elementary modes for a given network is unique (up to an arbitrary scaling factor). Given the fundamental nature of elementary modes in relation to uniqueness and non-decomposability, the term `pathway' can be defined as an elementary mode. Note that the set of elementary modes will change as the set of expressed enzymes change during transitions from one cell state to another. Mathematically, the set of elementary modes is defined as the set of flux vectors, \mathbf, that satisfy the steady state condition, \mathbf\ \mathbf (\mathbf, \mathbf) = 0 where \mathbf is the stoichiometry matrix, \mathbf is the vector of rates, \mathbf the vector of steady ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry refers to the relationship between the quantities of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions. Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products, leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of the products can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated. This is illustrated in the image here, where the balanced equation is: : Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. This particular chemical equation is an example of complete combust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Systems Biology
Modelling biological systems is a significant task of systems biology and mathematical biology. Computational systems biology aims to develop and use efficient algorithms, data structures, visualization and communication tools with the goal of computer modelling of biological systems. It involves the use of computer simulations of biological systems, including cellular subsystems (such as the networks of metabolites and enzymes which comprise metabolism, signal transduction pathways and gene regulatory networks), to both analyze and visualize the complex connections of these cellular processes. An unexpected emergent property of a complex system may be a result of the interplay of the cause-and-effect among simpler, integrated parts (see biological organisation). Biological systems manifest many important examples of emergent properties in the complex interplay of components. Traditional study of biological systems requires reductive methods in which quantities of data are gathered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systems Biology
Systems biology is the computational modeling, computational and mathematical analysis and modeling of complex biological systems. It is a biology-based interdisciplinary field of study that focuses on complex interactions within biological systems, using a holistic approach (holism instead of the more traditional reductionist, reductionism) to biological research. Particularly from the year 2000 onwards, the concept has been used widely in biology in a variety of contexts. The Human Genome Project is an example of applied systems thinking in biology which has led to new, collaborative ways of working on problems in the biological field of genetics. One of the aims of systems biology is to model and discover emergent property, emergent properties, properties of cell (biology), cells, tissue (biology), tissues and organisms functioning as a system whose theoretical description is only possible using techniques of systems biology. These typically involve metabolic networks or cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomedical Engineering
Biomedical engineering (BME) or medical engineering is the application of engineering principles and design concepts to medicine and biology for healthcare purposes (e.g., diagnostic or therapeutic). BME is also traditionally logical sciences to advance health care treatment, including diagnosis, monitoring, and therapy. Also included under the scope of a biomedical engineer is the management of current medical equipment in hospitals while adhering to relevant industry standards. This involves procurement, routine testing, preventive maintenance, and making equipment recommendations, a role also known as a Biomedical Equipment Technician (BMET) or as clinical engineering. Biomedical engineering has recently emerged as its own study, as compared to many other engineering fields. Such an evolution is common as a new field transition from being an interdisciplinary specialization among already-established fields to being considered a field in itself. Much of the work in biomedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Engineering
Biological engineering or bioengineering is the application of principles of biology and the tools of engineering to create usable, tangible, economically-viable products. Biological engineering employs knowledge and expertise from a number of pure and applied sciences, such as mass and heat transfer, kinetics, biocatalysts, biomechanics, bioinformatics, separation and purification processes, bioreactor design, surface science, fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, and polymer science. It is used in the design of medical devices, diagnostic equipment, biocompatible materials, renewable energy, ecological engineering, agricultural engineering, process engineering and catalysis, and other areas that improve the living standards of societies. Examples of bioengineering research include bacteria engineered to produce chemicals, new medical imaging technology, portable and rapid disease diagnostic devices, prosthetics, biopharmaceuticals, and tissue-engineered organs. Bioengineering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
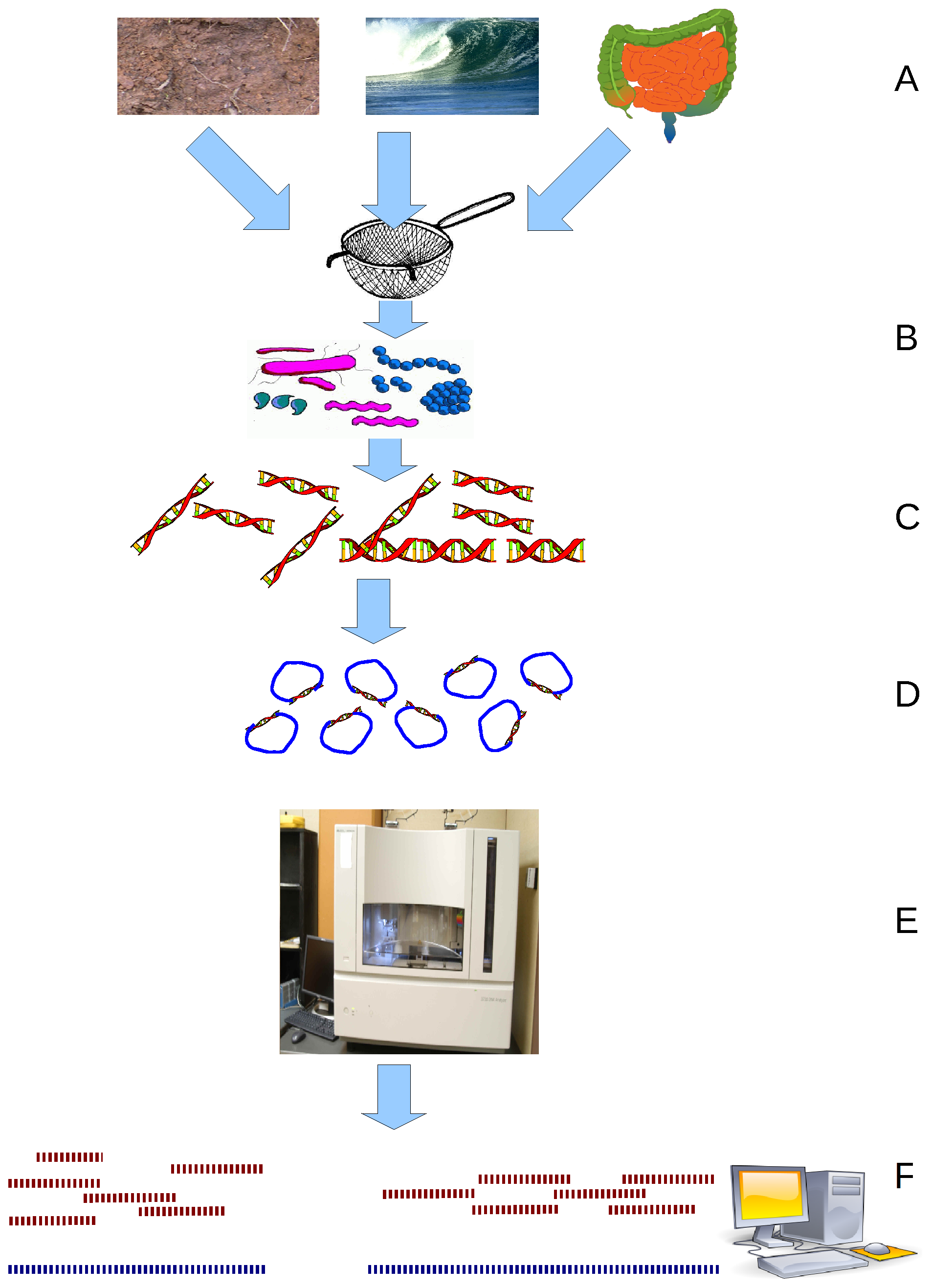
Metagenomics
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental or clinical samples by a method called sequencing. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics, community genomics or microbiomics. While traditional microbiology and microbial genome sequencing and genomics rely upon cultivated clonal cultures, early environmental gene sequencing cloned specific genes (often the 16S rRNA gene) to produce a profile of diversity in a natural sample. Such work revealed that the vast majority of microbial biodiversity had been missed by cultivation-based methods. Because of its ability to reveal the previously hidden diversity of microscopic life, metagenomics offers a powerful lens for viewing the microbial world that has the potential to revolutionize understanding of the entire living world. As the price of DNA sequencing continues to fall, metagenomics now allows microbial ecology to be investigated at a much greater s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Network
A metabolic network is the complete set of metabolic and physical processes that determine the physiological and biochemical properties of a cell. As such, these networks comprise the chemical reactions of metabolism, the metabolic pathways, as well as the regulatory interactions that guide these reactions. With the sequencing of complete genomes, it is now possible to reconstruct the network of biochemical reactions in many organisms, from bacteria to human. Several of these networks are available online: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), EcoCyc, BioCyc and metaTIGER. Metabolic networks are powerful tools for studying and modelling metabolism. Uses Metabolic networks can be used to detect comorbidity patterns in diseased patients. Certain diseases, such as obesity and diabetes, can be present in the same individual concurrently, sometimes one disease being a significant risk factor for the other disease. The disease phenotypes themselves are normally the conse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Control Analysis
Metabolic control analysis (MCA) is a mathematical framework for describing metabolic, signaling, and genetic pathways. MCA quantifies how variables,elastsuch as fluxes and species concentrations, depend on network parameters. In particular, it is able to describe how network-dependent properties, called control coefficients, depend on local properties called elasticities or Elasticity Coefficients. MCA was originally developed to describe the control in metabolic pathways but was subsequently extended to describe signaling and genetic networks. MCA has sometimes also been referred to as ''Metabolic Control Theory,'' but this terminology was rather strongly opposed by Henrik Kacser, one of the founders. More recent work has shown that MCA can be mapped directly on to classical control theory and are as such equivalent. Biochemical systems theory is a similar formalism, though with rather different objectives. Both are evolutions of an earlier theoretical analysis by Jose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CC-BY Icon
A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work".A "work" is any creative material made by a person. A painting, a graphic, a book, a song/lyrics to a song, or a photograph of almost anything are all examples of "works". A CC license is used when an author wants to give other people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that the author has created. CC provides an author flexibility (for example, they might choose to allow only non-commercial uses of a given work) and protects the people who use or redistribute an author's work from concerns of copyright infringement as long as they abide by the conditions that are specified in the license by which the author distributes the work. There are several types of Creative Commons licenses. Each license differs by several combinations that condition the terms of distribution. They were initially released on December 16, 2002, by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the naturally occurring proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L- stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, ''sericum''. Serine's structure w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |