|
Dover Western Heights
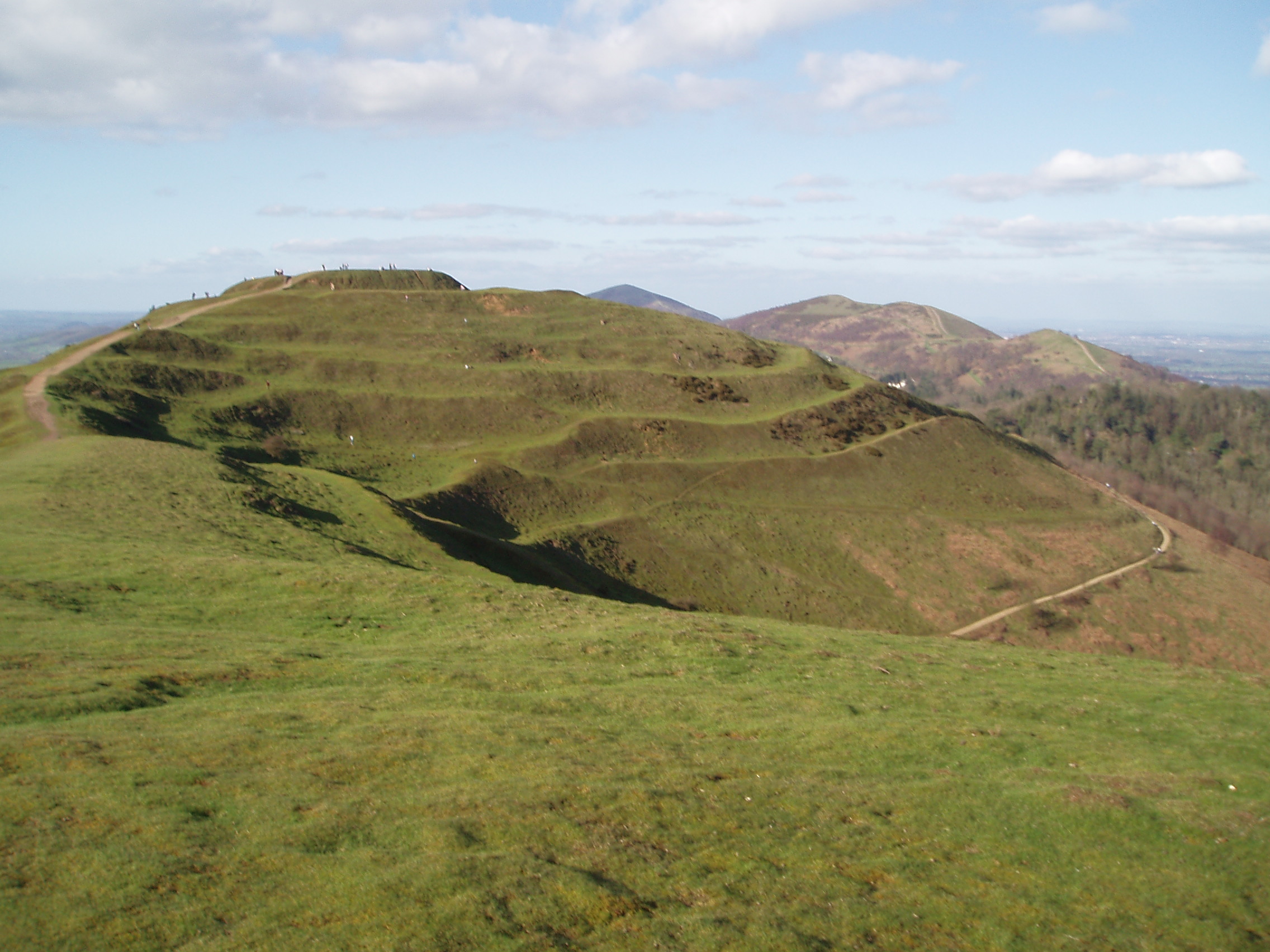
The Western Heights of Dover is a series of forts and ditches in Dover, England. They were created in the 18th and 19th centuries to augment the existing defences and protect the key port of Dover from both seaward and landward attack; by the start of the 20th century Dover Western Heights was collectively reputed to be the "strongest and most elaborate" fortification in the country. The Army finally withdrew from the Heights in 1956–61; they are now a local nature reserve. Introduction First given Siege, earthworks in 1779 against the Armada of 1779, planned invasion that year, the high ground west of Dover was properly fortified in 1804 when Lieutenant-Colonel William Twiss was instructed to modernise the existing defences. This was part of a huge British anti-invasion preparations of 1803–1805#Fortifications, programme of fortification in response to Napoleon's planned invasion of the United Kingdom. It followed a sustained period of related work by Twiss on upgrading th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd (Reserve) Battalion, Buffs (East Kent Regiment)
The East Kent Militia, later the 3rd Battalion, Buffs (East Kent Regiment) was an auxiliary regiment raised in Kent in South East England. From its formal creation in 1760 the regiment served in home and colonial defence in all of Britain's major wars until 1918, seeing active service in the Second Boer War and supplying thousands of reinforcements to the Buffs during World War I. Background The universal obligation to military service in the Shire levy was long established in England and its legal basis was updated by two acts of 1557 ( 4 & 5 Ph. & M. cc. 2 and 3), which placed selected men, the 'Trained Bands', under the command of Lords Lieutenant appointed by the monarch. This is seen as the starting date for the organised county militia in England.Grierson, pp. 6–7. The Kent Trained Bands were on high alert during the Armada crisis in 1588 and saw some active service during the English Civil War. The Militia was re-established in 1662 after the Restoration of the Monarch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Heights From Dover Castle
Western may refer to: Places *Western, Nebraska, a village in the US *Western, New York, a town in the US *Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia *Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia *Western world, countries that identify with shared "Western" culture *Western United States, a region of the United States Arts and entertainment Films * ''Western'' (1997 film), a French road movie directed by Manuel Poirier * ''Western'' (2017 film), a German-Austrian film Genres *Western (genre), a category of fiction and visual art centered on the American Old West **Western fiction, the Western genre as featured in literature **Western film, the western genre in film **Western music (North America), a type of American folk music Music * ''Westerns'' (EP), an EP by Pete Yorn *WSTRN, a British hip hop group from west London *"Western" a song by Black Midi from ''Schlagenheim'' Business *The Western, a closed hotel/casino in Las Vegas, United States *Western Cartri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barracks
Barracks are buildings used to accommodate military personnel and quasi-military personnel such as police. The English word originates from the 17th century via French and Italian from an old Spanish word 'soldier's tent', but today barracks are usually permanent buildings. The word may apply to separate housing blocks or to complete complexes, and the plural form often refers to a single structure and may be English plurals#Plural in form but singular in construction, singular in construction. The main objective of barracks is to separate soldiers from the civilian population and reinforce discipline, training, and ''esprit de corps''. They have been called "discipline factories for soldiers". Like industrial factories, some are considered to be shoddy or dull buildings, although others are known for their magnificent architecture such as Collins Barracks, Dublin, Collins Barracks in Dublin and others in Paris, Berlin, Madrid, Vienna, or London. From the rough barracks of 19th- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borstal
A borstal is a type of youth detention centre. Such a detention centre is more commonly known as a borstal school in India, where they remain in use today. Until the late 20th century, borstals were present in the United Kingdom, several member states of the Commonwealth and the Republic of Ireland. Borstals were run by HM Prison Service and were intended to reform young offenders. The word originated from the first such institution established in 1902 near the English village of Borstal in Kent, and is sometimes used loosely to apply to other kinds of youth institutions and reformatories, such as approved schools and youth detention centres. The court sentence was officially called "borstal training". Borstals were originally for offenders under 21, but in the 1930s the maximum age was increased to 23. The Criminal Justice Act 1982 abolished the borstal system in the UK, replacing borstals with youth custody centres. In India, borstal schools are used for the imprisonm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HM Prison Service
His Majesty's Prison Service (HMPS) is a part of HM Prison and Probation Service (formerly the National Offender Management Service), which is the part of His Majesty's Government charged with managing most of the prisons within England and Wales (Scotland and Northern Ireland have their own prison services: the Scottish Prison Service and the Northern Ireland Prison Service, respectively). The Director General of HMPS, currently Phil Copple, is the administrator of the prison service. The Director General reports to the Secretary of State for Justice and also works closely with the Prisons Minister, a junior ministerial post within the Ministry of Justice. The statement of purpose for His Majesty's Prison Service states that " isMajesty's Prison Service serves the public by keeping in custody those committed by the courts. Our duty is to look after them with humanity and help them lead law abiding and useful lives in custody and after release". The Ministry of Justice's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobilisation
Mobilization (alternatively spelled as mobilisation) is the act of assembling and readying military troops and supplies for war. The word ''mobilization'' was first used in a military context in the 1850s to describe the preparation of the Prussian Army. Mobilization theories and tactics have continuously changed since then. The opposite of mobilization is demobilization. Mobilization institutionalized the Levée en masse (engl. ''mass levy of conscripts'') that was first introduced during the French Revolution. It became an issue with the introduction of conscription, and the introduction of the railways in the 19th century. A number of technological and societal changes promoted the move towards a more organized way of deployment. These included the telegraph to provide rapid communication, the railways to provide rapid movement and concentration of troops, and conscription to provide a trained Military reserve force, reserve of soldiers in case of war. History Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Jervois
Lieutenant General Sir William Francis Drummond Jervois (10 September 1821 – 17 August 1897) was a British military engineer and diplomat. After joining the British Army in 1839, he saw service, as a second captain, in South Africa. In 1858, as a major, he was appointed Secretary of a Royal Commission set up to examine the state and efficiency of British land-based fortifications against naval attack; and this led to further work in Canada and South Australia. From 1875 to 1888 he was, consecutively, Governor of the Straits Settlements, Governor of South Australia and Governor of New Zealand. Early life Born on 10 September 1821 in Cowes in the Isle of Wight, Jervois was the son of General William Jervois (pronounced "Jarvis"), and his wife Elizabeth Jervois (née Maitland). From a military family of Huguenot descent, he was educated at Dr. Burney's Academy, Gosport, before entering the Royal Military Academy, Woolwich. Military service Upon graduating from Woolwich, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
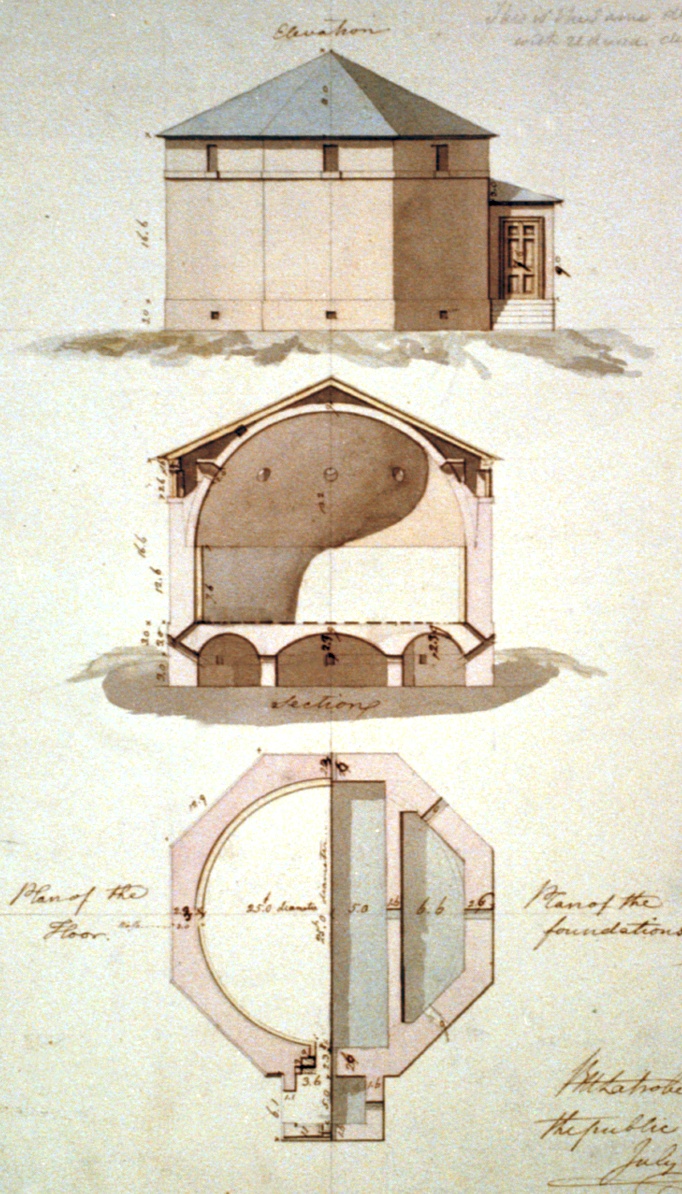
Gunpowder Magazine
A gunpowder magazine is a magazine (building) designed to store the explosive gunpowder in wooden barrels for safety. Gunpowder, until superseded, was a universal explosive used in the military and for civil engineering: both applications required storage magazines. Most magazines were purely functional and tended to be in remote and secure locations. They are the successor to the earlier powder towers and powder houses. In Australia Historic magazines were at the following locations, among others: * Jack's Magazine, Saltwater River, Victoria * Goat Island, Sydney * Spectacle Island (Port Jackson) * North Arm Powder Magazine * Dry Creek explosives depot In Canada There are magazines at: * Citadel Hill (Fort George) * Citadel of Quebec, Quebec City, Quebec *Parc de l'Esplanade, Quebec City, Quebec *Cole Island, Esquimalt, British Columbia * Fort Lennox, Île-aux-Noix, Quebec * Fort William Historical Park, Thunder Bay, Ontario *Fort York, Toronto In Ireland Ballincollig, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rampart (fortification)
In fortification architecture, a rampart is a length of Embankment (earthworks), embankment or wall forming part of the defensive boundary of a castle, hillfort, Human settlement, settlement or other fortified site. It is usually broad-topped and made of excavated earth and/or masonry.Friar, Stephen (2003). ''The Sutton Companion to Castles'', Sutton Publishing, Stroud, 2003, p. 241. Darvill, Timothy (2008). ''Oxford Concise Dictionary of Archaeology'', 2nd ed., Oxford University Press, Oxford and New York, p. 376. . Types The composition and design of ramparts varied from the simple mounds of earth and stone, known as dump ramparts, to more complex earth and timber defences (box ramparts and timberlaced ramparts), as well as ramparts with stone revetments. One particular type, common in Central Europe, used earth, stone and timber posts to form a ''Pfostenschlitzmauer'' or "post-slot wall". Vitrified ramparts were composed of stone that was subsequently fired, possibly to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outworks
An outwork is a minor fortification built or established outside the principal fortification limits, detached or semidetached. Outworks such as ravelins, lunettes (demilunes), flèches and caponiers to shield bastions and fortification curtains from direct battery were developed in the 16th century. Later, the increasing scale of warfare and the greater resources available to the besieger accelerated this development, and systems of outworks grew increasingly elaborate and sprawling as a means of slowing the attacker's progress and making it more costly. When taken by an enemy force, their lack of rear-facing ramparts left them totally open to fire from the main works. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
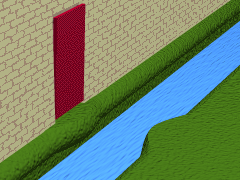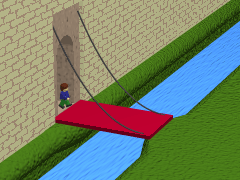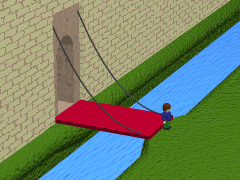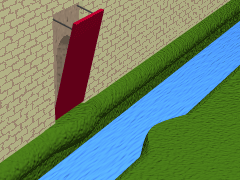
Drawbridge
A drawbridge or draw-bridge is a type of moveable bridge typically at the entrance to a castle or tower surrounded by a moat. In some forms of English, including American English, the word ''drawbridge'' commonly refers to all types of moveable bridges, such as bascule bridges, vertical-lift bridges and swing bridges, but this article concerns the narrower historical definition where the bridge is used in a defensive structure. As used in castles or defensive structures, drawbridges provide access across defensive structures when lowered, but can quickly be raised from within to deny entry to an enemy force. Castle drawbridges Middle Ages, Medieval castles were usually defended by a ditch or moat, crossed by a wooden bridge. In early castles, the bridge might be designed to be destroyed or removed in the event of an attack, but drawbridges became very common. A typical arrangement would have the drawbridge immediately outside a gatehouse, consisting of a wooden Deck (bridge), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |