|
Dry Creek-Port Adelaide Railway Line
The Dry Creek–Port Adelaide railway line is an eight-kilometre east–west freight railway line running through Adelaide's north-western suburbs. The line is managed by the Australian Rail Track Corporation (ARTC) and is an important link between Port Adelaide, Pelican Point and the main interstate rail routes which link Adelaide with Melbourne, Perth, Darwin and Sydney. Prior to 1988, a limited local passenger service operated, stopping at five intermediate stations along the line. Since May 1988, the line has been freight-only. History The railway from Dry Creek on the Kapunda railway line to Port Adelaide opened on 1 February 1868. Its original purpose was to allow goods and minerals from South Australia's mid-north (and from 1878, the Murray River at Morgan) to reach the Port without needing to travel via Adelaide. This line ran directly into Port Dock station (now closed) which was Port Adelaide's main rail yard in the 19th century. Over the years, various alteration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Creek Railway Station
Dry Creek railway station is located on the Gawler railway line, Gawler line. Situated in the inner northern Adelaide suburb of Dry Creek, South Australia, Dry Creek, it is from Adelaide railway station, Adelaide station. History Dry Creek railway station opened in 1856. The station was rebuilt in 1982 and a bogie exchange facility opened when the Adelaide-Port Augusta railway line, Adelaide-Crystal Brook line was converted to standard gauge. The exchange closed in October 1996, having been made redundant by the conversion of the Adelaide-Wolseley railway line, Adelaide to Wolseley line to standard gauge. To the west of the station lies the Australian Rail Track Corporation standard gauge line to Crystal Brook, South Australia, Crystal Brook. Dry Creek is where the Dry Creek-Port Adelaide railway line, Dry Creek to Port Adelaide railway line branches off via a Wye (rail), triangle junction, allowing trains from the north and south to head towards the branch line. To the wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethelton Railway Station
Ethelton station is located on the Outer Harbor line. Situated in the north-western Adelaide suburb of Ethelton, it is 13.1 kilometres from Adelaide station. History Ethelton station opened in 1916, following construction of the Commercial Road viaduct at Port Adelaide and a new bridge across the Port River. This new line diverted trains from Adelaide to Semaphore and Outer Harbor away from the congested rail yards at Port Dock station and to avoid heavy traffic along St Vincents Street in the centre of Port Adelaide. It has been unstaffed since the ticket office closed in 1980, and there is a small interchange for local buses adjacent to the station. The railway tracks through Ethelton are dual gauge and capable of carrying both broad gauge and trains. Until July 2008, the dual gauge tracks were used by freight trains from Dry Creek and the Rosewater loop which passed through Ethelton to access industrial facilities on the Lefevre Peninsula and the container terminal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outer Harbor And Port Dock Lines
The Outer Harbor line is a suburban commuter service in Adelaide, South Australia, that runs from Adelaide station through the north western suburbs to Port Adelaide and Outer Harbor. The Port Dock line is a service that shares its route with the Outer Harbor line until north of Alberton, where it branches along a spur to Port Dock station in Port Adelaide. History Opening in 1856, the inaugural railway between Adelaide and Port Dock railway station — named Port Adelaide until 1916 — was the second railway in the colony of South Australia, and the first government-owned railway in the British Empire. Port Adelaide junction was created when the railway was extended to cross the Port River to Le Fevre Peninsula. As industry developed on the west side of the Port River, a deeper harbour was required. Initially, this was at Semaphore, with the railway extended in 1882 as the now-closed Semaphore railway line to service the overseas shipping jetty there. The line was su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad Gauge
A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge (the distance between the rails) broader than the used by standard-gauge railways. Broad gauge of , more known as Russian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in former Soviet Union countries (CIS states, Baltic states, Rail transport in Georgia (country), Georgia, Ukraine) and Rail transport in Mongolia, Mongolia. Broad gauge of , commonly known as five foot gauge, is mainly used in Rail transport in Finland, Finland. Broad gauge of , commonly known as Irish gauge, is the dominant track gauge in Ireland, the Australian state of Rail transport in Victoria, Victoria and Railways in Adelaide, Adelaide in South Australia and Rail transport in Brazil, passenger trains of Brazil. Broad gauge of , commonly known as Iberian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in Spain and Portugal. Broad gauge of , commonly known as Indian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in Indian Railways, India, Pakistan Railways, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
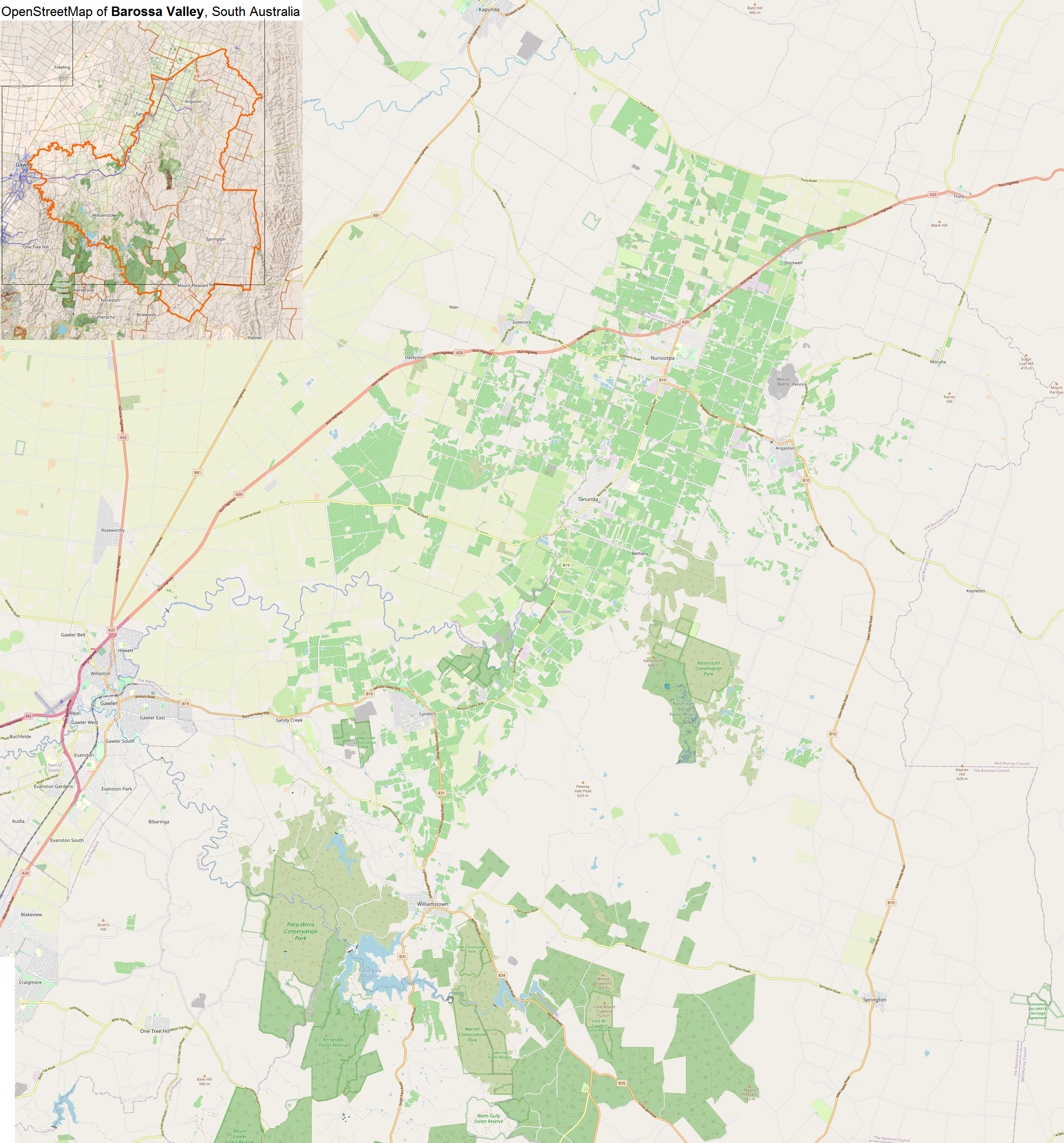
Barossa Valley
The Barossa Valley (Barossa German: ''Barossa Tal'') is a valley in South Australia located northeast of Adelaide city centre. The valley is formed by the North Para River. It is notable as a major list of wine-producing regions, wine-producing region and tourism, tourist destination. The Barossa Valley Way is the main road through the valley, connecting the main towns on the valley floor of Nuriootpa, South Australia, Nuriootpa, Tanunda, South Australia, Tanunda, Rowland Flat, South Australia, Rowland Flat and Lyndoch, South Australia, Lyndoch. The Barossa Trail walking and cycling path is long, and passes the main towns, starting from near Gawler, South Australia, Gawler on the Adelaide Plains, to Angaston, South Australia, Angaston to the east of the valley. History The traditional owners of the land including the Barossa Valley are the Peramangk people, who comprise a number of family groups. Evidence of their thousands of years of occupation can be seen all around the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
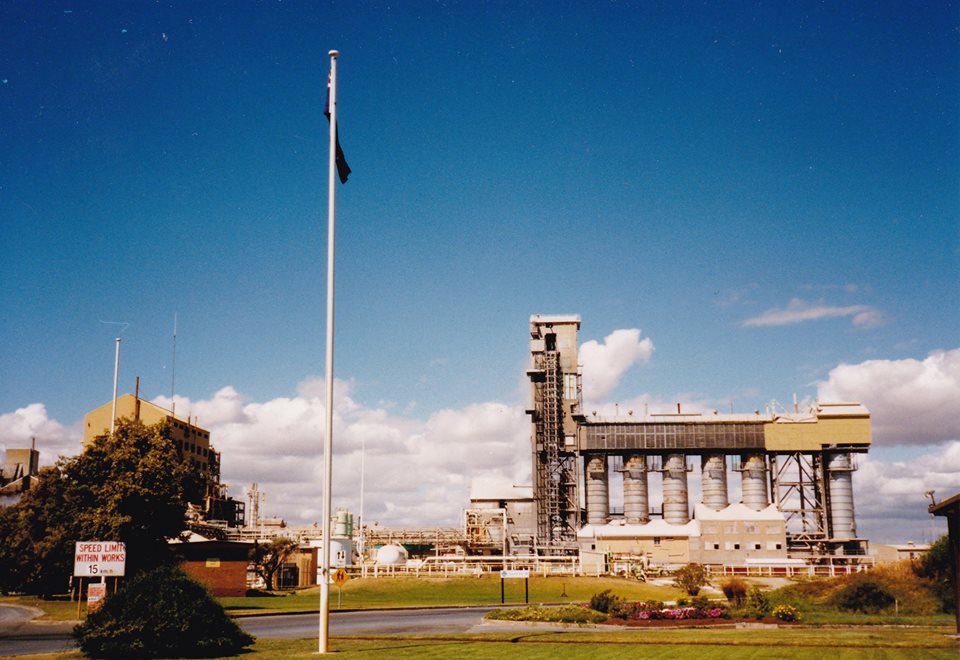
Penrice Stone Train
The Penrice Stone Train “The Stonie” was a limestone train in South Australia that operated from the Penrice Quarry near Angaston on the Barossa Valley line to Penrice Soda Products' soda ash factory in Osborne in Adelaide's north-western suburbs, and the co-located Readymix concrete batching plant. Penrice Soda Holdings 16 March 2007 History The train commenced operating in November 1950, initially being operated by the , and later by ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osborne, South Australia
Osborne is a suburb in the Australian state of South Australia located on the Lefevre Peninsula in the west of Adelaide about north-west of the Adelaide city centre. Description Osborne is bounded to the south by the suburb of Taperoo, South Australia, Taperoo, to the west by Gulf St Vincent and to the north west by the suburbs of North Haven, South Australia, North Haven and Outer Harbor, South Australia, Outer Harbor and to the east by the suburb of Torrens Island, South Australia, Torrens Island. History Osborne originally started as a Subdivision (land), private sub-division in Section 2015 in the Cadastral divisions of South Australia, cadastral unit of the Hundred of Port Adelaide. It was named after Captain R.W. Osborne (c.1834-1920). A portion was subsequently added to North Haven. The name was "formally submitted by the City of Port Adelaide at a council meeting held on 10 May 1945" and was formally adopted in 1951 by the Nomenclature Committee. Since 1951, its bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penrice Soda Products
Penrice Soda Products was a company founded in 1935 in South Australia. It was listed on the Australian Securities Exchange, named after its quarry near the small town of Penrice, South Australia. It was forced to close its soda ash production plant in Osborne (South Australia), Osborne and was placed in liquidation in August 2014. History Penrice Soda Products operations were founded by ICI Australia in 1935. The Adelaide International Bird Sanctuary, Dry Creek Saltfields and Osborne soda ash plant were acquired from ICI in 1989. The salt fields were sold to Ridley Inc., Ridley Corporation in 2005. Penrice Soda Products was listed on the Australian Securities Exchange in 2005. It was placed in liquidation in August 2014. Operations In addition to its large limestone and marble quarry just north of Angaston, South Australia, Angaston, it had a number of other establishments in South Australia, including the only Sodium carbonate, soda ash production facility in Australia, locate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICI Australia
Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) was a British chemical company. It was, for much of its history, the largest manufacturer in Britain. Its headquarters were at Millbank in London. ICI was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was a constituent of the FT 30 and later the FTSE 100 indices. ICI was formed in 1926 as a result of the merger of four of Britain's leading chemical companies. From the onset, it was involved in the production of various chemicals, explosives, fertilisers, insecticides, dyestuffs, non-ferrous metals, and paints; the firm soon become involved in plastics and a variety of speciality products, including food ingredients, polymers, electronic materials, fragrances and flavourings. During the Second World War, ICI's subsidiary ICI Nobel produced munitions for Britain's war effort; the wider company was also involved with Britain's nuclear weapons programme codenamed Tube Alloys. Throughout the 1940s and 1950s, ICI greatly expanded its activities in the pha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Railway Museum, Port Adelaide
The National Railway Museum, Port Adelaide, South Australia is the largest under-cover railway museum in Australia. More than 100 major exhibits, mainly from the South Australian Railways (SAR) and Commonwealth Railways and their successor, Australian National Railways Commission, Australian National, are displayed at its site. A large archival collection of photographs of those railways and records created by them is also managed by the museum. The museum operates with a large number of volunteers. History Mile End, 1964–1988 In 1963, a group of rail preservationists asked the South Australian Railways Commissioner to allocate land near the site of the former Mile End, South Australia, Mile End locomotive depot to hold a small collection of withdrawn steam locomotives. The first locomotive arrived in 1964 and in 1970 the site opened as the Mile End Railway Museum. Only a few exhibits were under cover and the effects of weather took their toll; an alternative, under-cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian National Railways Commission
The Australian National Railways Commission was an agency of the Government of Australia that was a railway operator between 1975 and 1998. It traded as Australian National Railways (ANR) in its early years, before being rebranded as Australian National. AN was widely used from 1980, the logo, logotype being registered as a trade mark. History The commission was established following an election commitment made during the 1972 Australian federal election, 1972 federal election by the Whitlam government, Whitlam federal government. The Whitlam government invited the state governments to hand over their railway systems to the federal government. On 1 July 1975, the Australian National Railways Commission took over responsibility for the operations of the federal government owned Commonwealth Railways and branded itself Australian National Railways. The state governments of Government of South Australia, South Australia and Government of Tasmania, Tasmania, whose railway sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |