|
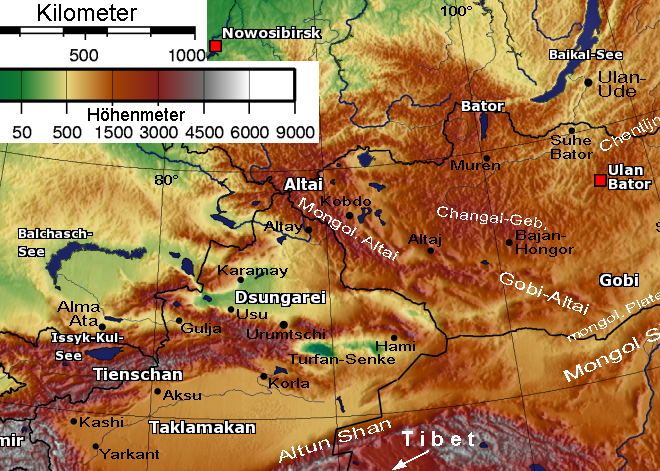
Dzhungarian Alatau
The Dzungarian Alatau ( mn, Зүүнгарын Алатау, ''Züüngaryn Alatau''; ; kk, Жетісу Алатауы, ''Jetısu Alatauy''; russian: Джунгарский Алатау, ''Dzhungarskiy Alatau'') is a mountain range that lies on the boundary of the Dzungaria region of China and the Zhetysu region of Kazakhstan. It has a length of and a maximum elevation of . Features The Dzhungraian Alatau consists of foothills, ridges, forts, and alpine meadows of the Northern Tian Shan (Trans-Ili Alatau, Ktmen). It is located at an altitude of 2,000m above sea level, and is over 400km long in the latitudinal direction. The Dzhungraian Alatau consists of two ranges that are distinctly parallel to each other: the northern (or main), and the southern range. The area includes several sub-parallel high mountain ranges, accompanied by low and short ranges and their spurs. It also holds the largest waterfall in Central Asia. A distinctive feature of the Dzunguarain Alatau is a ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dzungaria
Dzungaria (; from the Mongolian words , meaning 'left hand') is a geographical subregion in Northwest China that corresponds to the northern half of Xinjiang. It is thus also known as Beijiang, which means "Northern Xinjiang". Bounded by the Altai Mountains to the north and the Tian Shan mountain range to the south, Dzungaria covers approximately , and borders Kazakhstan to the west and Mongolia to the east. In contexts prior to the mid-18th century Dzungar genocide, the term "Dzungaria" could cover a wider area, conterminous with the Oirat-led Dzungar Khanate. Although Dzungaria is geographically, historically, and ethnically distinct from the Tarim Basin (or Nanjiang, ), the Manchu-led Qing dynasty integrated both areas into one province, Xinjiang. Dzungaria is Xinjiang's center of heavy industry, generates most of the region's GDP, and houses its political capital Ürümqi ( Oirat for 'beautiful pasture'). As such, Dzungaria continues to attract intraprovincial and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land, the List of countries and territories by land borders, most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces of China, provinces, five autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, four direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and two special administrative regions of China, Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the List of cities in China by population, most populous cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhetysu
Zhetysu, or Jeti-Suu ( kk, , Жетісу, pronounced ; ky, ''Jeti-Suu'', (), meaning "seven rivers"; also transcribed ''Zhetisu'', ''Jetisuw'', ''Jetysu'', ''Jeti-su'', ''Jity-su'', ''Жетысу'',, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency ''Джетысу'' etc. and ''Yedi-su'' in Turkish, هفتآب ''Haft-āb'' in Persian, Mongolian: “Долоон ус”, and Семире́чье ''Semiréchie'' in Russian), is a historical name of a part of Central Asia corresponding to the southeastern part of modern Kazakhstan. It owes its name, meaning "seven rivers" (literally, "seven waters") in Kazakh, to the rivers that flow from the southeast into Lake Balkhash. Zhetysu falls into today's Almaty Region and other South-Eastern parts of Kazakhstan and some parts of Northern Kyrgyzstan. Geography The lands of the 19th-century Semirechye Oblast included the steppes south of Lake Balkhash and parts of the Tian Shan Mountains around Lake Issyk Kul. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ... to Kazakhstan–Russia border, the north and west, China to China–Kazakhstan border, the east, Kyrgyzstan to Kazakhstan–Kyrgyzstan border, the southeast, Uzbekistan to Kazakhstan–Uzbekistan border, the south, and Turkmenistan to Kazakhstan–Turkmenistan border, the southwest, with a coastline along the Caspian Sea. Its capital is Astana, known as Nur-Sultan from 2019 to 2022. Almaty, Kazakhstan's largest city, was the country's capital until 1997. Kazakhstan is the world's largest landlocked country, the largest and northernmost Muslim world, Muslim-majority cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almaty
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to 1936 as an autonomous republic as part of the Soviet Union, then from 1936 to 1991 as a union republic and finally from 1991 as an independent state to 1997 when the government relocated the capital to Akmola (renamed Astana in 1998, Nur-Sultan in 2019, and back to Astana in 2022). Almaty is still the major commercial, financial, and cultural centre of Kazakhstan, as well as its most populous and most cosmopolitan city. The city is located in the mountainous area of southern Kazakhstan near the border with Kyrgyzstan in the foothills of the Trans-Ili Alatau at an elevation of 700–900 m (2,300–3,000 feet), where the Large and Small Almatinka rivers run into the plain. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arisen from the same cause, usually an orogeny. Mountain ranges are formed by a variety of geological processes, but most of the significant ones on Earth are the result of plate tectonics. Mountain ranges are also found on many planetary mass objects in the Solar System and are likely a feature of most terrestrial planets. Mountain ranges are usually segmented by Highland (geography), highlands or mountain passes and valleys. Individual mountains within the same mountain range do not necessarily have the same Structural geology, geologic structure or petrology. They may be a mix of different orogenic expressions and terranes, for example Thrust fault, thrust sheets, Fault-block mountain, uplifted blocks, Fold (geology), fold mountains, and vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vertical datum). The term ''elevation'' is mainly used when referring to points on the Earth's surface, while '' altitude'' or '' geopotential height'' is used for points above the surface, such as an aircraft in flight or a spacecraft in orbit, and '' depth'' is used for points below the surface. Elevation is not to be confused with the distance from the center of the Earth. Due to the equatorial bulge, the summits of Mount Everest and Chimborazo have, respectively, the largest elevation and the largest geocentric distance. Aviation In aviation the term elevation or aerodrome elevation is defined by the ICAO as the highest point of the landing area. It is often measured in feet and can be found in approach charts of the aerodrome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tian Shan
The Tian Shan,, , otk, 𐰴𐰣 𐱅𐰭𐰼𐰃, , tr, Tanrı Dağı, mn, Тэнгэр уул, , ug, تەڭرىتاغ, , , kk, Тәңіртауы / Алатау, , , ky, Теңир-Тоо / Ала-Тоо, , , uz, Tyan-Shan / Tangritog‘, , also known as the Tengri Tagh or Tengir-Too, meaning the ''Mountains of Heaven'' or the ''Heavenly Mountain'', is a large system of mountain ranges located in Central Asia. The highest peak in the Tian Shan is Jengish Chokusu, at high. Its lowest point is the Turpan Depression, which is below sea level. One of the earliest historical references to these mountains may be related to the Xiongnu word ''Qilian'' ( zh, s=祁连, t=祁連, first=t, p=Qílián) – according to Tang commentator Yan Shigu, ''Qilian'' is the Xiongnu word for sky or heaven. Sima Qian in the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' mentioned ''Qilian'' in relation to the homeland of the Yuezhi and the term is believed to refer to the Tian Shan rather than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allium
''Allium'' is a genus of monocotyledonous flowering plants that includes hundreds of species, including the cultivated onion, garlic, scallion, shallot, leek, and chives. The generic name ''Allium'' is the Latin word for garlic,Gledhill, David (2008). "The Names of Plants". Cambridge University Press. (hardback), (paperback). pp 43 and the type species for the genus is ''Allium sativum'' which means "cultivated garlic".''Allium'' In: Index Nominum Genericorum. In: Regnum Vegetabile (see ''External links'' below). Carl Linnaeus first described the genus ''Allium'' in 1753. Some sources refer to Greek ἀλέω (aleo, to avoid) by reason of the smell of garlic. Various ''Allium'' have been cultivated from the earliest times, and about a dozen species are economically important as crops, or garden vegetables, and an increasing number of species are important as ornamental plants. The decision to include a species in the genus ''Allium'' is taxonomically difficult, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China–Kazakhstan Border
The China–Kazakhstan border or the Sino-Kazakhstan border ( kz, Қазақстан-Қытай мемлекеттiк шекарасы, russian: Казахстанско-китайская государственная граница, zh, s=中哈边界, p=Zhōng-Hā biānjiè), is the international border between the People's Republic of China and the Republic of Kazakhstan. The border line between the two countries has been largely inherited from the border existing between the Soviet Union and the PRC and, earlier, between the Russian Empire and the Qing Empire; however, it has been fully demarcated only in the late 20th and early 21st century. According to the international boundary commissions that have carried out the border demarcation, the border is long. History The origins of the border date from the mid-19th century, when the Russian Empire expanded into Central Asia and was able to establish its control over the Lake Zaysan region. The establishment of the borde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dzungarian Gate
The Dzungarian Gate (or Altai Gap or Altay Gap) is a geographically and historically significant mountain pass between China and Central Asia. It has been described as the "one and only gateway in the mountain-wall which stretches from Manchuria to Afghanistan, over a distance of three thousand miles []." Given its association with details in a story related by Herodotus, it has been linked to the location of legendary Hyperborea. The Dzungarian Gate (; kk, Жетісу қақпасы ''Jetısu qaqpasy'' or Жоңғар қақпасы ''Joñğar qaqpasy'') is a straight valley which penetrates the Dzungarian Alatau mountain range along the border between Kazakhstan and Xinjiang, China. It currently serves as a railway corridor between China and the west. Historically, it has been noted as a convenient pass suitable for riders on horseback between the western Eurasian steppe and lands further east, and for its fierce and almost constant winds. In his ''Histories'', Herodotus r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |