|
Tower
A tower is a tall Nonbuilding structure, structure, taller than it is wide, often by a significant factor. Towers are distinguished from guyed mast, masts by their lack of guy-wires and are therefore, along with tall buildings, self-supporting structures. Towers are specifically distinguished from buildings in that they are built not to be habitable but to serve other functions using the height of the tower. For example, the height of a clock tower improves the visibility of the clock, and the height of a tower in a fortified building such as a castle increases the visibility of the surroundings for defensive purposes. Towers may also be built for observation tower, observation, leisure, or telecommunication purposes. A tower can stand alone or be supported by adjacent buildings, or it may be a feature on top of a larger structure or building. Etymology Old English ''torr'' is from Latin ''turris'' via Old French ''tor''. The Latin term together with Greek language, Greek τύ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observation Tower
An observation tower is a tower used to view events from a long distance and to create a full 360 degree range of vision to conduct long distance observations. Observation towers are usually at least tall and are made from stone, iron, and wood. Many modern towers are also used as TV towers, restaurants, or churches. The towers first appeared in the ancient world, as long ago as the Babylonian Empire. Observation towers that are used as guard posts or observation posts over an extended period to overlook an area are commonly called watchtowers instead. Similar instances of observation towers are recognised as Crow's nest, crow's nests, Observatory, observatories, Viewing platform, viewing platforms, etc. Construction and usage Observation towers are an easily visible sight on the countryside, as they must rise over trees and other obstacles to ensure clear vision. Older control rooms have often been likened to medieval chambers. The heavy use of stone, iron, and wood in their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watchtower
A watchtower or guardtower (also spelt watch tower, guard tower) is a type of military/paramilitary or policiary tower used for guarding an area. Sometimes fortified, and armed with heavy weaponry, especially historically, the structures are built in areas of established control. These include military bases, cities occupied by military forces, prisons and more. A common equipment is searchlights. It differs from a regular tower in that its primary use is military/policiary and from a turret in that it is usually a freestanding structure. Its main purpose is to provide a high, safe place from which a sentinel or guard may observe the surrounding area. In some cases, non-military towers, such as religious towers, may also be used as watchtowers. Similar constructions include: observation towers, which are generally civilian structures, and control towers, used on airports or harbours. History Military watchtowers The Romans built numerous towers as part of a sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle
A castle is a type of fortification, fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by Military order (monastic society), military orders. Scholars usually consider a ''castle'' to be the private fortified house, fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a mansion, palace, and villa, whose main purpose was exclusively for ''pleasance'' and are not primarily fortresses but may be fortified. Use of the term has varied over time and, sometimes, has also been applied to structures such as hill forts and 19th- and 20th-century homes built to resemble castles. Over the Middle Ages, when genuine castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain wall (fortification), curtain walls, arrowslits, and portcullises, were commonplace. European-style castles originated in the 9th and 10th centuries after the fall of the Carolingian Empire, which resulted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
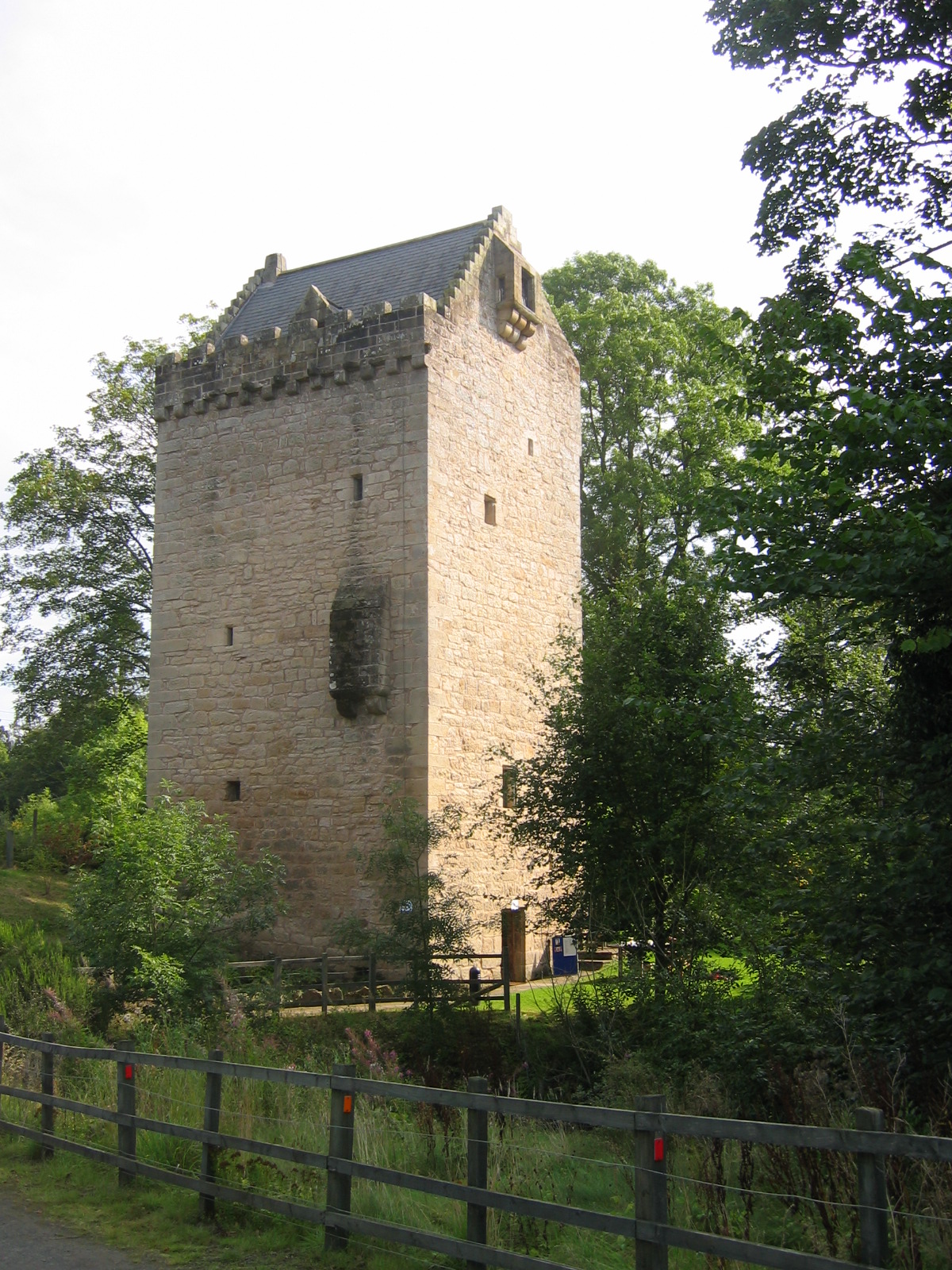
Towerhouse
A tower house is a particular type of stone structure, built for defensive purposes as well as habitation. Tower houses began to appear in the Middle Ages, especially in mountainous or limited access areas, to command and defend strategic points with reduced forces. At the same time, they were also used as an aristocrat's residence, around which a castle town was often constructed. Europe After their initial appearance in Ireland, Scotland, the Stins, Frisian lands, Spain, Northern Spain and England during the High Middle Ages, tower houses were also built in other parts of western Europe, especially in parts of France and Italy. In Italian medieval communes, urban ''palazzi'' with a very tall tower were increasingly built by the local highly competitive Patrician (post-Roman Europe), patrician families as power centres during times of internal strife. Most north Italian cities had a number of these by the end of the Middle Ages, but few now remain, notably Two Towers, Bologn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock Tower
Clock towers are a specific type of structure that house a turret clock and have one or more clock faces on the upper exterior walls. Many clock towers are freestanding structures but they can also adjoin or be located on top of another building. Some other buildings also have clock faces on their exterior but these structures serve other main functions. Clock towers are a common sight in many parts of the world with some being iconic buildings. One example is the Elizabeth Tower in London (usually called " Big Ben", although strictly this name belongs only to the bell inside the tower). Definition There are many structures that may have clocks or clock faces attached to them and some structures have had clocks added to an existing structure. According to the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat a structure is defined as a building if at least fifty percent of its height is made up of floor plates containing habitable floor area. Structures that do not meet this criter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guyed Mast
A guyed mast is a tall thin vertical structure that depends on guy lines (diagonal tensioned cables attached to the ground or a base) for stability. The mast itself has the compressive strength to support its own weight, but does not have the shear strength to stand unsupported or bear loads. It requires guy lines to stay upright and to resist lateral (shear) forces such as wind loads. Examples include masts on sailing vessels, towers for telecommunications, meteorology, and masts on cranes, power shovels, draglines, and derricks, starting with the simple gin pole. Applications The principal applications of guyed masts are the masts of sailing vessels, guyed towers, and as the main tower of heavy equipment such as cranes, power shovels, draglines, and derricks, the simplest of which is the gin pole. Guyed masts are frequently used for radio masts and towers. The mast can either support radio antennas (for VHF, UHF and other microwave bands) mounted at its top, or th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy-wires
A guy-wire, guy-line, guy-rope, down guy, or stay, also called simply a guy, is a tensioned cable designed to add stability to a freestanding structure. They are used commonly for ship masts, radio masts, wind turbines, utility poles, and tents. A thin vertical mast supported by guy wires is called a guyed mast. Structures that support antennas are frequently of a lattice construction and are called " towers". One end of the guy is attached to the structure, and the other is anchored to the ground at some distance from the mast or tower base. The tension in the diagonal guy-wire, combined with the compression and buckling strength of the structure, allows the structure to withstand lateral loads such as wind or the weight of cantilevered structures. They are installed radially, usually at equal angles about the structure, in trios and quads. As the tower leans a bit due to the wind force, the increased guy tension is resolved into a compression force in the tower or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wall Of Jericho (Neolithic)
Tell es-Sultan (, ''lit.'' Sultan's Hill), also known as Tel Jericho or Ancient Jericho, is an archaeological site and a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Palestine, in the city of Jericho, consisting of the remains of the oldest fortified city in the world. It is located adjacent to the Ein es-Sultan refugee camp, two kilometres north of the centre of the Palestinian city of Jericho. The tell was inhabited from the 10th millennium BCE, which makes Jericho among the oldest continually inhabited cities in the world. The site is notable for its role in the history of Levantine archaeology. The area was first identified as the site of ancient Jericho in modern times by Charles Warren in 1868, on the basis of its proximity to the large spring of Ein es-Sultan'','' that had been proposed as the spring of Elisha by Edward Robinson three decades earlier. History and archaeology Epipalaeolithic The droughts and cold of the Younger Dryas came to an end around 9600 BCE, ushering in the Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonbuilding Structure
A nonbuilding structure, often referred to simply as a structure, is any built structure or construction structure that is not a building, i.e. not designed for continuous human occupancy. The term is particularly used by architects, structural engineers, and Mechanical engineering, mechanical engineers to distinguish load-bearing structures not designed for continuous human occupancy. Examples * Aerial lift pylons * Avalanche dams * Barricade, BarriersPrasad, Deo K.. ''Designing with solar power: a source book for building integrated photovoltaics (BiPV''). Mulgrave, Vic.: Images ;, 2005. Print. * Beehive stone * Blast furnaces * Boat lifts * Brick#Methods of manufacture, Brick kilns * Bridges and bridge-like structures (Aqueduct (bridge), aqueducts, overpasses, Trestle bridge, trestles, viaducts, etc.) * Bus stops * Canals ** Aqueduct (water supply), Aqueduct *** Acequia * Carports * Chimneys and flue-gas stacks * Coke ovens * Communications towers * Conservatory (gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization ( ) was an ancient civilization created by the Etruscans, a people who inhabited Etruria in List of ancient peoples of Italy, ancient Italy, with a common language and culture, and formed a federation of city-states. After adjacent lands had been conquered its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria and northern Lazio, as well as what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto and western Campania. A large body of literature has flourished on the origins of the Etruscans, but the consensus among modern scholars is that the Etruscans were an indigenous population. The earliest evidence of a culture that is identifiably Etruscan dates from about 900 BC. This is the period of the Iron Age Villanovan culture, considered to be the earliest phase of Etruscan civilization, which itself developed from the previous late Bronze Age Proto-Villanovan culture in the same region, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
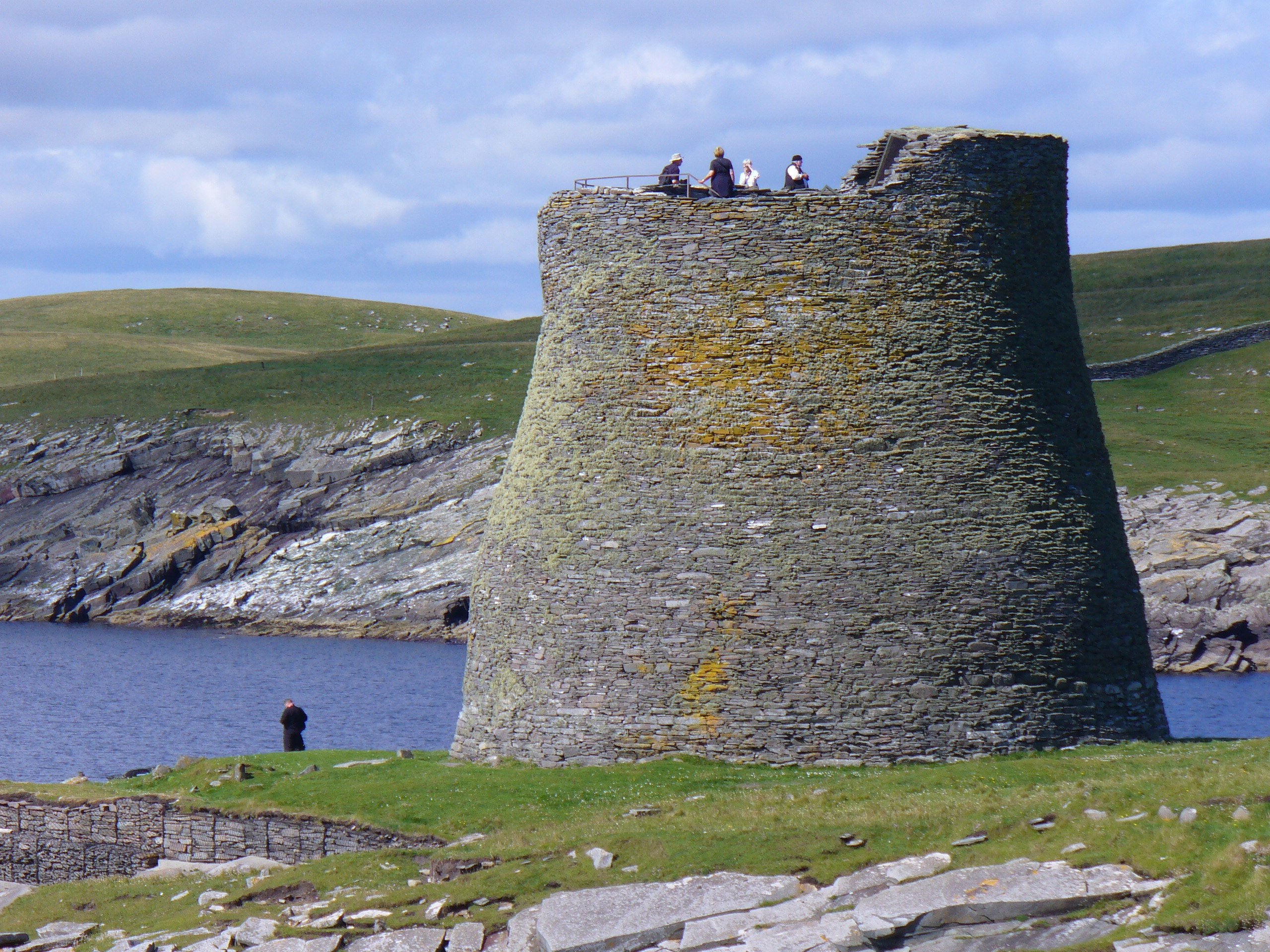
Broch
In archaeology, a broch is an British Iron Age, Iron Age drystone hollow-walled structure found in Scotland. Brochs belong to the classification "complex Atlantic roundhouse" devised by Scottish archaeologists in the 1980s. Brochs are roundhouse buildings found throughout Atlantic Scotland. The word broch is derived from the Scots language, Lowland Scots 'brough', meaning fort. In the mid-19th century, Scottish antiquaries called brochs 'burgs', after Old Norse borg, with the same meaning. Brochs are often referred to as Dun (fortification), dùns in the west, and they are the most spectacular of a complex class of buildings found in northern Scotland. There are approximately 571 candidate broch sites throughout the country, according to the Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland. The origin of brochs is still subject to ongoing research. While most archaeologists believed 80 years ago that brochs were built by immigrants, there is now little do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
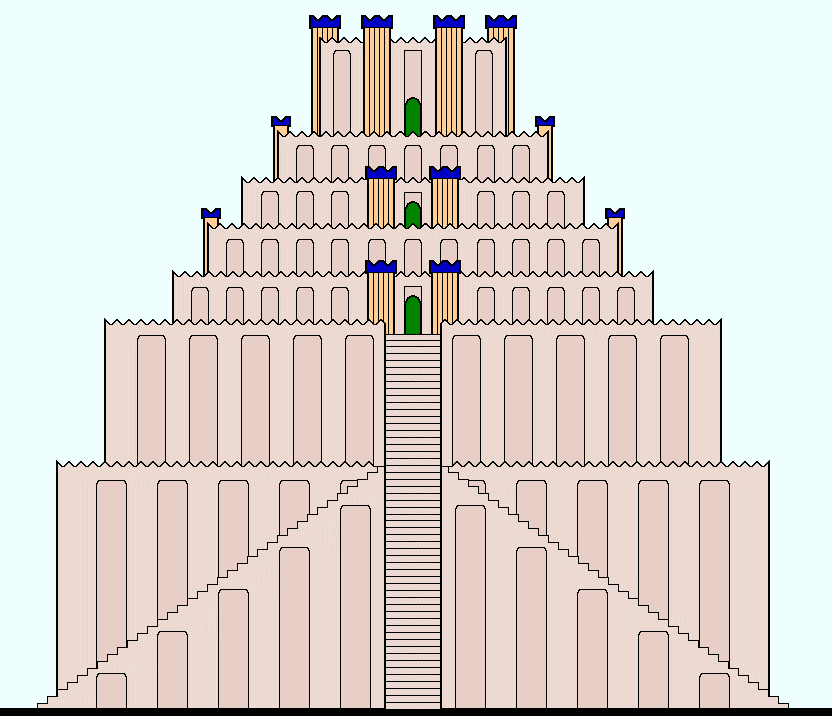
Etemenanki
Etemenanki () was a ziggurat dedicated to the Mesopotamian god Marduk in the ancient city of Babylon. It now exists only in ruins, located about south of Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq. Many scholars have identified Etemenanki as the ziggurat for the biblical account of the Tower of Babel. Construction It is unclear when Etemenanki was originally constructed. Andrew R. George says that it was constructed sometime between the 14th and the 9th century BCE. He argues as follows: The reference to a ziggurrat at Babylon in the Creation Epic (Enûma Eliš· VI 63: George 1992: 301–2) is more solid evidence, ... for a Middle Assyrian piece of this poem survives to prove the long-held theory that it existed already in the second millennium BC. There is no reason to doubt that this ziqqurrat, described as ''ziqqurrat apsî elite'', "the upper ziqqurrat of the Apsû", was [Etemenanki].Andrew R. George, George, Andrew (2007) "The Tower of Babel: Archaeology, history and cuneiform texts" ''Archiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |