|
EMD F3
The EMD F3 is a B-B freight- and passenger-hauling carbody diesel locomotive produced between July 1945 and February 1949 by General Motorsâ Electro-Motive Division. Final assembly was at GM-EMD's La Grange, Illinois plant. A total of 1,106 cab-equipped lead A units and 694 cabless booster B units were built. The F3 was the third model in GM-EMD's highly successful F-unit series of cab unit diesel locomotives, and it was the second most produced of the series. The F3 essentially differed from the EMD F2 in that it used the ânewâ D12 generator to produce more power and from the later EMD F7 in electrical equipment. Some late-model F3's had the same D27 traction motors, along with the heavier-duty electrical cables, used in the F7, and were referred to as model F5 by EMD's Engineering Department. Design The F3 used a 16-cylinder 567B series diesel engine developing at 800 rpm. The 567 was purpose-designed for locomotive service, and is a mechanically-aspira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Coast Hiawatha
The ''North Coast Hiawatha'' was a long-distance passenger train operated by Amtrak between Chicago, Illinois, and Seattle, Washington. The train was a successor to the Northern Pacific Railway's '' North Coast Limited'' and '' Mainstreeter''. Its name is a combination of ''North Coast Limited'' and ''Hiawatha'', a Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad (Milwaukee Road) train whose route it followed east of MinneapolisâSt. Paul. Created at the behest of Congress in 1971, the ''North Coast Hiawatha'' had an uncertain existence before being discontinued in 1979 amid a wave of Amtrak cuts. This left the ''Empire Builder'' as the lone train through Montana and North Dakota and severed some of these states' most populous cities from the rail network, including Missoula, Butte, Bozeman, Billings, and Bismarck. Rail advocates have called for the return of the ''North Coast Hiawatha'' ever since its discontinuation. Efforts have accelerated in the 2020s with the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Grange, Illinois
La Grange ( ; often spelled LaGrange) is a village (United States)#Illinois, village in Cook County, Illinois, United States. It is a suburb of Chicago. The population was 16,321 at the 2020 census. History The area around La Grange was first settled in the 1830s, when Chicago residents moved out to the west due to the rapid population increase in the city in the decade since its incorporation. The first settler, Robert Leitch, came to the area in 1830, seven years before the City of Chicago was incorporated. La Grange's location, at approximately from the Chicago Loop, is not considered far from the city by today's standards, but in that time the residents enjoyed the peace of rural life without much communication with urban residents. The village was officially incorporated on June 11, 1879. It was founded by Franklin Dwight Cossitt, who was born in Granby, Connecticut, and raised in Tennessee, and moved to Chicago in 1862 where he built a successful wholesale grocery busines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
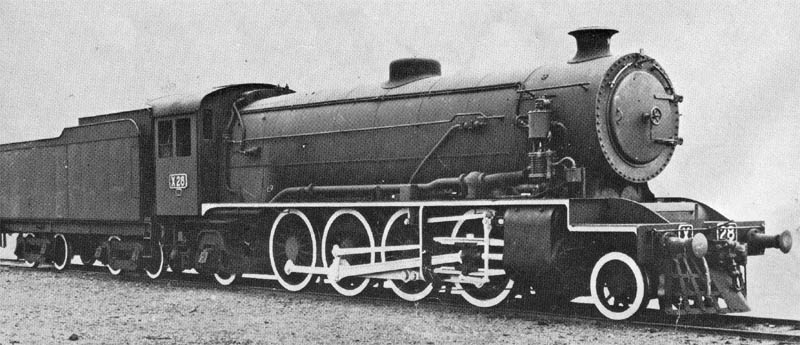
2-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and two trailing wheels on one axle, usually in a trailing truck. This configuration of steam locomotive is most often referred to as a Mikado, frequently shortened to Mike. It was also at times referred to on some railroads in the United States as the McAdoo Mikado and, during World War II, the MacArthur. The notation 2-8-2T indicates a tank locomotive of this wheel arrangement, the "T" suffix indicating a locomotive on which the water is carried in tanks mounted on the engine rather than in an attached tender. Overview The 2-8-2 wheel arrangement allowed the locomotive's firebox to be placed behind instead of above the driving wheels, thereby allowing a larger firebox that could be both wide and deep. This supported a greater rate of combustion and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MissouriâKansasâTexas Railroad
The MissouriâKansasâTexas Railroad was a Class I railroad company in the United States, with its last headquarters in Dallas, Texas. Established in 1865 under the name Union Pacific Railroad (UP), Southern Branch, it came to serve an extensive rail network in Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Missouri. In 1988, it merged with the Missouri Pacific Railroad; today, it is part of UP. In the 1890s, the MKT was commonly referred to as "the K-T", because for a time it was the KansasâTexas division of the Missouri Pacific Railroad and "KT" was its abbreviation in timetables as well as its stock exchange symbol. This soon evolved into the nickname "the Katy". The Katy was the first railroad to enter Texas from the north. Eventually, the Katy's core system linked Parsons, Emporia, Fort Scott, Junction City, Olathe, and Kansas City, Kansas; Kansas City, Joplin, Columbia, McKittrick, Jefferson City, and St. Louis, Missouri; Tulsa, Wagoner; and Oklahoma City, Oklahoma; Dalla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dieselization
Dieselisation (US: dieselization) is the process of equipping vehicles with a diesel engine or diesel engines. It can involve replacing an internal combustion engine powered by petrol (US: gasoline) fuel with an engine powered by diesel fuel, as occurred on a large scale with trucks, buses, farm tractors, trains, and building construction machinery after World War II. Alternatively it can involve replacing the entire plant or vehicle with one that is diesel-powered; the term commonly describes the generational replacement between the 1930s to 1970s of railway steam locomotives with diesel locomotives, and associated facilities. Water transport The two-stroke diesel engine for marine applications was introduced in 1908 and remains in use today. It is the most efficient prime mover to date, models such as the Wärtsilä-Sulzer RTA96-C offer a thermal efficiency of 50% and over 100,000 horsepower. First steps towards conversions using diesel engines as means of propulsion (on sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMD FT
The EMD FT is a diesel-electric locomotive that was produced between March 1939 and November 1945, by General Motors' Electro-Motive Corporation (EMC), later known as GM Electro-Motive Division (EMD). The "F" stood for Fourteen Hundred (1400) horsepower (rounded from 1350) and the "T" for Twin, as it came standard in a two-unit set. The design was developed from the TA model built for the C,RI&P in 1937, and was similar in cylinder count, axle count, length, and layout. All told 555 cab-equipped âAâ units were built, along with 541 cabless booster or âBâ units, for a grand total of 1,096 units. The locomotives were all sold to customers in the United States. It was the first model in EMD's very successful F-unit series of cab unit freight diesels and was the locomotive that convinced many U.S. railroads that the diesel-electric freight locomotive was the future. Many rail historians consider the FT one of the most important locomotive models of all time. Design an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head-end Power
In rail transport, head-end power (HEP), also known as electric train supply (ETS), is the electrical power distribution system on a passenger train. The power source, usually a locomotive (or a generator car) at the front or 'head' of a train, provides the electricity used for heating, lighting, electrical and other 'hotel' needs. The maritime equivalent is hotel electric power. A successful attempt by the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway in October 1881 to light the passenger cars on the London to Brighton route heralded the beginning of using electricity to light trains in the world. History Oil lamps were introduced in 1842 to light trains. Economics drove the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway to replace oil with coal gas lighting in 1870, but a gas cylinder explosion on the train led them to abandon the experiment. Oil-gas lighting was introduced in late 1870. Electrical lighting was introduced in October 1881 by using twelve Swan carbon filament incandescent lamps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, electrical insulation, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron beam, electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A archaism, term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''Electric current, current'' or ''voltage''. Direct current may be converted from an alternating current supply by use of a rectifier, which contains Electronics, electronic elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be converted into alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-stroke Diesel Engine
A two-stroke diesel engine is a diesel engine that uses compression ignition in a two-stroke combustion cycle. It was invented by Hugo GĂźldner in 1899.Mau (1984) p.7 In compression ignition, air is first compressed and heated; fuel is then injected into the cylinder, causing it to self-ignite. This delivers a power stroke each time the piston rises and falls, without any need for the additional exhaust and induction strokes of the four-stroke cycle. History According to the engineer who drew up Rudolf Dieselâs design for one of the first operational diesel engine, Motor 250/400, Imanuel Lauster, Diesel did not originally intend using the two-stroke principle for the diesel engine. Hugo GĂźldner designed what is believed to be the first operational two-stroke diesel engine in 1899, and he convinced MAN, Krupp and Diesel to fund building this engine with âł 10,000 each. GĂźldner's engine had a 175 mm work cylinder, and a 185 mm scavenging cylinder; both had a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roots Blower
The Roots blower is a positive displacement lobe pump which operates by pumping a fluid with a pair of meshing lobes resembling a set of stretched gears. Fluid is trapped in pockets surrounding the lobes and carried from the intake side to the exhaust. The Roots blower design does not incorporate any reduction in volume/increase in pressure as air or other fluid passes through, hence it can best be described as a blower rather than a supercharger unlike some other designs of "supercharger" such as cozette, centric, Shorrock supercharger, Powerplus supercharger and also the axial flow Eaton type supercharger which have internal "compression". The most common application of the Roots-type blower has been the induction device on two-stroke diesel engines, such as those produced by Detroit Diesel and Electro-Motive Diesel. Roots-type blowers are also used to supercharge four-stroke Otto cycle engines, with the blower being driven from the engine's crankshaft via a toot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traction Motor
A traction motor is an electric motor used for propulsion of a vehicle, such as locomotives, electric vehicle, electric or hydrogen vehicles, or electric multiple unit trains. Traction (engineering), Traction motors are used in electrically powered railway vehicles (electric multiple units) and other electric vehicles including electric milk floats, trolleybuses, elevators, roller coasters, and conveyor systems, as well as vehicles with electrical transmission systems (Diesel locomotive#Transmission types, dieselâelectric locomotives, electric hybrid vehicles), and battery electric vehicles. Traction motor companies The word ''traction'' from Latin, being the Agent (grammar), agent noun of ''trahere'' "to pull" in the sense of "drawn" was used for the naming of traction engines developed circa 1870. The first experimental electric traction motor tramway of 1875 was rapidly developed internationally for city use. In the 19th century traction motor passenger car companies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMD F7
The EMD F7 is a model of diesel-electric locomotive produced between February 1949 and December 1953 by the Electro-Motive Division of General Motors (EMD) and General Motors Diesel (GMD). Although originally promoted by EMD as a freight-hauling unit, the F7 was also capable of passenger service, and used in hauling trains such as the Santa Fe Railway's high-speed flagship trains, the '' Super Chief, & El Capitan'', and the Ontario Northland's '' Northlander''. History The F7 was the fourth model in GM-EMD's successful line of F-unit locomotives, and by far the best-selling cab unit of all time. In fact, more F7s were built than all other F-units combined. The F7 succeeded the F3 model in GM-EMD's F-unit series, and was replaced in turn by the F9. Final assembly was at GM-EMD's La Grange, Illinois, plant or GMD's London, Ontario, facility. There was no F4, -5 or -6 model; "7" was chosen to match the contemporary twin-engine E7, and was also applied to the new GP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |