Drawbridge on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A drawbridge or draw-bridge is a type of
A drawbridge or draw-bridge is a type of
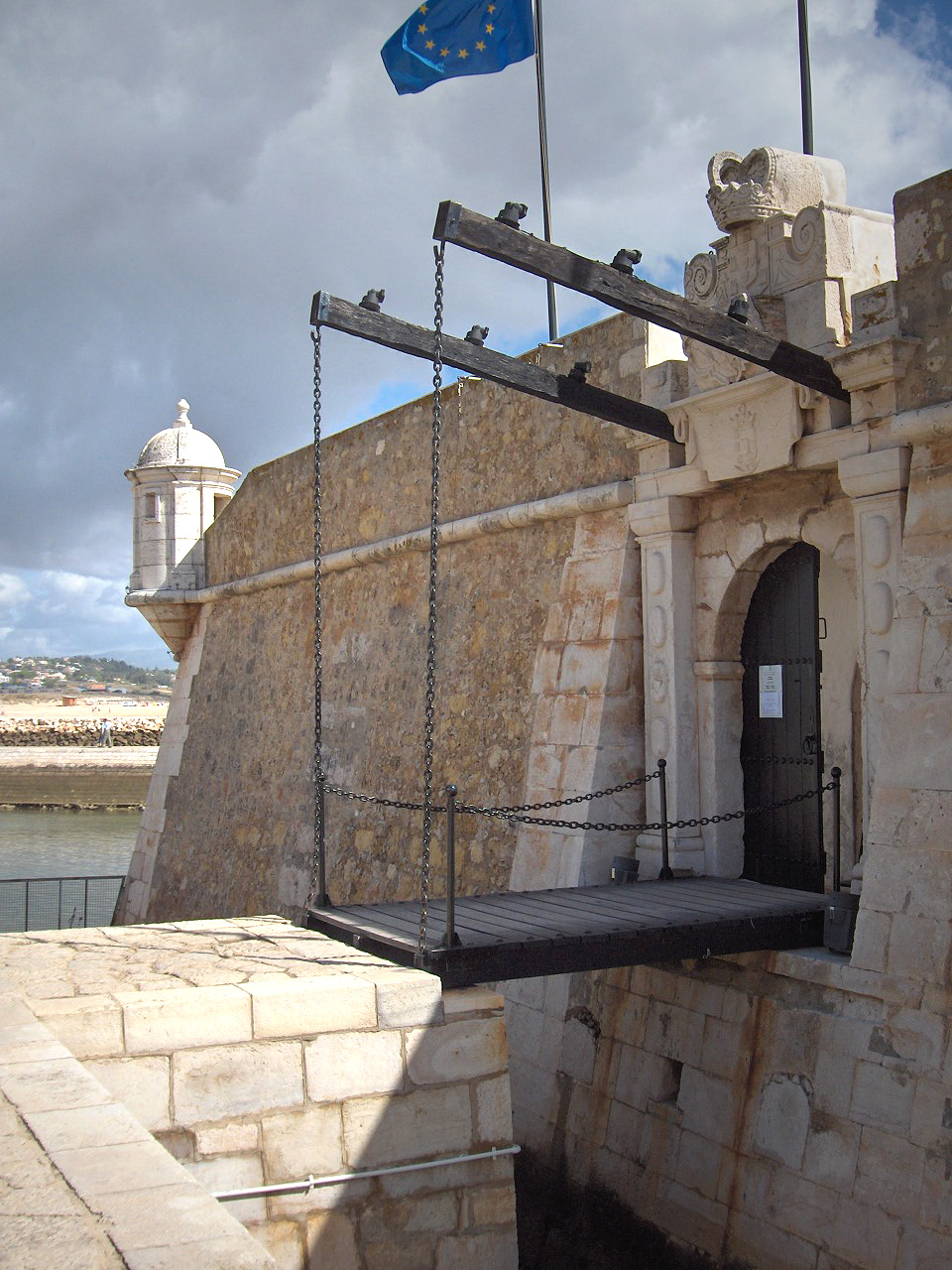


 A drawbridge or draw-bridge is a type of
A drawbridge or draw-bridge is a type of moveable bridge
A moveable bridge, or movable bridge, is a bridge that moves to allow passage for boats or barges. In American English, the term is synonymous with , and the latter is the common term, but drawbridge can be limited to the narrower, historical ...
typically at the entrance to a castle
A castle is a type of fortification, fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by Military order (monastic society), military orders. Scholars usually consider a ''castle'' to be the private ...
or tower surrounded by a moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch dug around a castle, fortification, building, or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. Moats can be dry or filled with water. In some places, moats evolved into more extensive water d ...
. In some forms of English, including American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken lang ...
, the word ''drawbridge'' commonly refers to all types of moveable bridges, such as bascule bridge
A bascule bridge (also referred to as a drawbridge or a lifting bridge) is a moveable bridge with a counterweight that continuously balances a span, or leaf, throughout its upward swing to provide clearance for boat traffic. It may be single- o ...
s, vertical-lift bridge
A vertical-lift bridge or just lift bridge is a type of movable bridge in which a span rises vertically while remaining parallel with the deck.
The vertical lift offers several benefits over other movable bridges such as the bascule and swi ...
s and swing bridge
A swing bridge (or swing span bridge) is a movable bridge that can be rotated horizontally around a vertical axis. It has as its primary structural support a vertical locating pin and support ring, usually at or near to its center of gravit ...
s, but this article concerns the narrower historical definition where the bridge is used in a defensive structure.
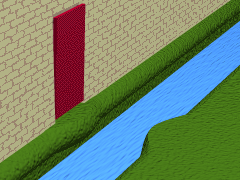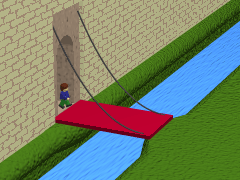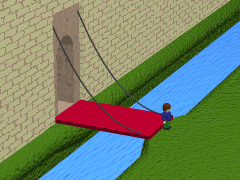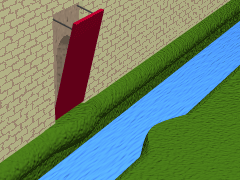
As used in castles or defensive structures, drawbridges provide access across defensive structures when lowered, but can quickly be raised from within to deny entry to an enemy force.
Castle drawbridges


Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
castle
A castle is a type of fortification, fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by Military order (monastic society), military orders. Scholars usually consider a ''castle'' to be the private ...
s were usually defended by a ditch or moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch dug around a castle, fortification, building, or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. Moats can be dry or filled with water. In some places, moats evolved into more extensive water d ...
, crossed by a wooden bridge. In early castles, the bridge might be designed to be destroyed or removed in the event of an attack, but drawbridges became very common. A typical arrangement would have the drawbridge immediately outside a gatehouse
A gatehouse is a type of fortified gateway, an entry control point building, enclosing or accompanying a gateway for a town, religious house, castle, manor house, or other fortification building of importance. Gatehouses are typically the most ...
, consisting of a wooden deck with one edge hinge
A hinge is a mechanical bearing that connects two solid objects, typically allowing only a limited angle of rotation between them. Two objects connected by an ideal hinge rotate relative to each other about a fixed axis of rotation, with all ...
d or pivoting at the gatehouse threshold, so that in the raised position the bridge would be flush against the gate, forming an additional barrier to entry. It would be backed by one or more portcullis
A portcullis () is a heavy, vertically closing gate typically found in medieval fortifications. It consists of a latticed Grille (architecture), grille made of wood and/or metal, which slides down grooves inset within each jamb of the gateway.
...
es and gates. Access to the bridge could be resisted with missiles from machicolations above or arrow slits in flanking tower
A tower is a tall Nonbuilding structure, structure, taller than it is wide, often by a significant factor. Towers are distinguished from guyed mast, masts by their lack of guy-wires and are therefore, along with tall buildings, self-supporting ...
s.
The bridge would be raised or lowered using ropes or chains attached to a windlass
The windlass is an apparatus for moving heavy weights. Typically, a windlass consists of a horizontal cylinder (barrel), which is rotated by the turn of a crank or belt. A winch is affixed to one or both ends, and a cable or rope is wound arou ...
in a chamber in the gatehouse above the gate-passage. Only a very light bridge could be raised in this way without any form of counterweight, so some form of bascule arrangement is normally found. The bridge may extend into the gate-passage beyond the pivot point, either over a pit into which the internal portion can swing (providing a further obstacle to attack), or in the form of counterweighted beams that drop into slots in the floor.
The raising chains could themselves be attached to counterweights. In some cases, a portcullis provides the weight, as at Alnwick
Alnwick ( ) is a market town in Northumberland, England, of which it is the traditional county town. The population at the 2011 Census was 8,116.
The town is south of Berwick-upon-Tweed and the Scottish border, inland from the North Sea ...
. By the 14th century, a bascule arrangement was provided by lifting arms (called "gaffs") above and parallel to the bridge deck whose ends were linked by chains to the lifting part of the bridge. In the raised position, the gaffs would fit into slots in the gatehouse wall ("rainures") which can often still be seen in places like Herstmonceux Castle
Herstmonceux Castle is a brick-built castle, dating from the 15th century, near Herstmonceux, East Sussex, England. It is one of the oldest significant brick buildings still standing in England. The castle was renowned for being one of the fi ...
. Inside the castle, the gaffs were extended to bear counterweights, or might form the side-timbers of a stout gate which would be against the roof of the gate-passage when the drawbridge was down, but would close against the gate-arch as the bridge was raised.
In France, working drawbridges survive at a number of château
A château (, ; plural: châteaux) is a manor house, or palace, or residence of the lord of the manor, or a fine country house of nobility or gentry, with or without fortifications, originally, and still most frequently, in French-speaking re ...
x, including the Château du Plessis-Bourré
Château du Plessis-Bourré is a château in the Loire Valley in France, situated in the Commune in France, commune of Écuillé in the Maine-et-Loire department.
Built in less than 5 years from 1468 to 1472 by Finance Minister Jean Bourré, the ...
. In England, two working drawbridges remain in regular use at Helmingham Hall, which dates from the early sixteenth century.
Turning bridge
A bridge pivoted on centraltrunnion
A trunnion () is a cylinder, cylindrical Boss (engineering), protrusion used as a mounting or pivoting point. First associated with cannons, they are an important military development.
In mechanical engineering (see the Trunnion#Trunnion bearin ...
s is called a ''turning bridge'', and may or may not have the raising chains characteristic of a drawbridge. The inner end carried counterweights enabling it to sink into a pit in the gate-passage, and when horizontal the bridge would often be supported by stout pegs inserted through the side walls. This was a clumsy arrangement, and many turning bridges were replaced with more advanced drawbridges.
Forts
Drawbridges were also used on forts withPalmerston Forts
The Palmerston Forts are a group of forts and associated structures around the coasts of the United Kingdom and Ireland.
The forts were built during the Victorian period on the recommendations of the 1860 Royal Commission on the Defence of the ...
using them in the form of Guthrie rolling bridges.
In art
Drawbridges have appeared in films as part of castle sets. When the drawbridge needs to be functional this may present engineering challenges since the set may not be able to support the weight of the bridge in the conventional manner. One solution is to build the drawbridge from steel and concrete before hiding the structural materials behind wood and plaster.See also
*Bascule bridge
A bascule bridge (also referred to as a drawbridge or a lifting bridge) is a moveable bridge with a counterweight that continuously balances a span, or leaf, throughout its upward swing to provide clearance for boat traffic. It may be single- o ...
* Double-beam drawbridge
A double-beam drawbridge, seesaw or folding bridge is a movable bridge . It opens by rotation about a horizontal axis parallel to the water. Historically, the double-beam drawbridge has emerged from the drawbridge. A (double-beam) drawbridge ha ...
* Drawbridge mentality
* Portcullis
A portcullis () is a heavy, vertically closing gate typically found in medieval fortifications. It consists of a latticed Grille (architecture), grille made of wood and/or metal, which slides down grooves inset within each jamb of the gateway.
...
* Linkspan
* Moveable bridges
A moveable bridge, or movable bridge, is a bridge that moves to allow passage for boats or barges. In American English, the term is synonymous with , and the latter is the common term, but drawbridge can be limited to the narrower, historical ...
References
{{Authority control Castle architecture Moveable bridges