|
East Bengal Legislative Assembly
The East Pakistan Provincial Assembly, known as the East Bengal Legislative Assembly between 1947 and 1955, was the provincial legislature of East Pakistan between 1947 and 1971. It was known as the East Bengal Assembly from 1947 to 1955 when the provincial name was changed. The legislature was a successor to the Bengal Legislative Council and the Bengal Legislative Assembly, which were divided between East Bengal and West Bengal during the partition of Bengal in 1947. It was the largest provincial legislature in Pakistan. Elections were held only twice in 1954 and 1970. During the Bangladesh War of Independence in 1971, most Bengali members elected to the Pakistani National Assembly and the East Pakistani provincial assembly became members of the Constituent Assembly of Bangladesh. History Partition of Bengal On 20 June 1947, 141 East Bengali legislators from the Bengal Legislative Assembly voted on the partition of Bengal, with 107 supporting joining Pakistan's Constitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th Provincial Assembly Of East Pakistan
Fifth is the Ordinal number (linguistics), ordinal form of the number 5, five. Fifth or The Fifth may refer to: * Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution, as in the expression "pleading the Fifth" * Fifth Avenue * Fifth column, a political term * Fifth disease, a contagious rash that spreads in school-aged children * Fifth force, a proposed force of nature in addition to the four known fundamental forces * Fifth of July (New York), historic celebration of an Emancipation Day in New York * Fifth (Stargate), Fifth (''Stargate''), a robotic character in the television series ''Stargate SG-1'' * Fifth (unit), a unit of volume formerly used for distilled beverages in the U.S. * 1st Battalion, 5th Marines * The fraction 1/5 * The royal fifth (Spanish and Portuguese), an old royal tax of 20% Music * A musical interval (music); specifically, a ** perfect fifth ** tritone, diminished fifth ** augmented fifth * Quartal and quintal harmony, Quintal harmony, in which chords concatena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
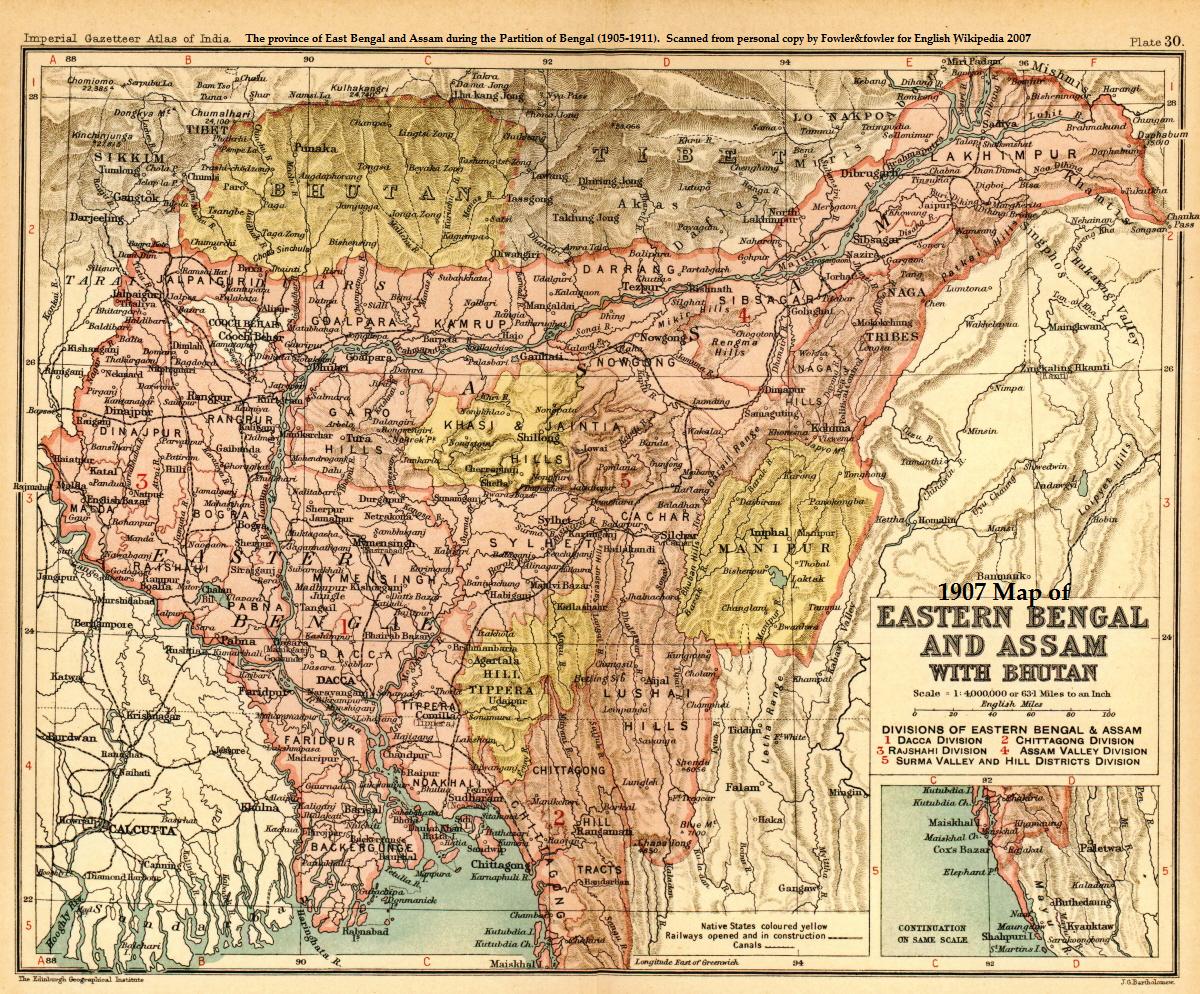
Colonial Assam
Colonial Assam (1826–1947) refers to the period in the history of Assam between the signing of the Treaty of Yandabo and the Independence of India when Assam was under British Empire, British colonial rule. The political institutions and social relations that were established or severed during this period continue to have a direct effect on contemporary events. The legislature and political alignments that evolved by the end of the British rule continued in the post Independence period. The immigration of farmers from East Bengal and tea plantation workers from Central India continue to affect contemporary politics, most notably that which led to the Assam Movement and its aftermath. British annexation of Assam The region that came to be known as undivided Goalpara district came under British rule after the British acquired the Deewani for Bengal Presidency, Bengal from the Mughal Empire, Mughal Emperor in 1765. Due to indigenous ethnic influences on the region the police ''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permanent Settlement
The Permanent Settlement, also known as the Permanent Settlement of Bengal, was an agreement between the East India Company and landlords of Bengal to fix revenues to be raised from land that had far-reaching consequences for both agricultural methods and productivity in the entire British Empire and the political realities of the Indian countryside. It was concluded in 1793 by the Company administration headed by Charles, Earl Cornwallis. It formed one part of a larger body of legislation, known as the Cornwallis Code. The Cornwallis Code of 1793 divided the East India Company's service personnel into three branches: revenue, judicial, and commercial. Revenues were collected by ''zamindars'', native Indians who were treated as landowners. This division created an Indian landed class that supported British authority. The Permanent Settlement was introduced first in Bengal and Bihar and later in Varanasi and also the northern district of Madras. The system eventually spread all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Bengal State Acquisition And Tenancy Act Of 1950
The East Bengal State Acquisition and Tenancy Act of 1950 was a law passed by the newly formed democratic Government of East Bengal in the Dominion of Pakistan (present day Bangladesh). The bill was drafted on 31 March 1948 during the early years of Pakistan and passed on 16 May 1951. Before passage of the legislature, landed revenue laws of Bengal consisted of the Permanent Settlement Regulations of 1793 and the Bengal Tenancy Act of 1885. The 1793 legislature created a landed aristocracy (see: Zamindars of Bengal) which was supposed to be loyal to the British Empire. The Act of 1885 defined the rights and liabilities of the peasants ('' ryats'') in relation to their superior lords ('' Zamindars''). After the end of the British rule in 1947, the law abolished the Zamindari system in the region, after which the lands of the state were under the federal government. It was seen as a democratic move to a ''people's state'' rather than a feudal class system. After East Bengal, I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jogendra Nath Mandal
Jogendranath Mandal ( Bengali: যোগেন্দ্রনাথ মন্ডল; 29 January 1904 – 5 October 1968) emerged as a prominent figure among the architects of the nascent state of Pakistan. He served as the inaugural Minister of Law and Labour, as well as the subsequent Minister of Commonwealth and Kashmir Affairs. Within the Interim Government of India, he had previously held the portfolio of law. Distinguished as a leader representing the Scheduled Castes (Dalits), Mandal vehemently opposed the partition of Bengal in 1947. His rationale rested on the apprehension that a divided Bengal would subject the Dalits to the dominance of the majority caste-Hindus in West Bengal (India). Eventually opting to maintain his base in East Pakistan, Mandal aspired for the welfare of the Dalits and assumed a ministerial role in Pakistan as the Minister of Law and Labour. However, a few years subsequent to the partition, he left for India for safety of himself and his family t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1950 East Pakistan Riots
The 1950 East Pakistan riots (, ) took place between Hindus and Muslims in East Pakistan, which resulted in several thousands of Hindus being killed in pogroms. Background In August 1947, British India was partitioned into the Dominions of India and Pakistan on the basis of religion. Pakistan was to become the homeland for the Muslims of former British India with a majority Muslim population. The province of Bengal with a marginal Muslim majority was also partitioned with the Muslim majority East Bengal going to Pakistan and Hindu majority West Bengal going to India. The Sylhet district of Assam was added to East Bengal after the Sylhet Referendum, where the majority voted for Pakistan. According to the 1941 census, East Bengal had 28% non-Muslim population, the majority of them being Bengali Hindus. West Bengal has a 30.2% Muslim population, the rest were Hindus. The area comprising East Bengal, especially the Dhaka and Chittagong Divisions, had been witness to numerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengali Language Movement
The Bengali language movement was a political movement in East Bengal (modern-day Bangladesh) in 1952, advocating the recognition of the Bengali language as a co-lingua franca of the then-Dominion of Pakistan to allow its use in government affairs, the continuation of its use as a medium of education, its use in media, currency and stamps, and to maintain its writing in the Bengali alphabet and Bengali script. When the Dominion of Pakistan was formed after the separation of the Indian subcontinent in 1947, when the British left, it was composed of various ethnic and linguistic groups, with the geographically non-contiguous East Bengal province having a mainly ethnicity, ethnic Bengali people, Bengali population. In 1948, the Governor-General of Pakistan, Government of the Dominion of Pakistan ordained as part of Islamization of East Pakistan or East Bengal that Urdu will be the sole federal language, alternately Bengali writing in the Perso-Arabic script or Roman script (Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhaka High Court
The High Court Division, Supreme Court of Bangladesh (), popularly known as High Court, is one of the two divisions of the Supreme Court of Bangladesh, the other division being the Appellate Division. It consists of the Chief Justice of Bangladesh and other judges of the High Court Division. The High Court Division exercises both original and appellate jurisdiction An appellate court, commonly called a court of appeal(s), appeal court, court of second instance or second instance court, is any court of law that is empowered to hear a case upon appeal from a trial court or other lower tribunal. Appellat ... in civil and criminal matters. Its primary jurisdiction, however, is writ jurisdiction, pursuant to which it is empowered under article 102 of the Constitution of Bangladesh to issue writs of certiorari, mandamus, quo warranto, prohibition and habeas corpus. History The High Court of Judicature for East Bengal (1947 - 1955) The High Court of Judicature for East Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Dacca
The University of Dhaka (), also known as Dhaka University (DU), is a public research university located in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Established in 1921, it is the oldest active university in the country. The University of Dhaka was founded in 1921 under the Dacca University Act 1920 of the Indian Legislative Council. The establishment of the university in Dhaka was initiated with 600 acres of land requisitioned by the British government in 1905 after a new province of East Bengal and Assam was formed with Dhaka as its capital. Part of the land requisitioned belonged to the estate of Nawab Bahadur Sir Khwaja Salimullah. It is modeled after British universities. Currently it is the largest public research university in Bangladesh, with a student body of 46,150 and a faculty of 1,992. It has made significant contributions to the modern history of Bangladesh. After the Partition of India, it became the focal point of progressive and democratic movements in Pakistan. Its students and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagannath Hall
Jagannath Hall of Dhaka University is a residence hall for students from religious minorities, including Buddhists, Christian, and Hindus. It is one of the three original residence halls that date from the founding of the university in 1921, and is modelled on the colleges of the University of Oxford, a complex of buildings including residences, meeting rooms, dining rooms, a prayer hall, gardens, and sporting facilities. Of the approximately 2000 students of the hall, half live in the residences, and half are non-residential students affiliated with the college. Several professors at the university hold the positions of house tutors and provost at the hall. In 1971, the Pakistan Army killed over 300 students at this Hindu-majority dormitory. Structures The hall includes four residential buildings: * Govinda Chandra Dev building * Sontosh Chandra Bhattacharya Bhavan (New Building) * October Memorial Building (October Smiriti Bhaban) * Jyotirmoy Guhathakurta building History Esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nurul Amin
Nurul Amin (15 July 1893 – 2 October 1974) was a Pakistani politician and jurist who served as the eighth prime minister of Pakistan from 7 December to 20 December 1971. His premiership term of only 13 days was the shortest served in Pakistani history. Starting his political career in 1948 as Chief Minister of East Bengal, he headed the Ministry of Supply. Despite being a Bengali, Amin was against the Bengali language movement of 1952. After participating in the 1970 Pakistani general election, He was appointed as the Prime Minister of Pakistan. He was the first and only vice president of Pakistan, serving from 1970 to 1972, and also led Pakistan during the Bangladesh War of Independence. Early life Nurul Amin was born on 15 July 1893 in Shahbazpur, Sarail located in Tippera District of the Bengal Presidency (now in Brahmanbaria District, Bangladesh). He belonged to a Bengali Muslim family from the village of Bahadurpur in Nandail, Mymensingh District. His father wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khawaja Nazimuddin
Sir Khawaja Nazimuddin (19 July 1894 – 22 October 1964), also spelled Khwaja Nazimuddin, was a Pakistani politician and statesman who served as the second Governor-General of Pakistan from 1948 to 1951, and later as the second Prime Minister of Pakistan from 1951 to 1953. Born into an aristocratic Nawab family in Bengal in 1894, he was educated at the Aligarh Muslim University before pursuing his post-graduation studies at the Cambridge University. Upon returning, he embarked on his journey as a politician on the platform of the All-India Muslim League. Initially, his political career revolved around advocating for educational reforms and development in Bengal. Later on, he started supporting the cause for a separate Muslim homeland, rising to become the party's principal Bengali leader and a close associate of Muhammad Ali Jinnah. He served as Prime Minister of Bengal in British India from 1943 to 1945, and later as the 1st Chief Minister of East Bengal in independent P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |